1. SCOPE
Indicators are required in Pharmacopeial tests and assays to determine the specified endpoint in a chemical reaction, to measure hydrogen-ion concentration (pH), or to indicate that a desired change in pH has been effected. The necessary solutions of indicators are listed among the Test Solutions, abbreviated TS.
2. PREPARATION OF SOME INDICATORS
Solution of indicators of the basic type and of the phthaleins are prepared by dissolving in alcohol.
With indicators containing an acidic group, the acid must first be neutralized with sodium hydroxide (NaOH) as follows: triturate 100 mg of the indicator in a smooth-surfaced mortar with the volume of 0.05 N sodium hydroxide specified in the directions for preparing its Test Solution, or with the equivalent of 0.02 N sodium hydroxide. After solubilization of the indicator, dilute the solution with carbon dioxide-free water to 200 mL (final concentration 0.05%). Store the solution in suitably resistant containers, protected from light.
3. pH RANGE AND COLOR CHANGE FOR SOME USEFUL INDICATORS
| Indicator
|
pH Range | Color Change |
|---|---|---|
| Malachite green oxalate | 0.0–2.0 | yellow–green |
| Thymol blue | 1.2–2.8 | red–yellow |
| Quinaldine red | 1.4–3.2 | colorless–red |
| Methyl yellow | 2.9–4.0 | red–yellow |
| Bromophenol blue | 3.0–4.6 | yellow–blue |
| Methyl orange | 3.2–4.4 | pink–yellow |
| Bromocresol green | 4.0–5.4 | yellow–blue |
| Methyl red | 4.2–6.2 | red–yellow |
| Bromocresol purple sodium salt | 5.0–6.8 | greenish yellow–purple-violet |
| Bromocresol purple | 5.2–6.8 | yellow–purple |
| Bromothymol blue | 6.0–7.6 | yellow–blue |
| Phenol red | 6.8–8.2 | yellow–red |
| Neutral red | 6.8–8.0 | red–orange |
| Cresol red | 7.2–8.8 | yellow–red |
| Thymol blue | 8.0–9.2 | yellow–blue |
| Thymolphthalein | 8.6–10.0 | colorless–blue |
| Phenolphthalein | 8.0–10.0 | colorless–red |
| p-Naphtholbenzein | 8.8–10.0 | orange–green |
| Nile blue hydrochloride | 9.0–13.0 | blue–pink |
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Reagent | Margareth R. C. Marques, Ph.D.
Senior Scientific Liaison (301) 816-8106 |
(HDQ) Headquarters |
Alphazurine 2G
—Use a suitable grade.
Azo Violet
[4-(p-Nitrophenylazo)resorcinol], C12H9N3O4—259.22—Red powder. It melts at about 193 , with decomposition.
, with decomposition.
Bismuth Sulfite
—Use a suitable grade.
Brilliant Green
—See Brilliant Green in the section Reagents.
Brilliant Yellow
(C.I. 24890), C26H18N4Na2O8S—592.49—Orange to rust-colored powder. Soluble in water.
Loss on drying  731
731 —Dry it in vacuum at 60
—Dry it in vacuum at 60 for 1 hour: it loses not more than 5% of its weight.
for 1 hour: it loses not more than 5% of its weight.
Bromocresol Blue
—Use Bromocresol Green.
Bromocresol Green
(Bromocresol Blue; Tetrabromo-m-cresol-sulfonphthalein), C21H14Br4O5S—698.01—White or pale buff-colored powder. Slightly soluble in water; soluble in alcohol and in solutions of alkali hydroxides. Transition interval: from pH 4.0 to 5.4. Color change: from yellow to blue.
Bromocresol Green Sodium Salt
—Use a suitable grade.
Bromocresol Purple
(Dibromo-o-cresolsulfonphthalein), C21H16Br2O5S—540.22—White to pink, crystalline powder. Insoluble in water; soluble in alcohol and in solutions of alkali hydroxides. Transition interval: from pH 5.2 to 6.8. Color change: from yellow to purple.
Bromocresol Purple Sodium Salt,
C21H15Br2O5SNa—562.20—Black powder. Soluble in water. Transition interval: from pH 5.0 to 6.8. Color change: from greenish yellow to purple-violet.
Melting range  741
741 :
:
 between 261
between 261 and 264
and 264 .
.
Bromophenol Blue
(3¢,3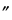 ,5¢,5
,5¢,5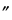 -Tetrabromophenolsulfonphthalein), C19H10Br4O5S—669.96—Pinkish crystals. Insoluble in water; soluble in alcohol and in solutions of alkali hydroxides. Transition interval: from pH 3.0 to 4.6. Color change: from yellow to blue.
