- British Pharmacopoeia Volume I & II
- Monographs: Medicinal and Pharmaceutical Substances
Atorvastatin Calcium Trihydrate |
 |
(Ph. Eur. monograph 2191)

C66H68CaF2N4O10,3H2O 1209 344423-98-9
HMG Co-A reductase inhibitor; lipid-regulating drug.
Ph Eur
Calcium (3R,5R)-7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-(1-methylethyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoate trihydrate.
97.0 per cent to 102.0 per cent (anhydrous substance).
White or almost white powder.
Very slightly soluble in water, slightly soluble in ethanol (96 per cent), practically insoluble in methylene chloride.
It shows polymorphism (5.9).
A. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison atorvastatin calcium trihydrate CRS.
If the spectra obtained in the solid state show differences, dissolve the substance to be examined and the reference substance separately in methanol R, evaporate to dryness and record new spectra using the residues.
B. Enantiomeric purity (see Tests).
C. Water (see Tests).
D. Ignite. The residue gives reaction (b) of calcium (2.3.1). Filtration may be necessary in case the residue does not completely dissolve.
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Solvent mixture anhydrous ethanol R, methanol R (50:50 V/V).
Test solution Dissolve 10 mg of the substance to be examined in 4 mL of the solvent mixture and dilute to 10.0 mL with hexane R.
Reference solution (a) Dissolve 2 mg of atorvastatin impurity E CRS in methanol R and dilute to 20.0 mL with the same solvent (solution A). Dissolve 10 mg of the substance to be examined in 1.25 mL of methanol R, add 0.75 mL of solution A and 2 mL of anhydrous ethanol R and dilute to 10.0 mL with hexane R.
Reference solution (b) To 2.0 mL of the test solution add 40.0 mL of the solvent mixture and dilute to 100.0 mL with hexane R. To 3.0 mL of this solution add 5 mL of the solvent mixture and dilute to 20.0 mL with hexane R.
- — size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
- — stationary phase: amylose derivative of silica gel for chromatography R (10 µm).
Mobile phase trifluoroacetic acid R, anhydrous ethanol R, hexane R (0.1:6:94 V/V/V).
Flow rate 1.0 mL/min.
Detection Spectrophotometer at 244 nm.
Injection 20 µL.
Run time 1.2 times the retention time of atorvastatin.
Relative retention With reference to atorvastatin (retention time = about 44 min): impurity E = about 0.8.
System suitability Reference solution (a):
- — resolution: minimum 2.0 between the peaks due to impurity E and atorvastatin.
- — impurity E: not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.3 per cent).
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Test solution (a) Dissolve 40.0 mg of the substance to be examined in dimethylformamide R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same solvent.
Test solution (b) Dissolve 50 mg of the substance to be examined in dimethylformamide R and dilute to 50.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (a) Dissolve 40.0 mg of atorvastatin calcium trihydrate CRS in dimethylformamide R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (b) Dilute 1.0 mL of test solution (b) to 100.0 mL with dimethylformamide R. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 10.0 mL with dimethylformamide R.
Reference solution (c) Dissolve 2.5 mg of atorvastatin impurity A CRS, 2.5 mg of atorvastatin impurity B CRS, 2.5 mg of atorvastatin impurity C CRS, 2.5 mg of atorvastatin impurity D CRS and 2.5 mg of the substance to be examined in dimethylformamide R and dilute to 50.0 mL with the same solvent.
- — size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
- — stationary phase: octylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 µm);
- — temperature: 35 °C.
- — mobile phase A: tetrahydrofuran R, acetonitrile R, 3.9 g/L solution of ammonium acetate R adjusted to pH 5.0 with glacial acetic acid R (12:21:67 V/V/V);
- — mobile phase B: tetrahydrofuran R, 3.9 g/L solution of ammonium acetate R adjusted to pH 5.0 with glacial acetic acid R, acetonitrile R (12:27:61 V/V/V);
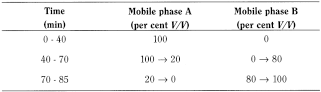
Flow rate 1.5 mL/min.
Detection Spectrophotometer at 244 nm.
Injection 20 µL of test solution (b) and reference solutions (b) and (c).
Identification of impurities Use the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) to identify the peaks due to impurities A, B, C and D.
