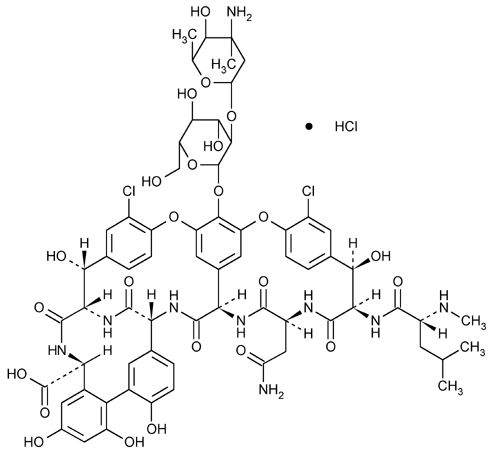
Vancomycin Hydrochloride
Vancomycin, monohydrochloride.
Vancomycin monohydrochloride.
(Sa)-(3S,6R,7R,22R,23S,26S,36R,38aR)-44-[[2-O-(3-Amino- 2,3,6-trideoxy-3-C-methyl-
[3S-[3R*,6S*(S*),7S*,22S*,23R*,26R*,36S*,38aS*]]-3-(2-Amino-2-oxoethyl)-44-[[2-O-(3-amino-2,3,6-trideoxy-3-C-methyl-
» Vancomycin Hydrochloride is the hydrochloride salt of a kind of vancomycin, a substance produced by the growth of Streptomyces orientalis (Fam. Streptomycetaceae), or a mixture of two or more such salts. It has a potency equivalent to not less than 900 µg of vancomycin per mg, calculated on the anhydrous basis.
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in tight containers.
USP Reference standards  11
11 —
—
USP Vancomycin Hydrochloride RS.
USP Vancomycin B with Monodechlorovancomycin RS.
USP Vancomycin Hydrochloride RS.
USP Vancomycin B with Monodechlorovancomycin RS.
Identification,
Infrared Absorption  197K
197K : undried.
: undried.
pH  791
791 :
between 2.5 and 4.5, in a solution containing 50 mg per mL.
:
between 2.5 and 4.5, in a solution containing 50 mg per mL.
Water, Method I  921
921 :
not more than 5.0%.
:
not more than 5.0%.
Chromatographic purity—
Triethylamine buffer—
Mix 4 mL of triethylamine and 2000 mL of water, and adjust with phosphoric acid to a pH of 3.2.
Solution A—
Prepare a mixture of Triethylamine buffer, acetonitrile, and tetrahydrofuran (92:7:1), and degas briefly.
Solution B—
Prepare a suitable mixture of Triethylamine buffer, acetonitrile, and tetrahydrofuran (70:29:1), and degas briefly.
Mobile phase—
Use variable mixtures of Solution A and Solution B as directed for Chromatographic system. Make adjustments if necessary (see System Suitability under Chromatography  621
621 ), changing the acetonitrile proportion in Solution A to obtain a retention time of 7.5 to 10.5 minutes for the main vancomycin peak.
), changing the acetonitrile proportion in Solution A to obtain a retention time of 7.5 to 10.5 minutes for the main vancomycin peak.
Resolution solution—
Prepare a solution of USP Vancomycin Hydrochloride RS in water containing 0.5 mg per mL, heat at 65 for 48 hours, and allow to cool.
for 48 hours, and allow to cool.
Test preparation A—
Prepare a solution of Vancomycin Hydrochloride in Solution A containing 10 mg per mL.
Test preparation B—
Transfer 2.0 mL of Test preparation A to a 50-mL volumetric flask, dilute with Solution A to volume, and mix.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 280-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 25-cm column that contains 5-µm packing L1. The flow rate is about 2 mL per minute. The chromatograph is programmed as follows.
)—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 280-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 25-cm column that contains 5-µm packing L1. The flow rate is about 2 mL per minute. The chromatograph is programmed as follows.
Chromatograph the Resolution solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the elution order is resolution compound 1, vancomycin B, and resolution compound 2. The resolution, R, between resolution compound 1 and vancomycin B is not less than 3.0; and the column efficiency, calculated from the vancomycin B peak, is not less than 1500 theoretical plates. Resolution compound 2 is eluted at between 3 and 6 minutes after the start of the period when the percentage of Solution B is increasing from 0% to 100%.
| Time (minutes) |
Solution A
(%) |
Solution B
(%) |
Elution |
| 0–12 | 100 | 0 | isocratic |
| 12–20 | 100®0 | 0®100 | linear gradient |
| 20–22 | 0 | 100 | isocratic |
| 22–23 | 0®100 | 100®0 | linear gradient |
| 23–30 | 100 | 0 | isocratic |
Procedure—
[note—Where baseline separation is not achieved, peak areas are defined by vertical lines extended from the valleys between peaks to the baseline. The main component peak may include a fronting shoulder, which is attributed to monodechlorovancomycin. This shoulder should not be integrated separately.] Separately inject equal volumes (about 20 µL) of Test preparation A and Test preparation B into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the area responses for all of the peaks. [note—Correct any peak observed in the chromatograms obtained from Test preparation A and Test preparation B by subtracting the area response of any peak observed in the chromatogram of Solution A at the corresponding elution time.] Calculate the percentage of vancomycin B in the specimen tested by the formula:
2500rB /(25rB + rA)
in which rB is the corrected area response of the main peak obtained in the chromatogram of Test preparation B; and rA is the sum of the corrected area responses of all the peaks, other than the main peak, in the chromatogram obtained from Test preparation A: not less than 80.0% of vancomycin B is found. Calculate the percentage of each other peak taken by the formula:
100rAi / (25rB + rA)
in which rAi is the corrected area response of any individual peak, other than the main peak, obtained in the chromatogram of Test preparation A: not more than 9.0% of any peak other than the main peak is found.
