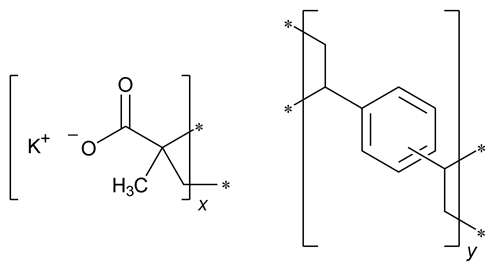
Polacrilin Potassium

 231
231 :
:
 (Official 1-Dec-2015)
(Official 1-Dec-2015)
(pol'' a kril' in poe tas' ee um).
DEFINITION
Polacrilin Potassium is the potassium salt of a unifunctional low-cross-linked carboxylic cation-exchange resin prepared from methacrylic acid and divinylbenzene. When previously dried at 105 for 6 h, it contains NLT 20.6% and NMT 25.1% of potassium (K).
for 6 h, it contains NLT 20.6% and NMT 25.1% of potassium (K).
IDENTIFICATION
• B. Identification Tests—General, Potassium  191
191
Sample solution A:
Shake 1 g with 10 mL of water.
Sample solution B:
Shake 1 g with 10 mL of 0.1 N hydrochloric acid.
Analysis:
Use the aqueous phase from Sample solution A and Sample solution B.
Acceptance criteria
Sample solution A:
Does not meet the requirements
Sample solution B:
Meets the requirements
ASSAY
• Content of Potassium
Sodium stock solution:
14.612 mg/mL of sodium chloride, previously dried at 125 for 30 min. This solution contains 5.76 mg/mL of sodium (Na).
for 30 min. This solution contains 5.76 mg/mL of sodium (Na).
Potassium stock solution:
745.5 µg/mL of potassium chloride, previously dried at 125 for 30 min. This solution contains 391 µg/mL of potassium (K).
for 30 min. This solution contains 391 µg/mL of potassium (K).
Surfactant solution:
Transfer 5.0 g of a suitable nonionic surfactant to a 250-mL beaker, add 200 mL of water, and stir to dissolve. Transfer this solution to a 500-mL volumetric flask, dilute with water to volume, and mix. [Note—To prevent foaming when using this solution, gently run the solution down the sides of the vessel, and use gentle action when mixing. ]
Diluted sodium solution:
Transfer 50.0 mL of Sodium stock solution and 10.0 mL of Surfactant solution to a 100-mL volumetric flask, dilute with water to volume, and mix gently to prevent foaming.
Standard solutions:
To three separate 500-mL volumetric flasks transfer, respectively, 3.0-, 4.0-, and 5.0-mL portions of Potassium stock solution. To each flask add 50.0 mL of Sodium stock solution and 10.0 mL of Surfactant solution, dilute with water to volume, and mix gently to prevent foaming. Each mL of these solutions contains 2.346, 3.128, and 3.910 µg of K, respectively.
Sample solution:
Transfer 1.4 g of Polacrilin Potassium, previously dried, to a 50-mL silica crucible, moisten with 4 mL of sulfuric acid, heat over a small flame until the acid has fumed off, moisten the residue with a few drops of sulfuric acid, and ignite strongly. Allow to cool, transfer, with the aid of water, to a 1000-mL volumetric flask, dilute with water to volume, and mix. Transfer 1.00 mL of this solution to a 100-mL volumetric flask, add 20.0 mL of Diluted sodium solution, dilute with water to volume, and mix gently to prevent foaming.
Instrumental conditions
Mode:
Flame photometry
Analytical wavelength:
766 nm
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solutions and Sample solution
Concomitantly determine the emittances of the Standard solutions and Sample solution, adjusting the instrument so that the most concentrated Standard solution gives a reading near 100%.
Prepare a standard curve by plotting the readings from the Standard solutions versus the square root of the potassium concentrations. From the curve, determine the concentration of potassium in the Sample solution.