Relative retention With reference to atorvastatin (retention time = about 33 min): impurity A = about 0.8; impurity B = about 0.9; impurity C = about 1.2; impurity D = about 2.1.
If necessary, adjust the mobile phase by increasing or decreasing the percentage of acetonitrile or the pH of the ammonium acetate solution to achieve a retention time of about 33 min for atorvastatin. For example, raising the pH would decrease the retention time of atorvastatin.
System suitability Reference solution (c):
- — resolution: minimum 1.5 between the peaks due to impurity B and atorvastatin.
- — impurities A, B: for each impurity, not more than 3 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.3 per cent);
- — impurities C, D: for each impurity, not more than 1.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.15 per cent);
- — unspecified impurities: for each impurity, not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.10 per cent);
- — total: not more than 15 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (1.5 per cent);
- — disregard limit: 0.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.05 per cent); disregard the peak due to dimethylformamide.
Maximum 0.4 per cent (anhydrous substance).
Atomic absorption spectrometry (2.2.23, Method I).
Solvent mixture hydrochloric acid R, water R, methanol R (2:25:75 V/V/V).
Test solution Dissolve 5.0 mg in the solvent mixture and dilute to 100.0 mL with the solvent mixture.
Reference solutions Prepare the reference solutions using sodium standard solution (50 ppm Na) R, diluting with the solvent mixture.
Source Sodium hollow-cathode lamp.
Wavelength 589.0 nm.
Atomisation device Air-acetylene flame.
Maximum 20 ppm.
Solvent mixture water R, methanol R (10:90 V/V).
It complies with test H with the following modifications.
Test solution Dissolve 0.250 g of the substance to be examined in 30 mL of the solvent mixture.
Reference solution Dilute 0.5 mL of lead standard solution (10 ppm Pb) R to 30 mL with the solvent mixture.
Blank solution 30 mL of the solvent mixture.
3.5 per cent to 5.5 per cent, determined on 0.130 g.
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29) as described in the test for related substances with the following modification.
Injection Test solution (a) and reference solution (a).
Calculate the percentage content of C66H68CaF2N4O10 from the declared content of atorvastatin calcium trihydrate CRS.
Specified impurities A, B, C, D, E.
Other detectable impurities (the following substances would, if present at a sufficient level, be detected by one or other of the tests in the monograph. They are limited by the general acceptance criterion for other/unspecified impurities and/or by the general monograph Substances for pharmaceutical use (2034). It is therefore not necessary to identify these impurities for demonstration of compliance. See also 5.10. Control of impurities in substances for pharmaceutical use): F, G, H.

A. (3R,5R)-3,5-dihydroxy-7-[5-(1-methylethyl)-2,3-diphenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]heptanoic acid (desfluoroatorvastatin),

B. (3RS,5SR)-7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-(1-methylethyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoic acid,

C. (3R,5R)-7-[2,3-bis(4-fluorophenyl)-5-(1-methylethyl)-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoic acid (fluoroatorvastatin),

D. 3-[(4-fluorophenyl)carbonyl]-2-(2-methylpropanoyl)-N,3-diphenyloxirane-2-carboxamide,

E. (3S,5S)-7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-(1-methylethyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoic acid (ent-atorvastatin),

F. (3R,5R)-7-[[(3R,5R)-7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-(1-methylethyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoyl]amino]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoic acid,

G. (3R,5R)-7-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-(1-methylethyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]-5-hydroxy-3-methoxyheptanoic acid (3-O-methylatorvastatin),

H. (4R,6R)-6-[2-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-(1-methylethyl)-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]ethyl]-4-hydroxytetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-one.
Ph Eur