- British Pharmacopoeia Volume I & II
- Monographs: Medicinal and Pharmaceutical Substances
Allopurinol |
 |
(Ph. Eur. monograph 0576)
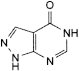
C5H4N4O 136.1 315-30-0
Xanthine oxidase inhibitor; treatment of gout and hyperuricaemia.
Ph Eur
1,5-Dihydro-4H-pyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-4-one.
97.0 per cent to 102.0 per cent (dried substance).
White or almost white powder.
Very slightly soluble in water and in ethanol (96 per cent). It dissolves in dilute solutions of alkali hydroxides.
First identification B.
Second identification: A, C, D.
A. Ultraviolet and visible absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.25).
Test solution Dissolve 10 mg in 1 mL of a 4 g/L solution of sodium hydroxide R and dilute to 100.0 mL with a 10.3 g/L solution of hydrochloric acid R. Dilute 10.0 mL of this solution to 100.0 mL with a 10.3 g/L solution of hydrochloric acid R.
Spectral range 220-350 nm.
Absorption maximum At 250 nm.
Absorption minimum At 231 nm.
Absorbance ratio A231/A250 = 0.52 to 0.62.
B. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison allopurinol CRS.
C. Dissolve 0.3 g in 2.5 mL of dilute sodium hydroxide solution R and add 50 mL of water R. Add slowly and with shaking 5 mL of silver nitrate solution R1. A white precipitate is formed which does not dissolve on the addition of 5 mL of ammonia R.
D. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution Dissolve 20 mg of the substance to be examined in concentrated ammonia R and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution Dissolve 20 mg of allopurinol CRS in concentrated ammonia R and dilute to 10 mL with the same solvent.
Plate TLC silica gel F254 plate R.
Mobile phase anhydrous ethanol R, methylene chloride R (40:60 V/V).
Application 10 µL.
Development Ever 2/3 of the plate.
Drying In air.
Detection Examine in ultraviolet light at 254 nm.
Results The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in position and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution.
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29). Use freshly prepared solutions. Store and inject them at 8 °C, using a cooled autosampler.
Test solution (a) Dissolve 25.0 mg of the substance to be examined in 2.5 mL of a 4 g/L solution of sodium hydroxide R and dilute immediately to 50.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Test solution (b) Dissolve 20.0 mg of the substance to be examined in 5.0 mL of a 4 g/L solution of sodium hydroxide R and dilute immediately to 250.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (a) Dilute 2.0 mL of test solution (a) to 100.0 mL with the mobile phase. Dilute 5.0 mL of this solution to 100.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (b) Dissolve 5 mg of allopurinol impurity A CRS, 5 mg of allopurinol impurity B CRS and 5.0 mg of allopurinol impurity C CRS in 5.0 mL of a 4 g/L solution of sodium hydroxide R and dilute immediately to 100.0 mL with the mobile phase. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 100.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (c) Dissolve 20.0 mg of allopurinol CRS in 5.0 mL of a 4 g/L solution of sodium hydroxide R and dilute immediately to 250.0 mL with the mobile phase.
- — size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
- — stationary phase: octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 µm).
Mobile phase 1.25 g/L solution of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R.
Flow rate 1.4 mL/min.
Detection Spectrophotometer at 230 nm.
Injection 20 µL of test solution (a) and reference solutions (a) and (b).
Run time Twice the retention time of allopurinol.
Elution order Impurity A, impurity B, impurity C, allopurinol.
Retention time allopurinol = about 10 min.
System suitability Reference solution (b):
- — resolution: minimum 1.1 between the peaks due to impurities B and C.
Limits:
- — impurity A: not more than twice the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.2 per cent);
- — impurity B: not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.1 per cent);
- — impurity C: not more than the area of the corresponding peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.1 per cent);
- — unspecified impurities: for each impurity, not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.10 per cent);
- — sum of impurities other than A, B and C: not more than 3 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.3 per cent);
- — disregard limit: 0.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.05 per cent).
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29). Use freshly prepared solutions. Store and inject them at 8 °C, using a cooled autosampler.
Solution A 1.25 g/L solution of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R.
Test solution Dissolve 50.0 mg of the substance to be examined in 5.0 mL of a 4 g/L solution of sodium hydroxide R and dilute immediately to 100.0 mL with solution A.
