- British Pharmacopoeia Volume I & II
- Monographs: Medicinal and Pharmaceutical Substances
Cyclizine Hydrochloride |
 |
(Ph. Eur. monograph 1092)
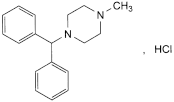
C18H22N2,HCl 302.8 305-25-3
Histamine H1 receptor antagonist; antihistamine.
Dipipanone and Cyclizine Tablets
Ph Eur
1-(Diphenylmethyl)-4-methylpiperazine hydrochloride.
98.5 per cent to 101.0 per cent (dried substance).
White or almost white, crystalline powder.
Slightly soluble in water and in ethanol (96 per cent).
First identification B, E.
Second identification A, C, D, E.
A. Ultraviolet and visible absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.25).
Test solution (a) Dissolve 20.0 mg in a 5 g/L solution of sulfuric acid R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same acid solution.
Test solution (b) Dilute 10.0 mL of test solution (a) to 100.0 mL with a 5 g/L solution of sulfuric acid R.
Spectral range 240-350 nm for test solution (a); 210-240 nm for test solution (b).
Resolution (2.2.25) Minimum 1.7.
Absorption maxima At 258 nm and 262 nm for test solution (a); at 225 nm for test solution (b).
Absorbance ratio A262/A258 = 1.0 to 1.1.
Specific absorbance at the absorption maximum at 225 nm 370 to 410 for test solution (b).
B. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison cyclizine hydrochloride CRS.
C. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution Dissolve 10 mg of the substance to be examined in methanol R and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution Dissolve 10 mg of cyclizine hydrochloride CRS in methanol R and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent.
Plate TLC silica gel GF 254 plate R.
Mobile phase concentrated ammonia R, methanol R, methylene chloride R (2:13:85 V/V/V).
Application 20 µL.
Development Over 2/3 of the plate.
Drying In air for 30 min.
Detection Expose to iodine vapour for 10 min.
Results The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in position, colour and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution.
D. Dissolve 0.5 g in 10 mL of ethanol (60 per cent) R, heating if necessary. Cool in iced water. Add 1 mL of dilute sodium hydroxide solution R and 10 mL of water R. Filter, wash the precipitate with water R and dry at 60 °C at a pressure not exceeding 0.7 kPa for 2 h. The melting point (2.2.14) is 105 °C to 108 °C.
E. It gives reaction (a) of chlorides (2.3.1).
4.5 to 5.5.
Dissolve 0.5 g in a mixture of 40 volumes of ethanol (96 per cent) R and 60 volumes of carbon dioxide-free water R and dilute to 25 mL with the same mixture of solvents.
Gas chromatography (2.2.28). Prepare the solutions immediately before use.
Test solution Dissolve 0.250 g of the substance to be examined in 4.0 mL of methanol R and dilute to 5.0 mL with 1 M sodium hydroxide.
Reference solution (a) Dissolve 25 mg of the substance to be examined in 10.0 mL of methanol R. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 50.0 mL with methanol R.
Reference solution (b) Dissolve 5 mg of the substance to be examined, 5.0 mg of cyclizine impurity A CRS and 5.0 mg of cyclizine impurity B CRS in methanol R and dilute to 20.0 mL with the same solvent.
- — material: fused silica;
- — size: l = 25 m, Ø = 0.33 mm;
- — stationary phase: poly(dimethyl)(diphenyl)siloxane R (film thickness 0.50 µm).
Carrier gas helium for chromatography R.
Flow rate 1.0 mL/min.
Split ratio 1:25.
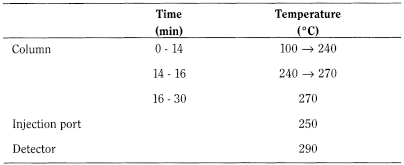
Detection Flame ionisation.
Injection 1 µL.
Relative retention With reference to cyclizine (retention time = about 15 min): impurity A = about 0.2; impurity B = about 0.7.
System suitability Reference solution (b):
- — peak-to-valley ratio: minimum 50, where Hp = height above the baseline of the peak due to impurity A and Hv = height above the baseline of the lowest point of the curve separating this peak from the peak due to methanol.
- — impurities A, B: for each impurity, not more than the area of the corresponding peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.5 per cent);
- — unspecified impurities: for each impurity, not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.10 per cent);
- — total: not more than 10 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (1.0 per cent);
- — disregard limit: 0.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.05 per cent).
Maximum 1.0 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in an oven at 130 °C.
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
In order to avoid overheating in the reaction medium, mix thoroughly throughout and stop the titration immediately after the end-point has been reached.
Dissolve 0.120 g in 15 mL of anhydrous formic acid R and add 40 mL of acetic anhydride R. Titrate with 0.1 M perchloric acid, determining the end-point potentiometrically (2.2.20).
1 mL of 0.1 M perchloric acid is equivalent to 15.14 mg of C18H23ClN2.
Protected from light.
Specified impurities A, B.
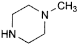
A. 1-methylpiperazine,
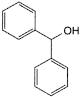
B. diphenylmethanol (benzhydrol).
Ph Eur