Calculate the percentage of potassium in the portion of sample taken:
Result = (CO/CU) × 100
| CO | = | = concentration of the Sample solution determined from the standard curve (µg/mL) |
| CU | = | = concentration of Polacrilin Potassium in the Sample solution (µg/mL) |
Acceptance criteria:
20.6%–25.1%
IMPURITIES
Delete the following:
• Iron  241
241
Sample:
0.10 g
Analysis:
Transfer the Sample to a suitable crucible, and ignite at a low heat until thoroughly ashed. Add to the carbonized mass 2 mL of nitric acid and 5 drops of sulfuric acid, and heat cautiously until white fumes are no longer evolved. Ignite, preferably in a muffle furnace, at 500 –600
–600 , until the carbon is completely burned off. Cool, add 4 mL of 6 N hydrochloric acid, cover, digest on a steam bath for 15 min, uncover, and slowly evaporate on a steam bath to dryness. Moisten the residue with 1 drop of hydrochloric acid, add 10 mL of hot water, and digest for 2 min. Dilute with water to 25 mL. Filter, if necessary. Rinse the crucible and the filter with 10 mL of water, combining the filtrate and rinsing in a 50-mL color-comparison tube, add 2 mL of hydrochloric acid, dilute with water to 45 mL, and mix.
, until the carbon is completely burned off. Cool, add 4 mL of 6 N hydrochloric acid, cover, digest on a steam bath for 15 min, uncover, and slowly evaporate on a steam bath to dryness. Moisten the residue with 1 drop of hydrochloric acid, add 10 mL of hot water, and digest for 2 min. Dilute with water to 25 mL. Filter, if necessary. Rinse the crucible and the filter with 10 mL of water, combining the filtrate and rinsing in a 50-mL color-comparison tube, add 2 mL of hydrochloric acid, dilute with water to 45 mL, and mix.
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 0.01%
• Limit of Sodium
Sample solution:
Transfer 2 g to a 400-mL borosilicate beaker, add 20 mL of sulfuric acid, cover with a borosilicate watch glass, and heat until charring is complete. While continuing to heat the beaker, add 20 mL of nitric acid dropwise. Continue to heat, and add nitric acid until all of the organic material has been destroyed as indicated by the contents of the beaker turning from brown to a very pale straw-colored or colorless solution. Continue to evaporate the solution, and if it turns brown during the evaporation, add nitric acid dropwise until the brown color disappears. Evaporate just to dryness, cool, and dissolve the residue in 40 mL of water and 10 mL of 6 N hydrochloric acid. Heat to boiling, cool, transfer to a 100-mL volumetric flask, dilute with water to volume, and mix.
Standard solutions:
To three separate 100-mL volumetric flasks add, respectively, 1.00, 2.00, and 3.00 mL of a solution containing 254.2 mg of sodium chloride in 1000 mL of water. Add water to volume, and mix to obtain sodium chloride solutions having concentrations equivalent to 1, 2, and 3 µg/mL of Na, respectively.
Instrumental conditions
Mode:
Flame photometry
Analytical wavelength:
589 nm
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solutions and Sample solution
Adjust the instrument so that the emission of the Standard solution with a concentration of 3 µg/mL reads close to 100% at 589 nm.
Determine the readings of the three Standard solutions at 589 nm. Readjust the wavelength setting to 580 nm, and determine the background emission reading for one of these Standard solutions.
Pipet 5 mL of the Sample solution into a 100-mL volumetric flask, add water to volume, and mix. Observe the emission reading of this solution at 589 nm, using the same instrument settings, then readjust the wavelength setting to 580 nm, and observe the background emission reading.
Subtract the corresponding background readings from the readings of Standard solutions and Sample solution.
Prepare a standard curve by plotting the corrected Standard solution readings versus the square root of the sodium concentration. From this standard curve, determine the sodium content in the sample taken.
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 0.20%
SPECIFIC TESTS
• Powder Fineness  811
811
Sample:
4 g
Analysis:
Transfer the Sample to a No. 100 standard sieve placed on top of a No. 200 standard sieve and pan. Using a soft 2-cm brush, brush the sample lightly across the No. 100 sieve until no more particles pass through. By brushing and tapping, dust off the particles on the underside of the No. 100 sieve into the No. 200 sieve. Obtain the weight of the material retained on the No. 100 sieve. Similarly, determine the weight of material retained by the No. 200 sieve.
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 1.0% is retained on the No. 100 sieve, and NMT 30.0% is retained on the No. 200 sieve.
ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
• Packaging and Storage:
Preserve in well-closed containers.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Hong Wang, Ph.D.
Senior Scientific Liaison (301) 816-8351 |
(EXC2010) Monographs - Excipients |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
USP38–NF33 Page 6793
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 31(6) Page 1671