SAMPLING
In order to reduce the effect of sampling bias in qualitative and quantitative results, it is necessary to ensure that the composition of the sample used be representative of the batch of drugs being examined. The following sampling procedures are the minimum considered applicable to vegetable drugs. Some articles, or some tests, may require more rigorous procedures involving more containers being sampled or more samples per container.
Gross Sample
Where external examination of containers, markings, and labels indicates that the batch can be considered to be homogeneous, take individual samples from the number of randomly selected containers indicated below. Where the batch cannot be considered to be homogeneous, divide it into sub-batches that are as homogeneous as possible, then sample each one as a homogeneous batch.
| No. of Containers in Batch (N) |
No. of Containers to be Sampled (n) |
| 1 to 10 | all |
| 11 to 19 | 11 |
| >19 | n = 10 + (N/10) |
(Round calculated “n” to next highest whole number.)
Samples are taken from the upper, middle, and lower sections of each container. If the crude material consists of component parts which are 1 cm or less in any dimension, and in the case of all powdered or ground materials, withdraw the sample by means of a sampling device that removes a core from the top to the bottom of the container, not less than two cores being taken in opposite directions. For materials with component parts over 1 cm in any dimension, withdraw samples by hand. In the case of large bales or packs, samples should be taken from a depth of 10 cm because the moisture content of the surface layer may be different from that of the inner layers.
Prepare the gross sample by combining and mixing the individual samples taken from each opened container, taking care not to increase the degree of fragmentation or significantly affect the moisture content.
Laboratory Sample
Prepare the laboratory sample by repeated quartering of the gross sample.
note—Quartering consists of placing the sample, adequately mixed, as an even and square-shaped heap and dividing it diagonally into four equal parts. The two opposite parts are then taken and carefully mixed. The process is repeated as necessary until the required quantity is obtained.
The laboratory sample should be of a size sufficient for performing all the necessary tests.
Test Sample
Unless otherwise directed in the individual monograph or test procedure below, prepare the test sample as follows:
Decrease the size of the laboratory sample by quartering, taking care that each withdrawn portion remains representative. In the case of unground or unpowdered drugs, grind the withdrawn sample so that it will pass through a No. 20 standard-mesh sieve, and mix the resulting powder well. If the material cannot be ground, reduce it to as fine a state as possible, mix by rolling it on paper or sampling cloth, spread it out in a thin layer and withdraw the portion for analysis.
METHODS OF ANALYSIS
Foreign Organic Matter
Test Sample—
Unless otherwise specified in the individual monograph, weigh the following quantities of the laboratory sample, taking care that the withdrawn portion is representative (quartering if necessary):
| Roots, rhizomes, bark, and herbs | 500 g |
| Leaves, flowers, seeds, and fruit | 250 g |
| Cut vegetable drugs (average weight of the pieces is less than 0.5 g) |
50 g |
Spread the sample out in a thin layer, and separate the foreign organic matter by hand as completely as possible. Weigh it, and determine the percentage of foreign organic matter in the weight of drug taken.
Total Ash
Accurately weigh a quantity of the Test Sample, representing 2 to 4 g of the air-dried material, in a tared crucible, and incinerate, gently at first, and gradually increase the temperature to 675 ± 25 , until free from carbon, and determine the weight of the ash. If a carbon-free ash cannot be obtained in this way, extract the charred mass with hot water, collect the insoluble residue on an ashless filter paper, incinerate the residue and filter paper until the ash is white or nearly so, then add the filtrate, evaporate it to dryness, and heat the whole to a temperature of 675 ± 25
, until free from carbon, and determine the weight of the ash. If a carbon-free ash cannot be obtained in this way, extract the charred mass with hot water, collect the insoluble residue on an ashless filter paper, incinerate the residue and filter paper until the ash is white or nearly so, then add the filtrate, evaporate it to dryness, and heat the whole to a temperature of 675 ± 25 . If a carbon-free ash cannot be obtained in this way, cool the crucible, add 15 mL of alcohol, break up the ash with a glass rod, burn off the alcohol, and again heat the whole to a temperature of 675 ± 25
. If a carbon-free ash cannot be obtained in this way, cool the crucible, add 15 mL of alcohol, break up the ash with a glass rod, burn off the alcohol, and again heat the whole to a temperature of 675 ± 25 . Cool in a desiccator, weigh the ash, and calculate the percentage of total ash from the weight of the drug taken.
. Cool in a desiccator, weigh the ash, and calculate the percentage of total ash from the weight of the drug taken.
Acid-Insoluble Ash
Boil the ash obtained as directed under Total Ash, above, with 25 mL of 3 N hydrochloric acid for 5 minutes, collect the insoluble matter on a tared filtering crucible or ashless filter, wash with hot water, ignite, and weigh. Determine the percentage of acid-insoluble ash calculated from the weight of drug taken.
Water-Soluble Ash
Boil the ash obtained as directed for Total Ash with 25 mL of water for 5 minutes. Collect the insoluble matter in a sintered-glass crucible or on an ashless filter paper. Wash with hot water, and ignite for 15 minutes at a temperature not exceeding 450 . Subtract the weight of this residue, in mg, obtained under Total Ash, and calculate the percentage of water-soluble ash with reference to the weight of sample as determined under Total Ash.
. Subtract the weight of this residue, in mg, obtained under Total Ash, and calculate the percentage of water-soluble ash with reference to the weight of sample as determined under Total Ash.
Alcohol-Soluble Extractives
Method 1 (hot extraction method)—
Transfer about 4 g of air-dried, coarsely powdered material, accurately weighed, to a glass-stoppered conical flask. Add 100 mL of alcohol, and weigh the flask. Shake, and allow to stand for 1 hour. Attach a reflux condenser to the flask, and boil gently for 1 hour, cool, and weigh. Readjust to the original weight with alcohol. Shake, and filter rapidly through a dry filter. Transfer 25 mL of the filtrate to a tared flat-bottomed dish, and evaporate on a water bath to dryness. Dry at 105 for 6 hours, cool in a desiccator for 30 minutes, and weigh without delay. Calculate the content, in mg per g, of alcohol-extractable matter in the test specimen.
for 6 hours, cool in a desiccator for 30 minutes, and weigh without delay. Calculate the content, in mg per g, of alcohol-extractable matter in the test specimen.
Method 2 (cold extraction method)—
Transfer about 4 g of air-dried, coarsely powdered material, accurately weighed, to a glass-stoppered conical flask. Add 100 mL of alcohol, insert a stopper into the flask, and macerate for 24 hours, shaking frequently during the first 8 hours and then allowing to stand for 18 hours. Filter rapidly, taking precautions against loss of alcohol. Evaporate 25 mL of the filtrate to dryness in a tared, flat-bottomed, shallow dish, and dry at 105 to constant weight. Calculate the content, in mg per g, of alcohol-extractable matter in the test specimen.
to constant weight. Calculate the content, in mg per g, of alcohol-extractable matter in the test specimen.
