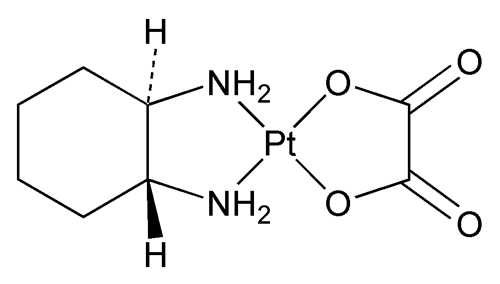
Oxaliplatin
C8H14N2O4Pt 397.29
[SP-4-2-(1R-trans)]-(1,2-Cyclohexanediamine-N,N¢)[ethanedioato(2-)-O,O¢]platinum;
cis-[(1R,2R)-1,2-Cyclohexanediamine-N,N¢][oxalato(2-)-O,O¢]platinum

 [61825-94-3].
[61825-94-3].
(ox al'' i pla' tin).
C8H14N2O4Pt 397.29
[SP-4-2-(1R-trans)]-(1,2-Cyclohexanediamine-N,N¢)[ethanedioato(2-)-O,O¢]platinum;
cis-[(1R,2R)-1,2-Cyclohexanediamine-N,N¢][oxalato(2-)-O,O¢]platinum
DEFINITION
Oxaliplatin contains NLT 98.0% and NMT 102.0% of C8H14N2O4Pt, calculated on the dried basis.
[Caution—Great care should be taken in handling Oxaliplatin, because it is a potentially cytotoxic agent.
]
IDENTIFICATION
• B.
The retention time of the major peak in the Sample solution corresponds to that in the Standard solution, as obtained in the Assay.
ASSAY
• Procedure
[Note—Use vigorous shaking and very brief sonication to dissolve the substance to be examined. Inject the Sample solution within 20 min of preparation. Polypropylene HPLC autosampler vials should be used. ]
Buffer:
Weigh 2.72 g of monobasic potassium phosphate (anhydrous) and 1.80 g of 1-pentanesulfonic acid sodium salt into a suitable container. Add 2000 mL of water, and mix well to completely dissolve all solids. Transfer 0.5 mL of triethylamine to the buffer solution, and mix thoroughly. Adjust the solution by dropwise addition of phosphoric acid to a pH of 4.30 ± 0.05.
Mobile phase:
Methanol and Buffer (3:17)
Oxaliplatin standard stock solution:
0.5 mg/mL of USP Oxaliplatin RS in water
Oxaliplatin related compound B standard stock solution:
Transfer USP Oxaliplatin Related Compound B RS to a suitable volumetric flask, add 25% of the final volume of methanol, and sonicate for approximately 2 min to disperse the solids. Add approximately 65% of the final volume of 0.001 M nitric acid, and sonicate for an additional 30 min to dissolve the solids. Allow to cool if necessary. Dilute with 0.001 M nitric acid to volume, and mix to obtain a solution having a known concentration of 0.125 mg/mL. [Note—USP Oxaliplatin Related Compound B RS is converted to (SP-4-2)-diaqua[(1R,2R)-cyclohexane-1,2-diamine-N,N¢]platinum in solution preparation. ]
Oxaliplatin related compound C standard stock solution:
0.1 mg/mL of USP Oxaliplatin Related Compound C RS in water
System suitability solution:
2 mg/mL of Oxaliplatin in 0.005 M sodium hydroxide. Allow this solution to stand at room temperature for at least 5 days. Transfer 10 mL of this solution, 10 mL of Oxaliplatin related compound B standard stock solution, and 5 mL of Oxaliplatin related compound C standard stock solution into a 100-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume. [Note—The preparation of the System suitability solution forms diaquodiaminocyclohexaneplatinum dimer. ]
Standard solution:
0.1 mg/mL of USP Oxaliplatin RS in water, from Oxaliplatin standard stock solution
Sample solution:
0.1 mg/mL of Oxaliplatin in water
Chromatographic system
Mode:
LC
Detector:
UV 210 nm
Column:
4.6-mm × 25-cm; 5-µm packing L1
Flow rate:
1 mL/min
Injection size:
50 µL
System suitability
Samples:
System suitability solution and Standard solution
[Note—The relative retention times, measured with respect to oxaliplatin, of oxaliplatin related compounds C and B and diaquodiaminocyclohexaneplatinum dimer are 0.8, 2.7, and 6, respectively. ]
Suitability requirements
Resolution:
NLT 2.0 between oxaliplatin and oxaliplatin related compound C, System suitability solution
Tailing factor:
Between 0.8 and 2.0 for the oxaliplatin peak, System suitability solution
Relative standard deviation:
NMT 2.0% for the oxaliplatin peak, Standard solution
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of C8H14N2O4Pt in the portion of Oxaliplatin taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × 100
| rU | = | = peak response from the Sample solution |
| rS | = | = peak response from the Standard solution |
| CS | = | = concentration of USP Oxaliplatin RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL) |
| CU | = | = concentration of Oxaliplatin in the Sample solution (mg/mL) |
Acceptance criteria:
98.0%–102.0% on the dried basis
IMPURITIES
Inorganic Impurities
• Limit of Silver
Sample stock solution:
Dissolve 100 mg of Oxaliplatin, weighed, in 50 mL of water to obtain a solution having a concentration of 2 mg/mL.
