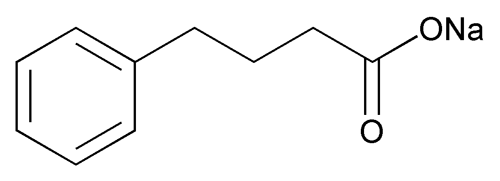
Sodium Phenylbutyrate

 231
231
(soe' dee um fen'' il bue' ti rate).
DEFINITION
Sodium Phenylbutyrate contains NLT 99.0% and NMT 101.0% of sodium phenylbutyrate (C10H11NaO2), calculated on the anhydrous basis.
IDENTIFICATION
• B. Identification Tests—General, Sodium  191
191
Sample solution:
Dissolve 150 mg in 2 mL of water.
Acceptance criteria:
Meets the requirements of the pyroantimonate precipitation test
ASSAY
• Procedure
Sample:
150 mg
Analysis:
Disperse the Sample in 50 mL of anhydrous acetic acid. [Note—The opalescence of the solution disappears during the titration. ] Titrate with 0.1 N perchloric acid VS, determining the endpoint potentiometrically. Each mL of 0.1 N perchloric acid is equivalent to 18.62 mg of sodium phenylbutyrate (C10H11NaO2).
Acceptance criteria:
99.0%–101.0% on the anhydrous basis
IMPURITIES
Delete the following:
Test preparation:
Standard lead solution:
Acceptance criteria:
 (Official 1-Dec-2015)
(Official 1-Dec-2015)
• Limit of Phenylbutyrate Related Compound C
Silylation solution:
To 2 mL of bis(trimethylsilyl)trifluoroacetamide add 0.04 mL of chlorotrimethylsilane, and mix.
Sample solution:
Dissolve 50.0 mg of Sodium Phenylbutyrate in 3 mL of water, and add 0.5 mL of hydrochloric acid. Extract with 2 quantities, each of 5 mL, of methylene chloride. Evaporate the combined methylene chloride extracts to dryness in a vial with a screw cap, and add 0.5 mL of the Silylation solution. Seal the vial, and heat at 70 ± 5 for 20 min.
for 20 min.
Standard stock solution:
0.5 mg/mL of USP Phenylbutyrate Related Compound C RS in methylene chloride
Diluted standard stock solution:
0.05 mg/mL of USP Phenylbutyrate Related Compound C RS in methylene chloride from Standard stock solution
Standard solution:
Place an amount of the Diluted standard stock solution, equivalent to 0.05 mg, in a vial with a screw cap, evaporate to dryness, and add 0.5 mL of the Silylation solution. Seal the vial, and heat at 70 ± 5 for 20 min.
for 20 min.
System suitability solution:
Prepare a solution containing 0.4 mg/mL of USP Sodium Phenylbutyrate RS in water. To 3 mL of this solution add 0.1 mL of hydrochloric acid. Extract with 2 quantities, each of 5 mL, of methylene chloride. Combine the methylene chloride extracts in a vial with a screw cap, and add 2 mL of Standard stock solution. Evaporate to dryness, and add 0.5 mL of the Silylation solution. Seal the vial, and heat at 70 ± 5 for 20 min.
for 20 min.
Chromatographic system
Mode:
GC
Detector:
Flame ionization
Column:
25-m × 0.25-mm fused silica capillary; coated with a 1.0-µm film of phase G27
Temperatures
Injector:
270
Detector:
270
Column:
See Table 1.
Table 1
| Initial Temperature ( |
Temperature Ramp ( |
Final Temperature ( |
Hold Time at Final Temperature (min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | 0 | 50 | 5 |
| 50 | 10 | 270 | 5 |
Carrier gas:
Helium
Flow rate:
0.9 mL/min
Injection volume:
1 µL
Split ratio:
1:100
System suitability
Sample:
System suitability solution
[Note—The relative retention times for phenylbutyrate related compound C and phenylbutyrate are about 0.98 and 1.0, respectively. ]
Suitability requirements
Resolution:
NLT 3.0 between the phenylbutyrate related compound C and phenylbutyrate peaks
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of phenylbutyrate related compound C in the portion of Sodium Phenylbutyrate taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (WS/WU) × 100
| rU | = | = peak response of phenylbutyrate related compound C from the Sample solution |
| rS | = | = peak response of phenylbutyrate related compound C from the Standard solution |
| WS | = | = amount of USP Phenylbutyrate Related Compound C RS taken to prepare the Standard solution (mg) |
| WU | = | = amount of Sodium Phenylbutyrate taken to prepare the Sample solution (mg) |
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 0.1%
• Organic Impurities
Mobile phase:
Methanol, glacial acetic acid, and water (49:1:50)
Impurity stock solution A:
0.1 mg/mL of USP Phenylbutyrate Related Compound A RS in methanol
Impurity standard solution A:
Dilute 1.0 mL of Impurity stock solution A with water to 50.0 mL. This solution contains 2 µg/mL of USP Phenylbutyrate Related Compound A RS.
