- British Pharmacopoeia Volume III
- Formulated Preparations: Specific Monographs
Ticarcillin and Clavulanic Acid Intravenous Infusion |
Ticarcillin Sodium and Potassium Clavulanate Intravenous Infusion
Penicillin antibacterial + beta-lactamase inhibitor.
Ticarcillin and Clavulanic Acid Intravenous Infusion is a sterile solution of Ticarcillin Sodium and Potassium Clavulanate in a suitable liquid. It is prepared by dissolving Ticarcillin and Clavulanic Acid for Intravenous Infusion in the requisite amount of the liquid stated on the label before use.
The intravenous infusion complies with the requirements stated under Parenteral Preparations.
Ticarcillin and Clavulanic Acid Intravenous Infusion should be used immediately after preparation but, in any case, within the period recommended by the manufacturer when prepared and stored strictly in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions.
Ticarcillin and Clavulanic Acid for Intravenous Infusion is a sterile material consisting of Ticarcillin Sodium and Potassium Clavulanate with or without excipients. It is supplied in a sealed container.
The methods of production, extraction and purification of Potassium Clavulanate used in the formulation of Ticarcillin and Clavulanic Acid Intravenous Infusion are such that potassium clavam-2-carboxylate is eliminated or present at a level not exceeding 0.01%.
The contents of the sealed container comply with the requirements for Powders for Injections or Infusions stated under Parenteral Preparations and with the following requirements.
90.0 to 105.0% of the stated amount.
90.0 to 105.0% of the stated amount.
In the Assay, the retention times of the two principal peaks in the chromatogram obtained with solution (1) correspond to those of the two principal peaks in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2).
pH of a solution containing the equivalent of 10% w/v of ticarcillin, 5.5 to 8.0, Appendix V L.
Carry out the method for liquid chromatography, Appendix III D, using the following solutions in a solution prepared by dissolving 10.35 g of sodium dihydrogen orthophosphate monohydrate in 1500 mL of water and adjusting the pH to 6.4 using 10m sodium hydroxide (solvent A). The solutions should be freshly prepared.
(1) Dissolve a quantity of the contents of a sealed container in sufficient solvent A to produce a solution containing the equivalent of 0.2% w/v of ticarcillin.
(2) 0.004% w/v of ticarcillin monosodium EPCRS.
(3) Dissolve 11 mg of ticarcillin monosodium EPCRS and 2.9 mg of ticarcillin impurity A EPCRS in 10 mL of 0.1m sodium hydroxide and allow to stand for 15 minutes (generation of ticarcillin impurity D). Transfer the solution into a 500 mL volumetric flask quantitatively, washing the beaker out with solvent A. Add 400 mL of solvent A, ensuring that all traces of the degraded solution are washed from the neck of the flask. Add 11 mg of ticarcillin impurity A EPCRS, 10 mg of ticarcillin impurity B BPCRS, 10 mg of ticarcillin impurity C BPCRS and 55 mg of ticarcillin monosodium EPCRS to the flask and dilute to 500 mL with solvent A.
(4) Dilute 1 volume of solution (2) to 40 volumes with solvent A.
(a) Use a stainless steel column (15 cm × 4.6 mm) packed with methylsilyl silica gel for chromatography (5 µm) with a pore size of 6 nm (ES Industries Chromegabond TMS C1 5u 60A is suitable).
(b) Use gradient elution and the mobile phase described below.
(c) Use a flow rate of 2 mL per minute.
(d) Use an ambient column temperature.
(e) Use a detection wavelength of 230 nm.
(f) Inject 20 µL of each solution.
Mobile phase A 540 volumes of acetonitrile and 2460 volumes of a buffer solution prepared as described below; adjust the pH of the mixture to 3.0 with 2m orthophosphoric acid. To prepare the buffer solution dissolve 10.35 g of sodium dihydrogen orthophosphate monohydrate and 4.83 g of tetrabutylammonium bromide in 3000 mL of water and mix.
Mobile phase B Equal volumes of acetonitrile and buffer solution; adjust the pH of the mixture to 3.0 with 2m orthophosphoric acid.

When the chromatograms are recorded under the prescribed conditions, the retention time of ticarcillin is about 14 minutes. If necessary, adjust the content of acetonitrile in mobile phase A to achieve the stated retention time. Retention times relative to ticarcillin are: ticarcillin impurity B, about 0.37; ticarcillin impurity C, about 0.42; ticarcillin impurity D, about 0.5; ticarcillin impurity A, about 1.6.