Sample solution:
1 mg/mL of Oxaliplatin in 0.5 M nitric acid from Sample stock solution
Standard stock solution:
Dilute a commercially available silver nitrate atomic absorption standard solution containing 1000 ppm of silver in 0.5 M nitric acid quantitatively, and stepwise if necessary, with 0.5 M nitric acid to obtain a 10-ppb solution.
Standard solution 1:
Mix 20 µL of the Sample stock solution and 8 µL of the Standard stock solution, and dilute with 0.5 M nitric acid to 40 µL.
Standard solution 2:
Mix 20 µL of the Sample stock solution and 16 µL of the Standard stock solution, and dilute with 0.5 M nitric acid to 40 µL.
Spectrometric conditions
Mode:
Atomic absorption spectrophotometer equipped with a silver hollow-cathode lamp and graphite furnace
Analytical wavelength:
Silver emission line of 328.1 nm
Blank:
0.5 M nitric acid
Analysis
Samples:
Sample solution, Standard solution 1, and Standard solution 2
Plot the absorbances of the Sample solution, Standard solution 1, and Standard solution 2 versus their concentrations, in ppb, of silver, and draw the straight line best fitting the three plotted points. The intercept on the x-axis of the extended regression line indicates the silver concentration in the Sample solution.
Calculate the silver, in ppm, in the portion of Oxaliplatin taken:
Result = (C/W) × 100
| C | = | = absolute value of the intercept, in ppb of silver, on the x-axis |
| W | = | = weight of Oxaliplatin taken for the preparation of the Sample stock solution (mg) |
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 5 ppm
• Heavy Metals
Standard stock solution:
Transfer 1 mL each of 1000-ppm standard solutions of cadmium, chromium, copper, iron, nickel, and lead (commercially available) to a 100-mL volumetric flask. Add 5 mL of nitric acid, and dilute with water to volume.
Internal standard solution:
Transfer 1 mL of a 10,000-ppm standard solution of yttrium (commercially available) to a 100-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with 5% nitric acid to volume.
Standard solutions:
Transfer 0.2, 2.0, and 20.0 mL of Standard stock solution to separate 100-mL volumetric flasks. Add 1.0 mL of Internal standard solution and 5.0 mL of nitric acid to each flask, and dilute with water to volume. The concentrations of these solutions are 0.02, 0.20, and 2.00 ppm, respectively.
Blank solution:
Transfer 1.0 mL of Internal standard solution and 5.0 mL of nitric acid to a 100-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume.
Sample solution:
Weigh 1 g of Oxaliplatin into a 100-mL volumetric flask, and add 80 mL of water. Stir vigorously for several min with a magnetic stirrer until no more sample seems to be dissolving. Add 5 mL of nitric acid, and mix again until the sample is completely dissolved. Remove the stirrer bar from the flask, rinsing it before removal. Add 1.0 mL of the Internal standard solution, and dilute with water to volume.
Spectrometric conditions
(See Plasma Spectrochemistry  730
730 .)
.)
Measure the responses of the elements cadmium, chromium, copper, iron, nickel, lead, and yttrium (internal standard), using an inductively coupled plasma–atomic optical emission spectrometer (ICP–OES), by measuring the emissions at 226.502, 283.563, 327.395, 259.940, 221.648, 220.353, and 371.029 nm, respectively. Optimize the instrument settings as directed by the manufacturer.