Impurity stock solution B:
0.02 mg/mL of USP Phenylbutyrate Related Compound B RS in methanol
Impurity standard solution B:
Dilute 1.0 mL of Impurity stock solution B with water to 50.0 mL. This solution contains 0.4 µg/mL of USP Phenylbutyrate Related Compound B RS.
System suitability solution:
Prepare a solution containing 20 mg/mL of USP Sodium Phenylbutyrate RS in methanol. Transfer 10 mL of this solution to a 50-mL volumetric flask, add 1.0 mL of Impurity stock solution B, and dilute with water to volume.
Sensitivity solution:
Dilute 6.0 mL of Impurity standard solution A with water to 10.0 mL. This solution contains 1.2 µg/mL of USP Phenylbutyrate Related Compound A RS.
Sample solution:
4.0 mg/mL of Sodium Phenylbutyrate, prepared as follows. Dissolve it first in methanol, using 20% of the final volume, and dilute with water to volume.
Chromatographic system
Mode:
LC
Detector:
UV 245 nm
Column:
4.6-mm × 25-cm; 5-µm base-deactivated end-capped packing L1
Flow rate:
1.3 mL/min
Injection volume:
20 µL
System suitability
Samples:
System suitability solution and Sensitivity solution
Suitability requirements
Resolution:
NLT 6 between phenylbutyrate and phenylbutyrate related compound B, System suitability solution
Signal-to-noise ratio:
NLT 10, Sensitivity solution
Analysis
Samples:
Impurity standard solution A, Impurity standard solution B, and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of phenylbutyrate related compound A or phenylbutyrate related compound B in the portion of Sodium Phenylbutyrate taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × 100
| rU | = | = peak response of respective impurity in the Sample solution |
| rS | = | = peak response of phenylbutyrate related compound A or phenylbutyrate related compound B in the respective Impurity standard solution |
| CS | = | = concentration of USP Phenylbutyrate Related Compound A RS or USP Phenylbutyrate Related Compound B RS in the respective Impurity standard solution (mg/mL) |
| CU | = | = concentration of Sodium Phenylbutyrate in the Sample solution (mg/mL) |
Calculate the percentage of any individual unspecified impurity in the portion of Sodium Phenylbutyrate taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × 100
| rU | = | = peak response of each unspecified impurity in the Sample solution |
| rS | = | = peak response of phenylbutyrate related compound A in Impurity standard solution A |
| CS | = | = concentration of USP Phenylbutyrate Related Compound A RS in Impurity standard solution A (mg/mL) |
| CU | = | = concentration of Sodium Phenylbutyrate in the Sample solution (mg/mL) |
Acceptance criteria:
See Table 2. Disregard any peak below 0.03%.
Table 2
| Name | Relative Retention Time |
Acceptance Criteria, NMT (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Phenylbutyrate related compound A | 0.3 | 0.1 |
| Phenylbutyrate related compound B | 0.7 | 0.01 |
| Sodium phenylbutyrate | 1.0 | — |
| Any individual unspecified Impurity | — | 0.05 |
| Total impurities | — | 0.1 |
SPECIFIC TESTS
• Water Determination, Method Ia  921
921 :
NMT 0.5%
:
NMT 0.5%
ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
• Packaging and Storage:
Preserve under argon in tight containers. Store at room temperature.
• USP Reference Standards  11
11
USP Phenylbutyrate Related Compound A RS
3-Benzoylpropionic acid;
4-Oxo-4-phenylbutanoic acid.
C10H10O3 178.18
3-Benzoylpropionic acid;
4-Oxo-4-phenylbutanoic acid.
C10H10O3 178.18
USP Phenylbutyrate Related Compound B RS
 -Tetralone;
-Tetralone;
3,4-Dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one.
C10H10O 146.19
3,4-Dihydronaphthalen-1(2H)-one.
C10H10O 146.19
USP Phenylbutyrate Related Compound C RS
4-Cyclohexylbutanoic acid.
C10H18O2 170.25
4-Cyclohexylbutanoic acid.
C10H18O2 170.25
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Elena Gonikberg, Ph.D.
Director - Chemical Medicines (301) 816-8251 |
(SM32010) Monographs - Small Molecules 3 |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
USP38–NF33 Page 5328
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 39(4)