Water-Soluble Extractives
Method 1 (hot extraction method)—
Proceed as directed for Method 1 (hot extraction method) under Alcohol-soluble Extractives, except to use water in place of alcohol.
Method 2 (cold extraction method)—
Proceed as directed for Method 2 (cold extraction method) under Alcohol-soluble Extractives, except to use water in place of alcohol.
Crude Fiber
Exhaust a weighed quantity of the Test Sample, representing about 2 g of the drug, with ether. Add 200 mL of boiling dilute sulfuric acid (1 in 78) to the ether-exhausted marc, in a 500-mL flask, and connect the flask to a reflux condenser. Reflux the mixture for 30 minutes, accurately timed, then filter through a linen or hardened-paper filter, and wash the residue on the filter with boiling water until the effluent washing is no longer acid. Rinse the residue back into the flask with 200 mL of boiling sodium hydroxide solution, adjusted to 1.25 percent by titration and free from sodium carbonate. Again reflux the mixture for 30 minutes, accurately timed, then rapidly filter through a tared filter, wash the residue with boiling water until the last washing is neutral, and dry it at 110 to constant weight. Incinerate the dried residue, ignite to constant weight, cool in a desiccator, and weigh the ash: the difference between the weight obtained by drying at 110
to constant weight. Incinerate the dried residue, ignite to constant weight, cool in a desiccator, and weigh the ash: the difference between the weight obtained by drying at 110 and that of the ash represents the weight of the crude fiber.
and that of the ash represents the weight of the crude fiber.
note—The boiling with acid and alkali should continue for 30 minutes, accurately timed, from the time that the liquid (which is cooled below the boiling point by being added to the cold flask) again boils. After the solution has been brought to boiling, the heat should be turned low enough just to maintain boiling. During the boiling, the flask should be gently rotated from time to time to wash down any particles that may adhere to the walls of the flask. A slow current of air introduced into the flask during the boiling operation aids in preventing excessive frothing.
Starch Content
Method 1—
The following is a general procedure for all reducing sugars and may be used to determine the starch content in botanical articles.
 method 1b—
method 1b—
Malt Extract—
Use clean new barley malt of known efficacy, and grind just before use. Prepare malt extract just prior to use. For every 80 mL of malt extract needed, digest 5 g of ground malt with 100 mL of water at room temperature for 2 hours. [note—If an electric mixer is used, stir the mixture for 20 minutes.] Filter to obtain a clear extract, filtering again, if necessary, and mix the infusion well.
Test Solution—
Extract about 5 g of the finely ground test specimen with five 10-mL portions of ether, using a filter that will completely retain the smallest starch granule. Allow the ether to evaporate from the residue, and wash with 250 mL of aqueous alcohol solution (10 in 100). Carefully wash the residue from the paper into a 500-mL beaker with about 100 mL of water. Heat to about 60 (avoiding, if possible, gelatinizing starch), and allow to stand for about 1 hour, stirring frequently to effect complete solution of sugars. Transfer to a wide-mouth bottle, rinse the beaker with a little warm water, and cool. Add an equal volume of alcohol, mix, and allow to stand for not less than 1 hour.
(avoiding, if possible, gelatinizing starch), and allow to stand for about 1 hour, stirring frequently to effect complete solution of sugars. Transfer to a wide-mouth bottle, rinse the beaker with a little warm water, and cool. Add an equal volume of alcohol, mix, and allow to stand for not less than 1 hour.
Centrifuge until the precipitate is closely packed on the bottom of the bottle, and decant the supernatant. Wash the precipitate with successive 50-mL portions of alcohol solution (50 in 100) by centrifuging and decanting through a suitable filter until the washings are sugar-free. [note—To test for the presence of sugar, transfer a few drops of the washings to a test tube, add 3 or 4 drops of a 20% solution of 1-naphthol in alcohol, prepared by dissolving 200 mg of 1-naphthol in 1 mL of alcohol and 2 mL of water. Shake the test tube well to allow uniform mixing, allow 2 to 4 mL of sulfuric acid to flow down the sides of the test tube, and hold the test tube upright. If sugar is present, the interface of the two liquids is colored faint to deep violet, and on shaking, the whole solution becomes blue-violet.]
Transfer the residue from the bottle and hardened filter to a beaker with about 50 mL of water. Immerse the beaker in boiling water, and stir constantly for 15 minutes or until all of the starch is gelatinized. Cool the beaker to 55 , add 20 mL of Malt Extract, and hold at this temperature for 1 hour. Heat again to boiling for a few minutes, cool to 55
, add 20 mL of Malt Extract, and hold at this temperature for 1 hour. Heat again to boiling for a few minutes, cool to 55 , add 20 mL of Malt Extract, and hold at this temperature for 1 hour or until the residue when treated with iodine TS shows no blue tinge upon microscopic examination. Cool, dilute with water to 250 mL, and filter.
, add 20 mL of Malt Extract, and hold at this temperature for 1 hour or until the residue when treated with iodine TS shows no blue tinge upon microscopic examination. Cool, dilute with water to 250 mL, and filter.
General Procedure—
Transfer 200 mL of the Test Solution to a flask fitted with a reflux condenser, add 20 mL of hydrochloric acid, and heat in a boiling water bath for 2½ hours. Cool, nearly neutralize with sodium hydroxide TS, complete neutralization with sodium carbonate TS, dilute with water to 500 mL, mix, and filter. The volume of aliquot taken depends on the starch content of the specimen under test (see Table 1). The aliquot should contain between 100 and 200 mg of dextrose. Transfer 50 mL of the filtrate to a 400-mL alkali-resistant glass beaker, add 50 mL of alkaline cupric tartarate TS, cover the beaker with a water glass, and heat. Adjust the flame in the burner so that the contents of the flask begin to boil in 4 minutes and continue boiling for exactly 2 minutes. Filter the hot solution at once through a sintered-glass filter. Wash the precipitate of cuprous oxide thoroughly with water at about 60 , then with 10 mL of alcohol, and finally with 10 mL of ether.
, then with 10 mL of alcohol, and finally with 10 mL of ether.