System suitability
Before samples are analyzed, the instrument must pass a suitable performance check. Generate the calibration curve, using the Blank solution and the Standard solutions, and run these solutions in the following order: the Blank solution, then the 0.02-, 0.20-, and 2.00-ppm solutions. The linear regression coefficient is NLT 0.99; the response of the Blank solution is between  5.0 and 5.0 ppb for each element; and the responses of yttrium obtained from the Standard solutions are drifted by NMT 5.0% of the response obtained from the Blank solution. Run the Standard solution of 0.20 ppm, and record the responses of each element: the relative standard deviations for replicate runs are NMT 5.0%; and the recovery against the calibration curve is between 95% and 105%. After samples are analyzed, the instrument must pass the same suitable performance check to ensure that the calibration is still valid.
5.0 and 5.0 ppb for each element; and the responses of yttrium obtained from the Standard solutions are drifted by NMT 5.0% of the response obtained from the Blank solution. Run the Standard solution of 0.20 ppm, and record the responses of each element: the relative standard deviations for replicate runs are NMT 5.0%; and the recovery against the calibration curve is between 95% and 105%. After samples are analyzed, the instrument must pass the same suitable performance check to ensure that the calibration is still valid.
Analysis
Sample:
Sample solution
Record the responses of each element, and determine the concentration of each element, using the calibration graph. Calculate the content of total elements, in ppm, in the portion of Oxaliplatin taken:
Result = [(SCi)/W] × 100
| Ci | = | = concentration of each element in the Sample solution (ppm) |
| W | = | = weight of Oxaliplatin taken to prepare the Sample solution (g) |
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 20 ppm
• Content of Platinum
Sample:
Ignite an empty porcelain crucible fitted with a lid in a furnace at 800 for 30 min. Cool in a desiccator, and weigh. Add 200 mg of the Oxaliplatin, weighed, to the crucible, and ignite in a furnace by stepwise increments as follows: introduce into the furnace; and increase the temperature to 200
for 30 min. Cool in a desiccator, and weigh. Add 200 mg of the Oxaliplatin, weighed, to the crucible, and ignite in a furnace by stepwise increments as follows: introduce into the furnace; and increase the temperature to 200 within 15 min, then to 400
within 15 min, then to 400 within 15 min, then to 600
within 15 min, then to 600 within 15 min, then finally to 800
within 15 min, then finally to 800 within 15 min. Allow to remain in the furnace at 800
within 15 min. Allow to remain in the furnace at 800 for 30 min. Remove, cool in a desiccator, and reweigh.
for 30 min. Remove, cool in a desiccator, and reweigh.
Calculate the percentage of platinum in the portion of Oxaliplatin taken:
Result = (W2/W1) × 100
| W2 | = | = weight of residue after ignition (mg) |
| W1 | = | = weight of oxaliplatin before ignition (mg) |
Acceptance criteria:
48.1%–50.1% of the oxaliplatin taken, on the dried basis
Organic Impurities
• Procedure 1: Limit of Oxalic Acid
[Note—Use vigorous shaking and very brief sonication to dissolve the substance to be examined. Inject the Sample solution within 20 min of preparation. Polypropylene HPLC autosampler vials should be used. ]
Buffer:
Add 1.36 g of potassium dihydrogen phosphate to 10 mL of 10% tetrabutylammonium hydroxide in water, and dilute with water to 1000 mL. Adjust with phosphoric acid to a pH of 6.0.
Mobile phase:
Acetonitrile and Buffer (1:4)
Standard stock solution:
0.06 mg/mL of USP Oxaliplatin Related Compound A RS in water
Standard solution:
15 µg/mL of USP Oxaliplatin Related Compound A RS in water, from the Standard stock solution
System suitability solution:
0.05 mg/mL of sodium nitrate in water. Transfer 2 mL of this solution and 25 mL of the Standard stock solution to a 100-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume.