The test is not valid unless, in the chromatogram obtained with solution (3), the resolution factor between the peaks due to impurity B and impurity C is at least 1.6 and the resolution factor between the peaks due to impurity C and impurity D is at least 1.6.
Identify any peaks in the chromatogram obtained with solution (1) corresponding to impurities A, B, C and D using the chromatogram obtained with solution (3). Multiply the area of any peak corresponding to impurity B by the following correction factor: 0.5; multiply the area of any peak corresponding to impurity C by the following correction factor: 0.6.
In the chromatogram obtained with solution (1):
the area of any peak corresponding to impurity A is not greater than twice the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (4%);
the area of any peak corresponding to impurity D is not greater than three times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (6%);
the area of any other secondary peak is not greater than 1.25 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (2.5%);
the sum of the areas of all the secondary peaks is not greater than six times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (2) (12%).
Disregard any peak with an area less than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with solution (4) (0.05%).
Carry out the test for bacterial endotoxins, Appendix XIV C. Dissolve the contents of the sealed container in water BET to give a solution containing the equivalent of 10 mg of ticarcillin per mL (solution A). The endotoxin limit concentration of solution A is 0.7 IU of endotoxin per mL.
Not more than 4.5% w/w, Appendix IX C. Use 0.3 g.
Determine the weight of the contents of 10 containers as described in the test for Uniformity of weight under Parenteral Preparations of the British Pharmacopoeia, Powders for Injections.
Carry out the method for liquid chromatography, Appendix III D, using the following solutions in a solution prepared by dissolving 7.8 g of sodium dihydrogen orthophosphate in 1000 mL of water and adjusting the pH to 6.4 using 5m sodium hydroxide (solvent B). The solutions should be stored at 2° to 8° and used within 4 hours.
(1) Dissolve a quantity of the mixed contents of the 10 containers in sufficient water to produce a solution containing the equivalent of 1.4% w/v of ticarcillin. Dilute 1 volume to 10 volumes with solvent B.
(2) 0.15% w/v of ticarcillin monosodium EPCRS and 0.009% w/v of lithium clavulanate EPCRS in solvent B.
(3) 0.1% w/v of each of ampicillin trihydrate BPCRS and ticarcillin monosodium EPCRS in solvent B.
(a) Use a stainless steel column (15 cm × 4.6 mm) packed with end-capped phenylethyl silica gel for chromatography (4 µm) (Phenomenex Synergi 4µ Polar-RP 80A is suitable).
(b) Use gradient elution and the mobile phase described below.
(c) Use a flow rate of 2 mL per minute.
(d) Use a column temperature of 30°.
(e) Use a detection wavelength of 230 nm.
(f) Inject 20 µL of each solution.
Mobile phase A Dissolve 31.2 g of sodium dihydrogen orthophosphate in 4000 mL of water and adjust the pH to 3.9 using 1m orthophosphoric acid.
Mobile phase B acetonitrile.
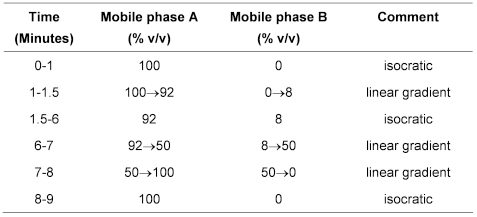
The Assay is not valid unless, in the chromatogram obtained with solution (3), the resolution factor between the peaks due to ampicillin and ticarcillin is at least 4.0 and the symmetry factor of the peak corresponding to ticarcillin is less than 2.0.
Calculate the content of C15H16N2O6S2 and C8H9NO5 in a container of average content weight using the declared content of C15H15N2NaO6S2 in ticarcillin monosodium EPCRS and the declared content of C8H8LiNO5 in lithium clavulanate EPCRS. Each mg of C15H15N2NaO6S2 is equivalent to 1.057 mg of C15H16N2O6S2. Each mg of C8H8LiNO5 is equivalent to 0.9711 mg of C8H9NO5
The label of the sealed container states the quantity of Ticarcillin Sodium contained in it, in terms of the equivalent amount of ticarcillin, and the quantity of Potassium Clavulanate, in terms of the equivalent amount of clavulanic acid.
The label of the sealed container states that the preparation contains penicillin.
The impurities limited by the requirements of this monograph include those listed under Ticarcillin Sodium.