Table 1. Determination of the Optimum Aliquot
| % of Expected Starch Content | Aliquot in mL |
| 60 | 25 |
| 50 | 35 |
| 40 | 50 |
| 30 | 50 |
| 20 | 50 |
For solutions of reducing sugars of comparatively high purity, proceed as directed under Method 1A to determine the amount of reduced copper obtained by weighing the dried cuprous oxide. For solutions of reducing sugars containing large amounts of organic impurities, including sucrose, proceed as directed under Method 1B to determine the amount of reduced copper obtained by titration with sodium thiosulfate.
method 1a—
Dry the precipitate obtained under General Procedure for 30 minutes in an oven at 110 ± 2 , cool to room temperature in a desiccator, and weigh. Refer to Table 2 to find the quantity of dextrose, in mg, corresponding to the weight of cuprous oxide found. Determine the percentage of dextrose and then the content of starch by the following formula:
, cool to room temperature in a desiccator, and weigh. Refer to Table 2 to find the quantity of dextrose, in mg, corresponding to the weight of cuprous oxide found. Determine the percentage of dextrose and then the content of starch by the following formula:
| wt. of dextrose in mg × 0.1 × 500 | ||
| wt. of sample in g × aliquot in mL | ||
Table 2. Calculating Dextrose (Applicable when Cu2O is weighed directly) (Expressed in mg)
| Cuprous Oxide (Cu2O) | Dextrose (d-Glucose) | Cuprous Oxide (Cu2O) | Dextrose (d-Glucose) | Cuprous Oxide (Cu2O) | Dextrose (d-Glucose) | Cuprous Oxide (Cu2O) | Dextrose (d-Glucose) | Cuprous Oxide (Cu2O) | Dextrose (d-Glucose) | Cuprous Oxide (Cu2O) | Dextrose (d-Glucose) |
| 10 | 4.0 | 90 | 38.9 | 170 | 75.1 | 250 | 112.8 | 330 | 152.2 | 410 | 193.7 |
| 12 | 4.9 | 92 | 39.8 | 172 | 76.0 | 252 | 113.7 | 332 | 153.2 | 412 | 194.7 |
| 14 | 5.7 | 94 | 40.6 | 174 | 76.9 | 254 | 114.7 | 334 | 154.2 | 414 | 195.8 |
| 16 | 6.6 | 96 | 41.5 | 176 | 77.8 | 256 | 115.7 | 336 | 155.2 | 416 | 196.8 |
| 18 | 7.5 | 98 | 42.4 | 178 | 78.8 | 258 | 116.6 | 338 | 156.3 | 418 | 197.9 |
| 20 | 8.3 | 100 | 43.3 | 180 | 79.7 | 260 | 117.6 | 340 | 157.3 | 420 | 199.0 |
| 22 | 9.2 | 102 | 44.2 | 182 | 80.6 | 262 | 118.6 | 342 | 158.3 | 422 | 200.1 |
| 24 | 10.0 | 104 | 45.1 | 184 | 81.5 | 264 | 119.5 | 344 | 159.3 | 424 | 201.1 |
| 26 | 10.9 | 106 | 46.0 | 186 | 82.5 | 266 | 120.5 | 346 | 160.3 | 426 | 202.2 |
| 28 | 11.8 | 108 | 46.9 | 188 | 83.4 | 268 | 121.5 | 348 | 161.4 | 428 | 203.3 |
| 30 | 12.6 | 110 | 47.8 | 190 | 84.3 | 270 | 122.5 | 350 | 162.4 | 430 | 204.4 |
| 32 | 13.5 | 112 | 48.7 | 192 | 85.3 | 272 | 123.4 | 352 | 163.4 | 432 | 205.5 |
| 34 | 14.3 | 114 | 49.6 | 194 | 86.2 | 274 | 124.4 | 354 | 164.4 | 434 | 206.5 |
| 36 | 15.2 | 116 | 50.5 | 196 | 87.1 | 276 | 125.4 | 356 | 165.4 | 436 | 207.6 |
| 38 | 16.1 | 118 | 51.4 | 198 | 88.1 | 278 | 126.4 | 358 | 166.5 | 438 | 208.7 |
| 40 | 16.9 | 120 | 52.3 | 200 | 89.0 | 280 | 127.3 | 360 | 167.5 | 440 | 209.8 |
| 42 | 17.8 | 122 | 53.2 | 202 | 89.9 | 282 | 128.3 | 362 | 168.5 | 442 | 210.9 |
| 44 | 18.7 | 124 | 54.1 | 204 | 90.9 | 284 | 129.3 | 364 | 169.6 | 444 | 212.0 |
| 46 | 19.6 | 126 | 55.0 | 206 | 91.8 | 286 | 130.3 | 366 | 170.6 | 446 | 213.1 |
| 48 | 20.4 | 128 | 55.9 | 208 | 92.8 | 288 | 131.3 | 368 | 171.6 | 448 | 214.1 |
| 50 | 21.3 | 130 | 56.8 | 210 | 93.7 | 290 | 132.3 | 370 | 172.7 | 450 | 215.2 |
| 52 | 22.2 | 132 | 57.7 | 212 | 94.6 | 292 | 133.2 | 372 | 173.7 | 452 | 216.3 |
| 54 | 23.0 | 134 | 58.6 | 214 | 95.6 | 294 | 134.2 | 374 | 174.7 | 454 | 217.4 |
| 56 | 23.9 | 136 | 59.5 | 216 | 96.5 | 296 | 135.2 | 376 | 175.8 | 456 | 218.5 |
| 58 | 24.8 | 138 | 60.4 | 218 | 97.5 | 298 | 136.2 | 378 | 176.8 | 458 | 219.6 |
| 60 | 25.6 | 140 | 61.3 | 220 | 98.4 | 300 | 137.2 | 380 | 177.9 | 460 | 220.7 |
| 62 | 26.5 | 142 | 62.2 | 222 | 99.4 | 302 | 138.2 | 382 | 178.9 | 462 | 221.8 |
| 64 | 27.4 | 144 | 63.1 | 224 | 100.3 | 304 | 139.2 | 384 | 180.0 | 464 | 222.9 |
| 66 | 28.3 | 146 | 64.0 | 226 | 101.3 | 306 | 140.2 | 386 | 181.0 | 466 | 224.0 |
| 68 | 29.2 | 148 | 65.0 | 228 | 102.2 | 308 | 141.2 | 388 | 182.0 | 468 | 225.1 |
| 70 | 30.0 | 150 | 65.9 | 230 | 103.2 | 310 | 142.2 | 390 | 183.1 | 470 | 226.2 |
| 72 | 30.9 | 152 | 66.8 | 232 | 104.1 | 312 | 143.2 | 392 | 184.1 | 472 | 227.4 |
| 74 | 31.8 | 154 | 67.7 | 234 | 105.1 | 314 | 144.2 | 394 | 185.2 | 474 | 228.3 |
| 76 | 32.7 | 156 | 68.6 | 236 | 106.0 | 316 | 145.2 | 396 | 186.2 | 476 | 229.6 |
| 78 | 33.6 | 158 | 69.5 | 238 | 107.0 | 318 | 146.2 | 398 | 187.3 | 478 | 230.7 |
| 80 | 34.4 | 160 | 70.4 | 240 | 108.0 | 320 | 147.2 | 400 | 188.4 | 480 | 231.8 |
| 82 | 35.3 | 162 | 71.4 | 242 | 108.9 | 322 | 148.2 | 402 | 189.4 | 482 | 232.9 |
| 84 | 36.2 | 164 | 72.3 | 244 | 109.9 | 324 | 149.2 | 404 | 190.5 | 484 | 234.1 |
| 86 | 37.1 | 166 | 73.2 | 246 | 110.8 | 326 | 150.2 | 406 | 191.5 | 486 | 235.2 |
| 88 | 38.0 | 168 | 74.1 | 248 | 111.8 | 328 | 151.2 | 408 | 192.6 | 488 | 236.3 |
Sodium Thiosulfate Solution—
Transfer 3.9 g of sodium thiosulfate, accurately weighed, to a 100-mL volumetric flask, dissolve in and dilute with water to volume, and mix.