Sensitivity solution:
1.5 µg/mL of USP Oxaliplatin Related Compound A RS in water, from the Standard solution
Sample solution:
2 mg/mL of Oxaliplatin in water
Chromatographic system
Mode:
LC
Detector:
UV 205 nm
Column:
4.6-mm × 25-cm; 5-µm packing L1
Column temperature:
40
Flow rate:
2 mL/min
Injection size:
20 µL
System suitability
Samples:
Standard solution, System suitability solution, and Sensitivity solution
[Note—The elution order is sodium nitrate, followed by oxalic acid. ]
Suitability requirements
Resolution:
NLT 2.0 between oxalic acid and sodium nitrate, System suitability solution
Relative standard deviation:
NMT 3.0% for the oxalic acid peak, Standard solution
Signal-to-noise ratio:
NLT 10, Sensitivity solution
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of oxalic acid in the portion of Oxaliplatin taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/(CU) × (Mr1/Mr2) × 100
| rU | = | = peak response of oxalic acid from the Sample solution |
| rS | = | = peak response of oxalic acid from the Standard solution |
| CS | = | = concentration of USP Oxaliplatin Related Compound A RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL) |
| CU | = | = concentration of Oxaliplatin in the Sample solution (mg/mL) |
| Mr1 | = | = molecular weight of anhydrous oxalic acid, 90.03 |
| Mr2 | = | = molecular weight of USP Oxaliplatin Related Compound A RS, 126.07 |
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 0.1%
• Procedure 2: Limit of (SP-4-2-)-Diaqua[(1R,2R)-cyclohexane-1,2-diamine-N,N¢]platinum, Oxaliplatin Related Compound C, and Unspecified Impurities
[Note—Use vigorous shaking and very brief sonication to dissolve the substance to be examined. Inject the Sample solution within 20 min of preparation. Polypropylene HPLC autosampler vials should be used. ]
Mobile phase, Oxaliplatin standard stock solution, Oxaliplatin related compound B standard stock solution, Oxaliplatin related compound C standard stock solution, System suitability solution, and Chromatographic system:
Proceed as directed in the Assay.
Standard solution:
0.01 mg/mL of oxaliplatin, 0.01 mg/mL of oxaliplatin related compound B, and 0.004 mg/mL of oxaliplatin related compound C in water, from Oxaliplatin standard stock solution, Oxaliplatin related compound B standard stock solution, and Oxaliplatin related compound C standard stock solution, respectively
Sample solution:
2 mg/mL of Oxaliplatin in water
System suitability
Samples:
System suitability solution and Standard solution
Suitability requirements
Resolution:
NLT 2.0 between oxaliplatin and oxaliplatin related compound C, System suitability solution
Tailing factor:
Between 0.8 and 2.0 for the oxaliplatin peak, System suitability solution
Relative standard deviation:
NMT 3.0% for the oxaliplatin, oxaliplatin related compound B, and oxaliplatin related compound C peaks, Standard solution
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of (SP-4-2)-diaqua[(1R,2R)-cyclohexane-1,2-diamine-N,N¢]platinum in the portion of Oxaliplatin taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × (Mr1/Mr2) × 100
| rU | = | = peak response of (SP-4-2)-diaqua[(1R,2R)-cyclohexane-1,2-diamine-N,N¢]platinum from the Sample solution |
| rS | = | = peak response of (SP-4-2)-diaqua[(1R,2R)-cyclohexane-1,2-diamine-N,N¢]platinum from the Standard solution |
| CS | = | = concentration of USP Oxaliplatin Related Compound B RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL) |
| CU | = | = concentration of Oxaliplatin in the Sample solution (mg/mL) |
| Mr1 | = | = molecular weight of (SP-4-2)-diaqua[(1R,2R)-cyclohexane-1,2-diamine-N,N¢]platinum, 345.30 |
| Mr2 | = | = molecular weight of USP Oxaliplatin Related Compound B RS, 433.28 |
[Note—USP Oxaliplatin Related Compound B RS is converted to (SP-4-2)-diaqua[(1R,2R)-cyclohexane-1,2-diamine-N,N¢]platinum in solution preparation. ]
Calculate the percentage of oxaliplatin related compound C in the portion of Oxaliplatin taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × 100