Limit of monodechlorovancomycin—
[note—The System suitability solution, Working standard solution, and Test solution are to be refrigerated immediately after preparation and during analysis, using a refrigerated autosampler. The solutions are stable at refrigerated conditions for 4 days.]
Mobile phase—
Prepare a filtered and degassed mixture in a 1-L volumetric flask that is initially half filled with water. Dissolve 2.2 g of 1-heptanesulfonic acid sodium salt, add 125 mL of acetonitrile and 10 mL of acetic acid, and dilute with water to volume, making adjustments if necessary (see System Suitability under Chromatography  621
621 ).
).
Rinse solution—
Prepare a solution containing approximately 10% (v/v) acetonitrile in water, to be used as the rinse solution for the needle and column.
System suitability solution—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of USP Vancomycin B with Monodechlorovancomycin RS that contains approximately 50 mg of vancomycin B in water in a 50-mL volumetric flask to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 1 mg of vancomycin B per mL.
Working standard solution—
Transfer 5.0 mL of the System suitability solution to a 100-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume. The final concentration is approximately 0.05 mg of vancomycin B per mL.
Test solution—
Transfer about 100 mg of Vancomycin Hydrochloride, accurately weighed, to a 100-mL volumetric flask, dilute with water to volume, and mix.
Blank:
water
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 280-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 25-cm column that contains packing L1 and is maintained at a constant temperature of about 60
)—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 280-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 25-cm column that contains packing L1 and is maintained at a constant temperature of about 60 . The flow rate is about 1.5 mL per minute. The autosampler cooler temperature is maintained at 5
. The flow rate is about 1.5 mL per minute. The autosampler cooler temperature is maintained at 5 . The Blank and Working standard solution run time is 90 minutes, and the System suitability solution and Test solution run time is 120 minutes. [note—This test is sensitive to temperature changes. To preheat the Mobile phase, Working standard solution, and Test solution, a length of tubing of at least 3 feet should be placed preceding the column within the column heater.] Chromatograph the Blank and the System suitability solution. There should be no peaks in the Blank chromatogram that interfere with the vancomycin B and monodechlorovancomycin peaks. The retention time of the vancomycin B peak is between 32 and 42 minutes. The monodechlorovancomycin elutes at a retention time ratio of approximately 1.1 compared to 1.0 for the main component, vancomycin B. The retention time of the monodechlorovancomycin peak in the Test solution chromatogram must be within ±3.0% of the mean retention time of the monodechlorovancomycin peaks in the chromatogram of the Working standard solution. The resolution, R, between vancomycin B and monodechlorovancomycin is not less than 1.5, using the chromatogram from the System suitability solution; and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections of the Working standard solution is not more than 2.0%.
. The Blank and Working standard solution run time is 90 minutes, and the System suitability solution and Test solution run time is 120 minutes. [note—This test is sensitive to temperature changes. To preheat the Mobile phase, Working standard solution, and Test solution, a length of tubing of at least 3 feet should be placed preceding the column within the column heater.] Chromatograph the Blank and the System suitability solution. There should be no peaks in the Blank chromatogram that interfere with the vancomycin B and monodechlorovancomycin peaks. The retention time of the vancomycin B peak is between 32 and 42 minutes. The monodechlorovancomycin elutes at a retention time ratio of approximately 1.1 compared to 1.0 for the main component, vancomycin B. The retention time of the monodechlorovancomycin peak in the Test solution chromatogram must be within ±3.0% of the mean retention time of the monodechlorovancomycin peaks in the chromatogram of the Working standard solution. The resolution, R, between vancomycin B and monodechlorovancomycin is not less than 1.5, using the chromatogram from the System suitability solution; and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections of the Working standard solution is not more than 2.0%.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 50 µL) of the Blank, System suitability solution, Working standard solution, and Test solution into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the peak area responses. Calculate the percentage of monodechlorovancomycin in the portion of Vancomycin Hydrochloride taken by the formula:
100 (CS / CU)(rU / rS) P
in which CS is the concentration, in mg per mL, of USP Vancomycin B with Monodechlorovancomycin RS in the Working standard solution; CU is the concentration, in mg per mL, of Vancomycin Hydrochloride in the Test solution; rU is the peak area response of the monodechlorovancomycin peak in the Test solution; rS is the average peak area response of the vancomycin B peak in the Working standard solution; and P is the vancomycin B potency, in mg per mg, of USP Vancomycin B with Monochlorovancomycin RS: not more than 4.7% of monodechlorovancomycin is found.
Assay—
Proceed with Vancomycin Hydrochloride as directed under Antibiotics—Microbial Assays  81
81 .
.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
Chromatographic Column—
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
| Monograph | Ahalya Wise, M.S.
Scientist 1-301-816-8161 |
(MDANT05) Monograph Development-Antibiotics |
| Reference Standards | Lili Wang, Technical Services Scientist 1-301-816-8129 RSTech@usp.org |
USP32–NF27 Page 3845
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 34(1) Page 111
Chromatographic columns text is not derived from, and not part of, USP 32 or NF 27.