Potassium Iodide Solution—
Dissolve 42 g of potassium iodide in 100 mL of water.
Sodium Acetate Solution—
Dissolve 5.74 g of sodium acetate in 10 mL of water.
Copper Solution—
Transfer about 0.3 g of pure electrolytic copper, accurately weighed, to a 250-mL flask, add 5 mL of nitric acid to dissolve the copper, add about 25 mL of water, and boil to expel red fumes. Add about 5 mL of bromine TS, and boil until the bromine is completely removed. Cool, add 10 mL of Sodium Acetate Solution followed by 10 mL of Potassium Iodide Solution, and titrate with Sodium Thiosulfate Solution to a light yellow color. Add enough starch TS to produce a marked blue color, and continue the titration. As the endpoint nears, add 2 g of potassium thiocyanate, and stir until completely dissolved. Continue titration until the precipitate is completely white. One mL of sodium thiosulfate solution is equivalent to about 10 mg of copper. [note—It is essential that the concentration of Potassium Iodide Solution be carefully regulated. If the solution contains less than 320 mg of copper at the completion of titration, add 4.2 to 5 g of potassium iodide to make a total solution of 100 mL. If greater amounts of Cu are present, add Potassium Iodide Solution slowly from buret with constant agitation in amounts proportionately greater.]
Procedure—
Wash the precipitated cuprous oxide obtained under General Procedure with water, cover this filter with a watch glass and dissolve the cuprous oxide with 5 mL of nitric acid directed under the watch glass with a pipet. Collect the filtrate in a 250-mL flask, wash the watch glass and the filter with water. Collect all the washings in the flask. Boil the contents of the flask to expel red fumes. Add about 5 mL of bromine TS, and boil until the bromine is completely removed. Cool, and proceed as directed under Copper Solution beginning with “add 10 mL of Sodium Acetate Solution.” From the volume of Sodium Thiosulfate Solution consumed, obtain the weight of copper, in mg, by multiplying by 1.1259 to obtain the weight, in mg, of cuprous oxide. From Table 2, find the quantity of dextrose, in mg, corresponding to the weight of cuprous oxide. The content of starch is equivalent to the weight, in mg, of dextrose obtained times 0.9. Conduct a blank determination, using 50 mL of alkaline cupric tartrate TS and 50 mL of Malt Extract. If the weight of the cuprous oxide so obtained exceeds 0.5 mg, correct the result of the determination accordingly. [note—The alkaline cupric tartrate TS deteriorates on standing and the quantity of cuprous oxide obtained in the blank determination increases.]
Method 2—
The following method is specific for dextrose (glucose), and because of its extreme sensitivity it may account for differences noted between values obtained from the same specimen. Duplicate determinations do not vary more than 2%.
Glucoamylase Solution—
Prepare a solution of glucoamylase in water containing 30 International Units (IU) per mL. Use glucoamylase obtained preferably from Rhizopus delemar. The total glucoamylase activity of the test specimen being used should be not less than 150 IU.
Acetate Buffer Solution—
Dissolve 16.4 g of sodium acetate in 100 mL of water, add 12.0 mL of glacial acetic acid, and mix. The pH of this solution is 4.8.
Phosphate Buffer—
Dissolve 3.63 g of tris (hydroxymethyl) aminomethane and 5.0 g of monobasic sodium phosphate in 50.0 mL of water. At 37 , adjust with phosphoric acid to a pH of 7.0, dilute with water to 100.0 mL, and mix. [note—The pH of the buffer medium is sensitive to temperature and should be adjusted to the desired pH at the temperature to be used during incubation.]
, adjust with phosphoric acid to a pH of 7.0, dilute with water to 100.0 mL, and mix. [note—The pH of the buffer medium is sensitive to temperature and should be adjusted to the desired pH at the temperature to be used during incubation.]
Enzyme Solution—
Dissolve 30 mg of glucose oxidase (Type II from Aspergillus niger), 3 mg of peroxidase (Type I from horseradish), and 10 mg of potassium ferrocyanide in 100 mL of Phosphate Buffer. [note—This mixture can be stored in a refrigerator for up to 10 days.]
18 N Sulfuric Acid—
Add slowly, while stirring, 54 mL of sulfuric acid to 102 mL of water, allow to cool to 25 , and mix.
, and mix.
Standard Solutions—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of USP Dextrose RS in water to obtain a solution containing 1.0 mg of USP Dextrose RS per mL. Quantitatively dilute a known volume of this solution with water to obtain Standard Solutions A, B, C, D, and E, having known concentrations of 10, 20, 25, 40, and 50 µg per mL of USP Dextrose RS, respectively. [note—Allow 4 hours for complete mutarotation before use.]
Test Solutions—
Extract about 5 g of finely ground test specimen with five 25-mL portions of 80% alcohol, and filter. Remove all the alcohol from the residue by drying in an air oven at 105 for about 8 hours. [Note 1—Any traces of alcohol remaining in the residue will inhibit glucoamylase.] Cool, and transfer the flask containing the dried test specimen to a desiccator. Transfer about 1 g, accurately weighed, of the test specimen to a previously tared flask, add 25 mL of water, and adjust with phosphoric acid to a pH between 5.0 and 7.0, if necessary. Boil the suspension for about 3 minutes, transfer the flask to an autoclave, and heat to 135
for about 8 hours. [Note 1—Any traces of alcohol remaining in the residue will inhibit glucoamylase.] Cool, and transfer the flask containing the dried test specimen to a desiccator. Transfer about 1 g, accurately weighed, of the test specimen to a previously tared flask, add 25 mL of water, and adjust with phosphoric acid to a pH between 5.0 and 7.0, if necessary. Boil the suspension for about 3 minutes, transfer the flask to an autoclave, and heat to 135 for 2 hours. Remove the flask from the autoclave, maintain the temperature near 55
for 2 hours. Remove the flask from the autoclave, maintain the temperature near 55 , and add 2.5 mL of Acetate Buffer Solution and sufficient water to adjust the total weight of the solution to 45 ± 1 g. Immerse the flask in a water bath maintained at 55 ± 1
, and add 2.5 mL of Acetate Buffer Solution and sufficient water to adjust the total weight of the solution to 45 ± 1 g. Immerse the flask in a water bath maintained at 55 ± 1 , and add 5 mL of Glucoamylase Solution. Continuously swirl the flask for 2 hours to effect hydrolysis, filter through filter paper into a 250-mL volumetric flask, wash quantitatively with water, and collect all the washings in the flask. Dilute the contents of the flask with water to volume, and mix. Transfer 1 mL of an aliquot containing 20 to 60 µg of d-glucose to each of five test tubes. [Note 2—In order to obtain the range of concentration of glucose in the hydrolysate, quantitatively dilute, if necessary, with water to volume.] Add 2 mL of Enzyme Solution to each of the five test tubes, and place the test tubes in the dark at 37 ± 1
, and add 5 mL of Glucoamylase Solution. Continuously swirl the flask for 2 hours to effect hydrolysis, filter through filter paper into a 250-mL volumetric flask, wash quantitatively with water, and collect all the washings in the flask. Dilute the contents of the flask with water to volume, and mix. Transfer 1 mL of an aliquot containing 20 to 60 µg of d-glucose to each of five test tubes. [Note 2—In order to obtain the range of concentration of glucose in the hydrolysate, quantitatively dilute, if necessary, with water to volume.] Add 2 mL of Enzyme Solution to each of the five test tubes, and place the test tubes in the dark at 37 ± 1 for exactly 30 minutes to develop the color. At the end of 30 minutes, add 2 mL of 18 N Sulfuric Acid to each of the test tubes to stop the reaction, and mix.
