- British Pharmacopoeia Volume I & II
- Monographs: Medicinal and Pharmaceutical Substances
Calcium Folinate |
 |
(Ph Eur monograph 0978)
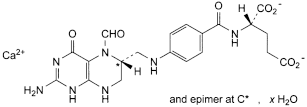
C20H21CaN7O7,xH2O 511.5 1492-18-8
(anhydrous)
Antidote to folic acid antagonists.
Ph Eur
Calcium (2S)-2-[[4-[[[(6RS)-2-amino-5-formyl-4-oxo1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydropteridin-6-yl]methyl]amino]benzoyl]amino]pentanedioate.
- — calcium folinate (C20H21CaN7O7): 97.0 per cent to 102.0 per cent (anhydrous substance);
- — calcium (Ca; Ar 40.08): 7.54 per cent to 8.14 per cent (anhydrous substance).
It contains a variable amount of water.
White or light yellow, amorphous or crystalline, hygroscopic powder.
Sparingly soluble in water, practically insoluble in acetone and in ethanol (96 per cent).
The amorphous form may produce supersaturated solutions in water.
First identification A, B, D.
Second identification A, C, D.
A. Specific optical rotation (see Tests).
B. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Preparation Discs.
Comparison calcium folinate CRS.
If the spectra obtained show differences, dissolve the substance to be examined and the reference substance separately in the minimum volume of water R and add dropwise sufficient acetone R to produce a precipitate. Allow to stand for 15 min, collect the precipitate by centrifugation, wash the precipitate with 2 small quantities of acetone R and dry. Record new spectra using the residues.
C. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution Dissolve 15 mg of the substance to be examined in a 3 per cent V/V solution of ammonia R and dilute to 5 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution Dissolve 15 mg of calcium folinate CRS in a 3 per cent V/V solution of ammonia R and dilute to 5 mL with the same solvent.
Plate cellulose for chromatography F254 R as the coating substance.
Mobile phase The lower layer of a mixture of 1 volume of isoamyl alcohol R and 10 volumes of a 50 g/L solution of citric acid R previously adjusted to pH 8 with ammonia R.
Application 5 µL.
Development Over a path of 15 cm.
Drying In air.
Detection Examine in ultraviolet light at 254 nm.
Results The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in position and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution.
D. It gives reaction (b) of calcium (2.3.1).
Carry out the tests and the assay as rapidly as possible, protected from actinic light.
Dissolve 1.25 g in carbon dioxide-free water R, heating at 40 °C if necessary, and dilute to 50.0 mL with the same solvent.
Solution S is clear (2.2.1) and its absorbance (2.2.25) at 420 nm is not greater than 0.60. Use water R as the compensation liquid.
6.8 to 8.0 for solution S.
+ 14.4 to + 18.0 (anhydrous substance), determined on solution S.
Head-space gas chromatography (2.2.28): use the standard additions method.
Test solution Dissolve 0.25 g of the substance to be examined in water R and dilute to 10.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution Dilute 0.125 g of acetone R, 0.750 g of anhydrous ethanol R and 0.125 g of methanol R in water R and dilute to 1000.0 mL with water R.
- — material: fused silica;
- — size: l = 10 m, Ø = 0.32 mm;
- — stationary phase: styrene-divinylbenzene copolymer R.
Carrier gas nitrogen for chromatography R.
Flow rate 4 mL/min.
- — equilibration temperature: 80 °C;
- — equilibration time: 20 min;
- — pressurisation time: 30 s.
Temperature:

Detection Flame ionisation.
Injection At least 3 times.
- — acetone: maximum 0.5 per cent;
- — ethanol: maximum 3.0 per cent;
- — methanol: maximum 0.5 per cent.
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Test solution Dissolve 10.0 mg of the substance to be examined in water R and dilute to 10.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (a) Dissolve 10.0 mg of calcium folinate CRS in water R and dilute to 10.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (b) Dilute 1.0 mL of reference solution (a) to 100.0 mL with water R.
Reference solution (c) Dissolve 10.0 mg of formylfolic acid CRS (impurity D) in the mobile phase and dilute to 100.0 mL with the mobile phase. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 10.0 mL with water R.
Reference solution (d) Dilute 1.0 mL of reference solution (b) to 10.0 mL with water R.
Reference solution (e) Dilute 5.0 mL of reference solution (c) to 10.0 mL with reference solution (b).
- — size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4 mm;
- — stationary phase: octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 µm);
- — temperature: 40 °C.
Mobile phase Mix 220 mL of methanol R and 780 mL of a solution containing 2.0 mL of tetrabutylammonium hydroxide solution (400 g/L) R and 2.2 g of disodium hydrogen phosphate R, previously adjusted to pH 7.8 with phosphoric acid R.