| rU | = | = peak response of oxaliplatin related compound C from the Sample solution |
| rS | = | = peak response of oxaliplatin related compound C from the Standard solution |
| CS | = | = concentration of USP Oxaliplatin Related Compound C RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL) |
| CU | = | = concentration of Oxaliplatin in the Sample solution (mg/mL) |
Calculate the percentage of diaquodiaminocyclohexaneplatinum dimer in the portion of Oxaliplatin taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × (Mr1/Mr2) × (1/F) × 100
| rU | = | = peak response of diaquodiaminocyclohexaneplatinum dimer from the Sample solution |
| rS | = | = peak response of oxaliplatin related compound B from the Standard solution |
| CS | = | = concentration of USP Oxaliplatin Related Compound B RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL) |
| CU | = | = concentration of Oxaliplatin in the Sample solution (mg/mL) |
| Mr1 | = | = molecular weight of (SP-4-2)-diaqua[(1R,2R)-cyclohexane-1,2-diamine-N,N¢]platinum, 345.30 |
| Mr2 | = | = molecular weight of USP Oxaliplatin Related Compound B RS, 433.28 |
| F | = | = relative response factor for diaquodiaminocyclohexaneplatinum dimer, measured with respect to USP Oxaliplatin Related Compound B RS, 2.5 |
Calculate the percentage of any other unspecified impurity in the portion of Oxaliplatin taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × 100
| rU | = | = peak response of any other unspecified impurity from the Sample solution |
| rS | = | = peak response of oxaliplatin from the Standard solution |
| CS | = | = concentration of oxaliplatin in the Standard solution (mg/mL) |
| CU | = | = concentration of Oxaliplatin in the Sample solution (mg/mL) |
Acceptance criteria
Individual impurities:
See Impurity Table 1.
Total impurities:
NMT 0.30%. [Note—Total impurities include oxalic acid (from Procedure 1) and all impurities from Procedure 2 listed in Impurity Table 1. ]
Impurity Table 1
| Name | Relative Retention Time |
Relative Response Factor |
Acceptance Criteria, NMT (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Oxaliplatin related compound C | 0.8 | — | 0.1 |
| Oxaliplatin | 1.0 | — | — |
| (SP-4-2)-diaqua[(1R,2R)-cyclohexane-1,2-diamine-N,N’]platinum | 2.7 | — | 0.1 |
| Diaquodiaminocyclohexaneplatinum dimer | 6 | 2.5 | 0.1 |
| Any individual unspecified impurity |
— | — | 0.10 |
• Procedure 3: Limit of Oxaliplatin Related Compound D
[Note—Use vigorous shaking and very brief sonication to dissolve the substance to be examined. Inject the Sample solution within 20 min of preparation. Polypropylene HPLC autosampler vials should be used. ]
Mobile phase:
Methanol and ethanol (7:3)
Oxaliplatin related compound D standard stock solution:
0.05 mg/mL of USP Oxaliplatin Related Compound D RS in methanol
Oxaliplatin related compound D standard solution:
15 µg/mL of USP Oxaliplatin Related Compound D RS in methanol, from Oxaliplatin related compound D standard stock solution
Oxaliplatin standard stock solution:
0.75 mg/mL of USP Oxaliplatin RS in methanol
Oxaliplatin standard solution:
37.5 µg/mL of USP Oxaliplatin RS in methanol, from the Oxaliplatin standard stock solution
Standard solutions:
Transfer 40 mL of Oxaliplatin standard stock solution to separate 50-mL volumetric flasks. Add 1.0, 3.0, and 5.0 mL of Oxaliplatin related compound D standard solution to each flask, and dilute with methanol to volume. The concentration of oxaliplatin in these solutions is 0.6 mg/mL. The concentrations of oxaliplatin related compound D in these solutions are 0.3, 0.9, and 1.5 µg/mL, respectively.
System suitability solution:
Transfer 5.0 mL of Oxaliplatin standard solution and 4.0 mL of Oxaliplatin related compound D standard stock solution to a 50-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with methanol to volume.
Sample solution:
Transfer 30 mg of Oxaliplatin into a 50-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with methanol to volume.