for exactly 30 minutes to develop the color. At the end of 30 minutes, add 2 mL of 18 N Sulfuric Acid to each of the test tubes to stop the reaction, and mix.
Control Solution—
Transfer an accurately weighed quantity of about 0.4 g of starch to a previously tared flask and proceed as directed under Test Solutions beginning with “add 25 mL of water and, adjust the pH with phosphoric acid.”
Procedure—
Concomitantly determine the absorbances of the Standard Solutions and the Test Solutions at the wavelength of maximum absorbance at about 540 nm, with a suitable spectrophotometer, using the Control Solution as the blank to set the instrument. Plot the absorbance values of the Standard Solutions versus concentration, in µg per mL, of dextrose, and draw the straight line best fitting the five plotted points. From the graph so obtained, determine the concentration, C, in µg per mL, of dextrose in each of the Test Solutions, calculate the average concentration, in µg per mL, of the solution under test. The percentage of starch content in the weight of the test specimen taken by the equation is calculated by the formula:
(0.9C / 106)(V1)(250 / V0)(100 / E)(100 / W) = 2.25CV1 / V0EW
in which E is the weight, in g, of the test specimen taken; V0 is the volume, in mL, of the aliquot taken from the 250-mL volumetric flask; W is the percentage of dry weight of the test specimen; and V1 is the volume, in mL, if extra dilution is done (see Note 2 under Test Solutions). [note—V0 is 1.0 when no extra dilution is done.]
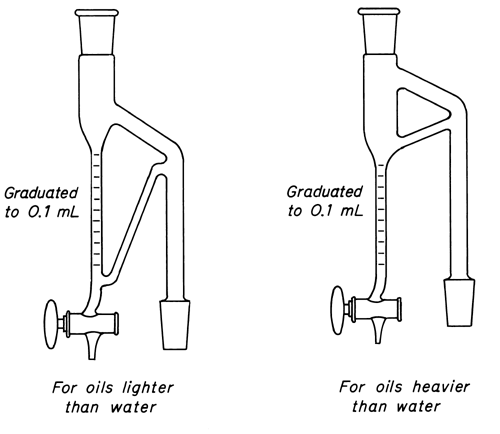
Volatile Oil Determination
Set up a round-bottom, shortneck, 1-liter flask in a heating mantle set over a magnetic stirrer. Insert an egg-shaped stirring bar magnet in the flask, and attach a cold-finger condenser and an appropriate volatile oil trap of the type illustrated.
Coarsely comminute a sufficient quantity of the drug to yield from 1 to 3 mL of volatile oil. Small seeds, fruits, or broken leaves of herbs ordinarily do not need comminution. Very fine powders are to be avoided. If this is not possible, it may be necessary to mix them with purified sawdust or purified sand. Place a suitable quantity of the drug, accurately weighed, in the flask, and fill it one-half with water. Attach the condenser and the proper separator. Boil the contents of the flask, using a suitable amount of heat to maintain gentle boiling for 2 hours, or until the volatile oil has been completely separated from the drug and no longer collects in the graduated tube of the separator.
If a proper quantity of the volatile oil has been obtained in the graduated tube of the separator, it can be read to tenths of 1 mL, and the volume of volatile oil from each 100 g of drug can be calculated from the weight of the drug taken. The graduations on the separator “for oils heavier than water” are so placed that oil remains below the aqueous condensate that automatically flows back into the flask.
Water Content
For unground or unpowdered drugs, prepare about 10 g of the Laboratory Sample by cutting, granulating, or shredding, so that the parts are about 3 mm in thickness. Seeds or fruits smaller than 3 mm should be cracked. Avoid the use of high-speed mills in preparing the sample, and exercise care that no appreciable amount of moisture is lost during the preparation and that the portion taken is representative of the Laboratory Sample. Determine the water content as directed for Procedure for Articles of Botanical Origin in the Method III (Gravimetric) under Water Determination  921
921 .
.
TEST FOR AFLATOXINS
Caution—Aflatoxins are highly dangerous, and extreme care should be exercised in handling aflatoxin materials.
This test is provided to detect the possible presence of aflatoxins B1, B2, G1, and G2 in any material of plant origin. Unless otherwise specified in the individual monograph, use the following method.
Zinc Acetate–Aluminum Chloride Reagent—
Dissolve 20 g of zinc acetate and 5 g of aluminum chloride in sufficient water to make 100 mL.
Sodium Chloride Solution—
Dissolve 5 g of sodium chloride in 50 mL of water.
Test Solution 1—
Grind about 200 g of plant material to a fine powder. Transfer about 50 g of the powdered material, accurately weighed, to a glass-stoppered flask. Add 200 mL of a mixture of methanol and water (17:3). Shake vigorously by mechanical means for not less than 30 minutes, and filter. [note—If the solution has interfering plant pigments, proceed as directed for Test Solution 2.] Discard the first 50 mL of the filtrate, and collect the next 40-mL portion. Transfer the filtrate to a separatory funnel. Add 40 mL of Sodium Chloride Solution and 25 mL of solvent hexane, and shake for 1 minute. Allow the layers to separate, and transfer the lower aqueous layer to a second separatory funnel. Extract the aqueous layer in the separatory funnel twice, each time with 25 mL of methylene chloride, by shaking for 1 minute. Allow the layers to separate each time, separate the lower organic layer, and collect the combined organic layers in a 125-mL conical flask. Evaporate the organic solvent to dryness on a water bath. Cool the residue. If interferences exist in the residue, proceed as directed for Cleanup Procedure; otherwise, dissolve the residue obtained above in 0.2 mL of a mixture of chloroform and acetonitrile (9.8:0.2), and shake by mechanical means if necessary.