Flow rate 1 mL/min.
Detection Spectrophotometer at 280 nm.
Injection 10 µL of the test solution and reference solutions (b), (c), (d) and (e).
Run time 2.5 times the retention time of folinate.
System suitability Reference solution (e):
- — resolution: minimum 2.2 between the peaks due to folinate and impurity D.
- — impurity D: not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) (1 per cent);
- — impurities A, B, C, E, F, G: for each impurity, not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (1 per cent);
- — sum of impurities other than D: not more than 2.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (2.5 per cent);
- — disregard limit: the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (d) (0.1 per cent).
Maximum 0.5 per cent.
Dissolve 0.300 g in 50 mL of water R heating at 40 °C if necessary. Add 10 mL of 2M nitric acid and titrate with 0.005 M silver nitrate determining the end-point potentiometrically (2.2.20).
1 mL of 0.005 M silver nitrate is equivalent to 0.177 mg of Cl.
Maximum 50 ppm.
1.0 g complies with test F. Prepare the reference solution using 5 mL of lead standard solution (10 ppm Pb) R.
Maximum 20 ppm.
Test solution Dissolve 1.00 g in water R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solutions Prepare the reference solutions using platinum standard solution (30 ppm Pt) R, diluted as necessary with a mixture of 1 volume of nitric acid R and 99 volumes of water R.
Source Platinum hollow-cathode lamp.
Wavelength 265.9 nm.
Maximum 17.0 per cent.
Dissolve 0.100 g in a mixture of 50 mL of the titration solvent and 15 mL of formamide R. Stir for about 6 min before titrating and use a suitable titrant that does not contain pyridine.
Less than 0.5 IU/mg, if intended for use in the manufacture of parenteral preparations without a further appropriate procedure for the removal of bacterial endotoxins.
Dissolve 0.400 g in 150 mL of water R and dilute to 300 mL with the same solvent. Carry out the complexometric titration of calcium (2.5.11).
1 mL of 0.1 M sodium edetate is equivalent to 4.008 mg of Ca.
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29) as described in the test for related substances with the following modifications.
Injection Test solution and reference solution (a).
- — repeatability: maximum relative standard deviation of 2.0 per cent after 6 injections of reference solution (a).
Calculate the percentage content of C20H21CaN7O7 from the declared content of calcium folinate CRS.
In an airtight container, protected from light. If the substance is sterile, store in a sterile, airtight, tamper-proof container.
Specified impurities A, B, C, D, E, F, G.
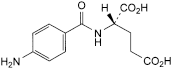
A. (2S)-2[(4-aminobenzoyl)amino]pentanedioic acid,
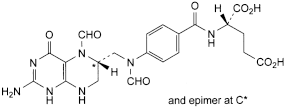
B. (2S)-2-[[4-[[[(6RS)-2-amino-5-formyl-4-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydropteridin-6-yl]methyl]formylamino]benzoyl]amino]pentanedioic acid (5,10-diformyltetrahydrofolic acid),
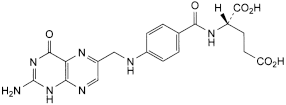
C. (2S)-2-[[4-[[(2-amino-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropteridin-6-yl)methyl]amino]benzoyl]amino]pentanedioic acid (folic acid),
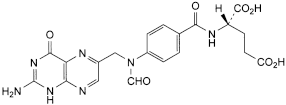
D. (2S)-2-[[4-[[(2-amino-4-oxo-1,4-dihydropteridin-6-yl)methyl]formylamino]benzoyl]amino]pentanedioic acid (10-formylfolic acid),
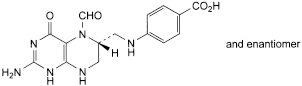
E. 4-[[[(6RS)-2-amino-5-formyl-4-oxo-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydropteridin-6-yl]methyl]amino]benzoic acid (5-formyltetrahydropteroic acid),
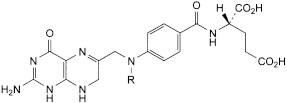
F. R = CHO: (2S)-2-[[4-[[(2-amino-4-oxo-1,4,7,8-tetrahydropteridin-6-yl)methyl]formylamino]benzoyl]amino]pentanedioic acid (10-formyldihydrofolic acid),
G. R = H: (2S)-2-[[4-[[(2-amino-4-oxo-1,4,7,8-tetrahydropteridin-6-yl)methyl]amino]benzoyl]amino]pentanedioic acid (dihydrofolic acid).
Ph Eur