Chromatographic system
Mode:
LC
Detector:
UV 254 nm
Column:
4.6-mm × 25-cm; 5-µm packing L70
Column temperature:
40
Flow rate:
0.3 mL/min
Injection size:
20 µL
Run time:
30 min
System suitability
Samples:
0.9-µg/mL Standard solution and System suitability solution
Suitability requirements
Resolution:
NLT 1.5 between oxaliplatin and oxaliplatin related compound D, System suitability solution
Relative standard deviation:
NMT 3.0% for the peak height ratio of oxaliplatin related compound D to the sum of oxaliplatin and oxaliplatin related compound D; 0.9-µg/mL Standard solution
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solutions and Sample solution
Plot a calibration curve for the Standard solutions with the peak response ratios of oxaliplatin related compound D to the sum of oxaliplatin and oxaliplatin related compound D on the y-axis and the concentrations of oxaliplatin related compound D, in µg/mL, on the x-axis. Read the concentration of oxaliplatin related compound D, in µg/mL, in the Sample solution from the calibration curve obtained.
Calculate the percentage of oxaliplatin related compound D in the portion of Oxaliplatin taken:
Result = (C/W) × 5
| C | = | = concentration of oxaliplatin related compound D in the Sample solution (µg/mL) |
| W | = | = weight of Oxaliplatin taken to prepare the Sample solution (mg) |
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 0.1%
SPECIFIC TESTS
• Acidity
Sample solution:
Dissolve 100 mg in 50 mL of carbon dioxide-free water, and add 0.5 mL of phenolphthalein TS.
Acceptance criteria:
The solution is colorless, and NMT 0.6 mL of 0.01 M sodium hydroxide is required to change the color to pink.
• Bacterial Endotoxins Test  85
85 :
NMT 1.0 USP Endotoxin Unit/mg of oxaliplatin
:
NMT 1.0 USP Endotoxin Unit/mg of oxaliplatin
• Loss On Drying  731
731 :
Dry 1 g at 100
:
Dry 1 g at 100 to 105
to 105 for 2 h: it loses NMT 0.5% of its weight.
for 2 h: it loses NMT 0.5% of its weight.
• Microbial Enumeration Tests  61
61 and Tests for Specified Microorganisms
and Tests for Specified Microorganisms  62
62 :
The total aerobic microbial count does not exceed 20 cfu/g, and the total combined molds and yeast count does not exceed 5 cfu/g.
:
The total aerobic microbial count does not exceed 20 cfu/g, and the total combined molds and yeast count does not exceed 5 cfu/g.
• Optical Rotation, Specific Rotation  781S
781S :
Between +74.5
:
Between +74.5 and +78.0
and +78.0 , measured at 20
, measured at 20
Sample solution:
5 mg/mL, in water
ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
• Packaging and Storage:
Preserve in tight containers, protected from light. Store at room temperature.
• USP Reference Standards  11
11
USP Endotoxin RS
USP Oxaliplatin Related Compound A RS
Oxalic acid dihydrate.
C2H2O4·2H2O 126.07
Oxalic acid dihydrate.
C2H2O4·2H2O 126.07
USP Oxaliplatin Related Compound B RS
[SP-4-2-(1R-trans)]-(1,2-Cyclohexanediamine-N,N¢) dinitratoplatinum(II).
C6H14N4O6Pt 433.28
[SP-4-2-(1R-trans)]-(1,2-Cyclohexanediamine-N,N¢) dinitratoplatinum(II).
C6H14N4O6Pt 433.28
USP Oxaliplatin Related Compound C RS
[1R-trans-(1,2-Cyclohexanediamine-N,N¢)]-trans-dihydroxido-[oxalato(2-)-O,O¢]platinum(IV).
C8H16N2O6Pt 431.30
[1R-trans-(1,2-Cyclohexanediamine-N,N¢)]-trans-dihydroxido-[oxalato(2-)-O,O¢]platinum(IV).
C8H16N2O6Pt 431.30
USP Oxaliplatin Related Compound D RS
cis-[(1S,2S)-1,2-Cyclohexanediamine-N,N¢][oxalato(2-)-O,O¢]platinum.
C8H14N2O4Pt 397.29
cis-[(1S,2S)-1,2-Cyclohexanediamine-N,N¢][oxalato(2-)-O,O¢]platinum.
C8H14N2O4Pt 397.29
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Feiwen Mao, M.S.
Senior Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8320 |
(SM32010) Monographs - Small Molecules 3 |
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8339 |
(GCM2010) General Chapters - Microbiology | |
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8339 |
(GCM2010) General Chapters - Microbiology | |
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8339 |
(GCM2010) General Chapters - Microbiology | |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
USP35–NF30 Page 4143
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 35(6) Page 1467