Test Solution 2—
Collect 100 mL of the filtrate from the start of the flow, and transfer to a 250-mL beaker. Add 20 mL of Zinc Acetate–Aluminum Chloride Reagent and 80 mL of water. Stir, and allow to stand for 5 minutes. Add 5 g of a suitable filtering aid, such as diatomaceous earth, mix, and filter. Discard the first 50 mL of the filtrate, and collect the next 80-mL portion. Proceed as directed for Test Solution 1, beginning with “Transfer the filtrate to a separatory funnel.”
Cleanup Procedure—
Place a medium-porosity sintered-glass disk or a glass wool plug at the bottom of a 10-mm × 300-mm chromatographic tube. Prepare a slurry of 2 g of silica gel with a mixture of ethyl ether and solvent hexane (3:1), pour the slurry into the column, and wash with 5 mL of the same solvent mixture. Allow the absorbent to settle, and add to the top of the column a layer of 1.5 g of anhydrous sodium sulfate. Dissolve the residue obtained above in 3 mL of methylene chloride, and transfer it to the column. Rinse the flask twice with 1-mL portions of methylene chloride, transfer the rinses to the column, and elute at a rate not greater than 1 mL per minute. Add successively to the column 3 mL of solvent hexane, 3 mL of ethyl ether, and 3 mL of methylene chloride; elute at a rate not greater than 3 mL per minute; and discard the eluates. Add to the column 6 mL of a mixture of methylene chloride and acetone (9:1), and elute at a rate not greater than 1 mL per minute, preferably without the aid of vacuum. Collect this eluate in a small vial, add a boiling chip if necessary, and evaporate to dryness on a water bath. Dissolve the residue in 0.2 mL of a mixture of chloroform and acetonitrile (9.8:0.2), and shake by mechanical means if necessary.
Aflatoxin Solution—
[Caution—Aflatoxins are highly toxic. Handle with care.
] Dissolve accurately weighed quantities of aflatoxin B1, aflatoxin B2, aflatoxin G1, and aflatoxin G2 in a mixture of chloroform and acetonitrile (9.8:0.2) to obtain a solution having concentrations of 0.5 µg per mL each of aflatoxin B1 and aflatoxin G1, and 0.1 µg per mL each of aflatoxin B2 and aflatoxin G2.
Procedure—
Separately apply 2.5 µL, 5 µL, 7.5 µL, and 10 µL of the Aflatoxin Solution and three 10-µL applications of either Test Solution 1 or Test Solution 2 to a suitable thin-layer chromatographic plate (see Chromatography  621
621 ) coated with a 0.25-mm layer of chromatographic silica gel mixture. Superimpose 5 µL of the Aflatoxin Solution on one of the three 10-µL applications of the Test Solution. Allow the spots to dry, and develop the chromatogram in an unsaturated chamber containing a solvent system consisting of a mixture of chloroform, acetone, and isopropyl alcohol (85:10:5) until the solvent front has moved not less than 15 cm from the origin. Remove the plate from the developing chamber, mark the solvent front, and allow the plate to air-dry. Locate the spots on the plate by examination under UV light at 365 nm: the four applications of the Aflatoxin Solution appear as four clearly separated blue fluorescent spots; the spot obtained from the Test Solution that was superimposed on the Aflatoxin Solution is no more intense than that of the corresponding Aflatoxin Solution; and no spot from any of the other Test Solutions corresponds to any of the spots obtained from the applications of the Aflatoxin Solution. If any spot of aflatoxins is obtained in the Test Solution, match the position of each fluorescent spot of the Test Solution with those of the Aflatoxin Solution to identify the type of aflatoxin present. The intensity of the aflatoxin spot, if present in the Test Solution, when compared with that of the corresponding aflatoxin in the Aflatoxin Solution will give an approximate concentration of aflatoxin in the Test Solution.
) coated with a 0.25-mm layer of chromatographic silica gel mixture. Superimpose 5 µL of the Aflatoxin Solution on one of the three 10-µL applications of the Test Solution. Allow the spots to dry, and develop the chromatogram in an unsaturated chamber containing a solvent system consisting of a mixture of chloroform, acetone, and isopropyl alcohol (85:10:5) until the solvent front has moved not less than 15 cm from the origin. Remove the plate from the developing chamber, mark the solvent front, and allow the plate to air-dry. Locate the spots on the plate by examination under UV light at 365 nm: the four applications of the Aflatoxin Solution appear as four clearly separated blue fluorescent spots; the spot obtained from the Test Solution that was superimposed on the Aflatoxin Solution is no more intense than that of the corresponding Aflatoxin Solution; and no spot from any of the other Test Solutions corresponds to any of the spots obtained from the applications of the Aflatoxin Solution. If any spot of aflatoxins is obtained in the Test Solution, match the position of each fluorescent spot of the Test Solution with those of the Aflatoxin Solution to identify the type of aflatoxin present. The intensity of the aflatoxin spot, if present in the Test Solution, when compared with that of the corresponding aflatoxin in the Aflatoxin Solution will give an approximate concentration of aflatoxin in the Test Solution.
GENERAL METHOD FOR PESTICIDE RESIDUES ANALYSIS
Definition—
Where used in this Pharmacopeia, the designation pesticide applies to any substance or mixture of substances intended to prevent, destroy, or control any unwanted species of plants or animals causing harm during or otherwise interfering with the production, processing, storage, transport, or marketing of pure articles. The designation includes substances intended for use as growth regulators, defoliants, or desiccants, and any substance applied to crops before or after harvest to protect the product from deterioration during storage and transport.
Limits—
Within the United States, many botanicals are treated as dietary supplements and are subject to the statutory provisions of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act that governs foods but not drugs. Limits for pesticides for foods are determined by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), and where no limit is set, the limit is zero. The limits contained herein, therefore, are not applicable in the United States when articles of botanical origins are labeled for food purposes. The limits, however, may be applicable in other countries where the presence of pesticide residues is permitted. Unless otherwise specified in the individual monograph, the article under test contains not more than the amount of any pesticide indicated in Table 3. The limits applying to pesticides not listed in Table 3 and whose presence is suspected for any reason comply with the regulations of the EPA. Where a pesticide is not listed in Table 3 or in EPA regulations, calculate the limit by the formula:
AM / 100B
in which A is the acceptable daily intake (ADI), in mg per kg of body weight; M is the body weight, in kg; and B is the daily dose of the article, in kg.