Reference solution Dissolve 5.0 mg of allopurinol impurity D CRS and 5.0 mg of allopurinol impurity E CRS in 5.0 mL of a 4 g/L solution of sodium hydroxide R and dilute immediately to 100.0 mL with solution A. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 100.0 mL with solution A.
- — size: l = 0.05 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
- — stationary phase: base-deactivated octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (3 µm).
Mobile phase methanol R, 1.25 g/L solution of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R (10:90 V/V).
Flow rate 2 mL/min.
Detection Spectrophotometer at 230 nm.
Injection 20 µL.
Run time 1.5 times the retention time of impurity E.
Retention times Impurity D = about 3.6 min; impurity E = about 4.5 min.
System suitability Reference solution:
- — resolution: minimum 2.0 between the peaks due to impurities D and E.
- — impurity D: not more than the area of the corresponding peak in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution (0.1 per cent);
- — impurity E: not more than the area of the corresponding peak in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution (0.1 per cent).
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Under the following conditions, any hydrazine in the sample reacts with benzaldehyde to give benzaldehyde azine.
Solvent mixture Mix equal volumes of dilute sodium hydroxide solution R and methanol R.
Solution A Dissolve 2.0 g of benzaldehyde R in the solvent mixture and dilute to 50.0 mL with the solvent mixture. Prepare immediately before use.
Test solution Dissolve 250.0 mg of the substance to be examined in 5 mL of the solvent mixture. Add 4 mL of solution A, mix and allow to stand for 2.5 h at room temperature. Add 5.0 mL of hexane R and shake for 1 min. Allow the layers to separate and use the upper layer.
Reference solution Dissolve 10.0 mg of hydrazine sulfate R in the solvent mixture by sonicating for about 2 min and dilute to 50.0 mL with the solvent mixture. Dilute 1.0 mL to 20.0 mL with the solvent mixture. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 20.0 mL with the solvent mixture. To 5.0 mL of the solution obtained, add 4 mL of solution A, mix and allow to stand for 2.5 h at room temperature. Add 5.0 mL of hexane R and shake for 1 min. Allow the layers to separate and use the upper layer.
Blank solution To 5 mL of the solvent mixture add 4 mL of solution A, mix and allow to stand for 2.5 h at room temperature. Add 5.0 mL of hexane R and shake for 1 min. Allow the layers to separate and use the upper layer.
- — size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.0 mm;
- — stationary phase: cyanosilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 µm) with a pore size of 10 nm;
- — temperature: 30 °C.
Mobile phase 2-propanol R, hexane R (5:95 V/V).
Flow rate 1.5 mL/min.
Detection Spectrophotometer at 310 nm.
Injection 20 µL.
Relative retention With reference to benzaldehyde (retention time = about 2.8 min): benzaldehyde azine = about 0.8.
System suitability Reference solution:
- — resolution: minimum 2 between the peaks due to benzaldehyde azine and benzaldehyde;
- — signal-to-noise ratio: minimum 20 for the peak due to benzaldehyde azine.
- — impurity F: the area of the peak due to benzaldehyde azine in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is not more than the area of the corresponding peak in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution (10 ppm of hydrazine sulfate equivalent to 2.5 ppm of hydrazine).
Maximum 20 ppm.
1.0 g complies with test C. Prepare the reference solution using 2 mL of lead standard solution (10 ppm Pb) R.
Maximum 0.5 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in an oven at 105 °C.
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29) as described in the test for related substances with the following modification.
Injection Test solution (b) and reference solution (c).
Calculate the percentage content of C5H4N4O from the declared content of allopurinol CRS.
Specified impurities: A, B, C, D, E, F.
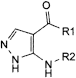
A. R1 = NH2, R2 = H: 5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxamide,
B. R1 = NH2, R2 = CHO: 5-(formylamino)-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxamide,
D. R1 = O-C2H5, R2 = H: ethyl 5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylate,
E. R1 = O-C2H5, R2 = CHO: ethyl 5-(formylamino)-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxylate,
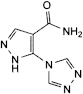
C. 5-(4H-1,2,4-triazol-4-yl)-1H-pyrazole-4-carboxamide,
F. H2N-NH2: diazane (hydrazine).
Ph Eur