Table 3
| Substance | Limit (mg/kg) |
| Alachlor | 0.02 |
| Aldrin and Dieldrin (sum of) | 0.05 |
| Azinphos-methyl | 1.0 |
| Bromopropylate | 3.0 |
| Chlordane (sum of cis- and trans- isomers and oxychlordane) |
0.05 |
| Chlorfenvinphos | 0.5 |
| Chlorpyrifos | 0.2 |
| Chlorpyrifos-methyl | 0.1 |
| Cypermethrin (and isomers) | 1.0 |
| DDT (sum of p,p¢-DDT, o,p¢-DDT, p,p¢-DDE, and p,p¢-TDE) |
1.0 |
| Deltamethrin | 0.5 |
| Diazinon | 0.5 |
| Dichlorvos | 1.0 |
| Dithiocarbamates (as CS2) | 2.0 |
| Endosulfan (sum of endosulfan isomers and endosulfan sulfate) |
3.0 |
| Endrin | 0.05 |
| Ethion | 2.0 |
| Fenitrothion | 0.5 |
| Fenvalerate | 1.5 |
| Fonofos | 0.05 |
| Heptachlor (sum of heptachlor and heptachlor epoxide) |
0.05 |
| Hexachlorobenzene | 0.1 |
| Hexachlorocyclohexane isomers (other than |
0.3 |
| Lindane ( |
0.6 |
| Malathion | 1.0 |
| Methidathion | 0.2 |
| Parathion | 0.5 |
| Parathion-methyl | 0.2 |
| Permethrin | 1.0 |
| Phosalone | 0.1 |
| Piperonyl butoxide | 3.0 |
| Pirimiphos-methyl | 4.0 |
| Pyrethrins (sum of) | 3.0 |
| Quintozene (sum of quintozene, pentachloroaniline and methyl pentachlorophenyl sulfide) |
1.0 |
If the article is intended for the preparation of extracts, tinctures, or other pharmaceutical forms whose preparation method modifies the content of pesticides in the finished product, calculate the limits by the formula:
AME / 100B
in which E is the extraction factor of the preparation method, determined experimentally; and A, M, and B are as defined above.
Sampling—
Method—
For articles in containers holding less than 1 kg, mix the contents, and withdraw a quantity sufficient for the tests. For articles in containers holding between 1 and 5 kg, withdraw equal portions from the upper, middle, and lower parts of the container, each of the samples being sufficient to carry out the tests. Thoroughly mix the samples, and withdraw an amount sufficient to carry out the tests. For containers holding more than 5 kg, withdraw three samples, each weighing not less than 250 g, from the upper, middle, and lower parts of the container. Thoroughly mix the samples, and withdraw a portion sufficient to carry out the tests.
Size of Sampling—
If the number of containers, n, is three or fewer, withdraw samples from each container as indicated above. If the number of containers is more than three, take samples from
containers, rounding up to the nearest whole number if necessary.
note—Conduct tests without delay to avoid possible degradation of the residues. If this is not possible, store the samples in hermetic containers suitable for food contact, at a temperature below 0 , and protected from light.
, and protected from light.
Reagents—
Use reagents and solvents that are free from any contaminants, especially pesticides, that might interfere with the analysis. It is often necessary to use special grade solvents suitable for pesticide residue analysis or solvents that have recently been redistilled in an apparatus made entirely of glass. In any case, suitable blank tests must be performed.
Preparation of Apparatus—
Clean all equipment, especially glassware, to ensure that it is free from pesticides. Soak all glassware for a minimum of 16 hours in a solution of phosphate-free detergent, rinse with copious quantities of distilled water, and then wash with acetone, followed by hexane or heptane.
Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of Pesticide Residues—
Use validated analytical procedures that satisfy the following criteria. The method, especially with respect to its purification steps, is suitable for the combination of pesticide residue and substance under test, and is not susceptible to interference from co-extractives. Measure the limits of detection and quantification for each pesticide matrix combination to be analyzed: the method is shown to recover between 70% and 110% of each pesticide; the repeatability and reproducibility of the method are not less than the appropriate values indicated in Table 4; and the concentrations of test and reference solutions and the setting of the apparatus are such that a linear response is obtained from the analytical detector.
Table 4
| Concentration of the Pesticide (mg/kg) |
Repeatability (difference, ± mg/kg) |
Reproducibility (difference, ± mg/kg) |
| 0.010 | 0.005 | 0.01 |
| 0.100 | 0.025 | 0.05 |
| 1.000 | 0.125 | 0.25 |
TEST FOR PESTICIDES
Unless otherwise specified in the individual monograph, the following methods may be used for the analysis of pesticides. Depending on the substance being examined, it may be necessary to modify, sometimes extensively, the procedure described hereafter. Additionally, it may be necessary to perform another method with another column having a different polarity, another detection method (e.g., mass spectrometry), or a different method (e.g., immunochemical method) to confirm the results.
Extraction—
[note—Use the following procedure for the analysis of samples of articles having a water content of less than 15%. Samples having a higher water content may be dried, provided that the drying procedure does not significantly affect the pesticide content.] To 10 g of the coarsely powdered substance under test, add 100 mL of acetone, and allow to stand for 20 minutes. Add 1 mL of a solution in toluene containing 1.8 g of carbophenothion per mL. Mix in a high-speed blender for 3 minutes. Filter this solution, and wash the residue with two 25-mL portions of acetone. Combine the filtrate and the washings, and heat, in a rotary evaporator, maintaining the temperature of the bath below 40 until the solvent has almost completely evaporated. To the residue add a few mL of toluene, and heat again until the acetone is completely removed. Dissolve the residue in 8 mL of toluene. Pass through a membrane filter having a 45-µm porosity, rinse the flask and the filter with toluene, dilute with toluene to 10.0 mL (Solution A), and mix.
until the solvent has almost completely evaporated. To the residue add a few mL of toluene, and heat again until the acetone is completely removed. Dissolve the residue in 8 mL of toluene. Pass through a membrane filter having a 45-µm porosity, rinse the flask and the filter with toluene, dilute with toluene to 10.0 mL (Solution A), and mix.
Purification—
Organochlorine, Organophosphorus, and Pyrethroid Insecticides—
The size-exclusion chromatograph is equipped with a 7.8-mm × 30-cm stainless steel column containing 5-µm packing L21. Toluene is used as the mobile phase at a flow rate of about 1 mL per minute.
Performance of the Column—
Inject 100 µL of a solution in toluene containing, in each mL, 0.5 mg of methyl red and 0.5 mg of oracet blue. The column is not suitable unless the color of the eluate changes from orange to blue at an elution volume of about 10.3 mL. If necessary, calibrate the column, using a solution in toluene containing suitable concentrations of the pesticide of interest having the lowest molecular weight (for example, dichlorvos) and that having the highest molecular weight (for example, deltamethrin). Determine which fraction of the eluate contains both pesticides.
Purification of the Test Solution—
Inject a suitable volume (100 to 500 µL) of Solution A into the chromatograph. Collect the fraction (Solution B) as determined above under Performance of the Column. Organophosphorus pesticides elute between 8.8 and 10.9 mL. Organochlorine and pyrethroid pesticides elute between 8.5 and 10.3 mL.
Organochlorine and Pyrethroid Insecticides—
Into a 5-mm × 10-cm chromatographic column, introduce a piece of fat-free cotton and 0.5 g of silica gel treated as follows. Heat chromatographic silica gel in an oven at 150 for at least 4 hours. Allow to cool, and add dropwise a quantity of water corresponding to 1.5% of the weight of silica gel used. Shake vigorously until agglomerates have disappeared, and continue shaking by mechanical means for 2 hours. Condition the column with 1.5 mL of hexane. [note—Prepacked columns containing about 0.50 g of a suitable silica gel may also be used, provided they have been previously validated.] Concentrate Solution B almost to dryness, with the aid of a stream of helium or oxygen-free nitrogen, and dilute with toluene to a suitable volume (200 µL to 1 mL, according to the volume injected in the preparation of Solution B). Quantitatively transfer this solution to the column, and proceed with the chromatography, using 1.8 mL of toluene as the mobile phase. Collect the eluate (Solution C).
for at least 4 hours. Allow to cool, and add dropwise a quantity of water corresponding to 1.5% of the weight of silica gel used. Shake vigorously until agglomerates have disappeared, and continue shaking by mechanical means for 2 hours. Condition the column with 1.5 mL of hexane. [note—Prepacked columns containing about 0.50 g of a suitable silica gel may also be used, provided they have been previously validated.] Concentrate Solution B almost to dryness, with the aid of a stream of helium or oxygen-free nitrogen, and dilute with toluene to a suitable volume (200 µL to 1 mL, according to the volume injected in the preparation of Solution B). Quantitatively transfer this solution to the column, and proceed with the chromatography, using 1.8 mL of toluene as the mobile phase. Collect the eluate (Solution C).
Quantitative Analysis of Organophosphorus Insecticides—
Test Solution—
Concentrate Solution B almost to dryness, with the aid of a stream of helium, dilute with toluene to 100 µL, and mix.
Standard Solution—
Prepare at least three solutions in toluene containing each of the pesticides of interest and carbophenothion at concentrations suitable for plotting a calibration curve.
Chromatographic System—
The gas chromatograph is equipped with an alkali flame-ionization detector or a flame-photometric detector and a 0.32-mm × 30-m fused silica column coated with a 0.25-µm layer of phase G1. Hydrogen is used as the carrier gas. Other gases, such as helium or nitrogen, may also be used. The injection port temperature is maintained at 250 , and the detector is maintained at 275
, and the detector is maintained at 275 . The column temperature is maintained at 80
. The column temperature is maintained at 80 for 1 minute, then increased to 150
for 1 minute, then increased to 150 at a rate of 30
at a rate of 30 per minute, maintained at 150
per minute, maintained at 150 for 3 minutes, then increased to 280
for 3 minutes, then increased to 280 at a rate of 4
at a rate of 4 per minute, and maintained at this temperature for 1 minute. Use carbophenothion as the internal standard. [Note—If necessary, use a second internal standard to identify any possible interference with the peak corresponding to carbophenothion.] Inject the chosen volume of each solution, record the chromatograms, and measure the peak responses: the relative retention times are approximately those listed in Table 5. Calculate the content of each pesticide from the peak areas and the concentrations of the solution.
per minute, and maintained at this temperature for 1 minute. Use carbophenothion as the internal standard. [Note—If necessary, use a second internal standard to identify any possible interference with the peak corresponding to carbophenothion.] Inject the chosen volume of each solution, record the chromatograms, and measure the peak responses: the relative retention times are approximately those listed in Table 5. Calculate the content of each pesticide from the peak areas and the concentrations of the solution.
Table 5
| Substance | Relative Retention Time |
| Dichlorvos | 0.20 |
| Fonofos | 0.50 |
| Diazinon | 0.52 |
| Parathion-methyl | 0.59 |
| Chlorpyrifos-methyl | 0.60 |
| Pirimiphos-methyl | 0.66 |
| Malathion | 0.67 |
| Parathion | 0.69 |
| Chlorpyrifos | 0.70 |
| Methidathion | 0.78 |
| Ethion | 0.96 |
| Carbophenothion | 1.00 |
| Azinphos-methyl | 1.17 |
| Phosalone | 1.18 |
Quantitative Analysis of Organochlorine and Pyrethroid Insecticides—
Test Solution—
Concentrate Solution C almost to dryness, with the aid of a stream of helium or oxygen-free nitrogen, dilute with toluene to 500 µL, and mix.
Standard Solution—
Prepare at least three solutions in toluene containing each of the pesticides of interest and carbophenothion at concentrations suitable for plotting a calibration curve.
Chromatographic System—
The gas chromatograph is equipped with an electron-capture detector, a device allowing direct on-column cold injection, and a 0.32-mm × 30-m fused silica column coated with a 0.25-µm layer of phase G1. Hydrogen is used as the carrier gas. Other gases, such as helium or nitrogen, may also be used. The injection port temperature is maintained at 275 , and the detector is maintained at 300
, and the detector is maintained at 300 . The column temperature is maintained at 80
. The column temperature is maintained at 80 for 1 minute, then increased to 150
for 1 minute, then increased to 150 at a rate of 30
at a rate of 30 per minute, maintained at 150
per minute, maintained at 150 for 3 minutes, then increased to 280
for 3 minutes, then increased to 280 at a rate of 4
at a rate of 4 per minute, and maintained at this temperature for 1 minute. Use carbophenothion as the internal standard. [note—If necessary, use a second internal standard to identify any possible interference with the peak corresponding to carbophenothion.] Inject the chosen volume of each solution, record the chromatograms, and measure the peak responses: the relative retention times are approximately those listed in Table 6. Calculate the content of each pesticide from the peak areas and the concentrations of the solutions.
per minute, and maintained at this temperature for 1 minute. Use carbophenothion as the internal standard. [note—If necessary, use a second internal standard to identify any possible interference with the peak corresponding to carbophenothion.] Inject the chosen volume of each solution, record the chromatograms, and measure the peak responses: the relative retention times are approximately those listed in Table 6. Calculate the content of each pesticide from the peak areas and the concentrations of the solutions.
Table 6
| Substance | Relative Retention Time |
| 0.44 | |
| Hexachlorobenzene | 0.45 |
| 0.49 | |
| Lindane | 0.49 |
| 0.54 | |
| 0.56 | |
| Heptachlor | 0.61 |
| Aldrin | 0.68 |
| cis-Heptachlor epoxide | 0.76 |
| o, p¢-DDE | 0.81 |
| 0.82 | |
| Dieldrin | 0.87 |
| p, p¢-DDE | 0.87 |
| o, p¢-DDD | 0.89 |
| Endrin | 0.91 |
| 0.92 | |
| o, p¢-DDT | 0.95 |
| Carbophenothion | 1.00 |
| p, p¢-DDT | 1.02 |
| cis-Permethrin | 1.29 |
| trans-Permethrin | 1.31 |
| Cypermethrin* | 1.40 |
| Fenvalerate* | 1.47 |
| 1.49 | |
| Deltamethrin | 1.54 |
|
*
The substance shows several peaks.
|
|
Auxiliary Information— Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
| General Chapter | Yoshiyuki Tokiwa, Ph.D.
Senior Scientist 1-301-816-8321 |
(GC05) General Chapters 05 |
USP32–NF27 Page 182
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 27(5) Page 3072