-Tetrabromophenolsulfonphthalein), C19H10Br4O5S—669.96—Pinkish crystals. Insoluble in water; soluble in alcohol and in solutions of alkali hydroxides. Transition interval: from pH 3.0 to 4.6. Color change: from yellow to blue.
Bromophenol Blue Sodium
—The sodium salt of 3¢,3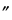 ,5¢,5
,5¢,5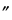 (Tetrabromophenolsulfonphthalein), C19H9Br4O5SNa—646.36—Pinkish crystals. Soluble in water and in alcohol. Transition interval: from pH 3.0 to 4.6. Color change: from yellow to blue.
(Tetrabromophenolsulfonphthalein), C19H9Br4O5SNa—646.36—Pinkish crystals. Soluble in water and in alcohol. Transition interval: from pH 3.0 to 4.6. Color change: from yellow to blue.
Bromothymol Blue
(3¢,3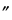 -Dibromothymolsulfonphthalein), C27H28Br2O5S—624.38—Cream-colored powder. Insoluble in water; soluble in alcohol and in solutions of alkali hydroxides. Transition interval: from pH 6.0 to 7.6. Color change: from yellow to blue.
-Dibromothymolsulfonphthalein), C27H28Br2O5S—624.38—Cream-colored powder. Insoluble in water; soluble in alcohol and in solutions of alkali hydroxides. Transition interval: from pH 6.0 to 7.6. Color change: from yellow to blue.
Congo Red
—See Congo Red in the section Reagents.
Cresol Red
(o-Cresolsulfonphthalein), C21H18O5S—382.43—Red-brown powder. Slightly soluble in water; soluble in alcohol and in dilute solutions of alkali hydroxides. Transition interval: from pH 7.2 to 8.8. Color change: from yellow to red.
Crystal Violet
(Hexamethyl-p-rosaniline Chloride), C25H30ClN3—407.98—Dark-green crystals. Slightly soluble in water; sparingly soluble in alcohol and in glacial acetic acid. Its solutions are deep violet in color.
Sensitiveness
—Dissolve 100 mg in 100 mL of glacial acetic acid, and mix. Pipet 1 mL of the solution into a 100-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with glacial acetic acid to volume: the solution is violet-blue in color and does not show a reddish tint. Pipet 20 mL of the diluted solution into a beaker, and titrate with 0.1 N perchloric acid VS, adding the perchloric acid slowly from a microburet: not more than 0.10 mL of 0.1 N perchloric acid is required to produce an emerald-green color.
4,5-Dihydroxy-3-(p-sulfophenylazo)-2,7-naphthalenedisulfonic Acid, Trisodium Salt
—See 2-(4-Sulfophenylazo)-1,8-dihydroxy-3,6-naphthalenedisulfonic Acid, Trisodium Salt.
Eosin Y
(Indicator grade Eosin Y, Sodium tetrabromofluorescein), C20H6Br4Na2O5—691.86 [17372-87-1]—Red to brownish-red pieces or powder. One g dissolves in about 2 mL of water and in 50 mL of alcohol. Dye content about 80%.
Eriochrome Black T
[Sodium 1-(1-Hydroxy-2-naphthylazo)5-nitro-2-naphthol-4-sulfonate], C20H12N3NaO7S—461.38—Brownish-black powder having a faint, metallic sheen. Soluble in alcohol, in methanol, and in hot water.
Sensitiveness
—To 10 mL of a 1 in 200,000 solution in a mixture of equal parts of methanol and water add sodium hydroxide solution (1 in 100) until the pH is 10: the solution is pure blue in color and free from cloudiness. Add 0.01 mg of magnesium ion (Mg): the color of the solution changes to red-violet, and with the continued addition of magnesium ion it becomes wine-red.
Eriochrome Black T Trituration
—Grind 200 mg of eriochrome black T to a fine powder with 20 g of potassium chloride.
Litmus
—Blue powder, cubes, or pieces. Partly soluble in water and in alcohol. Transition interval: from approximately pH 4.5 to 8. Color change: from red to blue. Litmus is unsuitable for determining the pH of alkaloids, carbonates, and bicarbonates.
Malachite Green Oxalate,
[C23H25N2+]2 · [C2HO4 ]2 · C2H2O4—927.00—The oxalate salt, crystallized with oxalic acid, of a triphenylmethane dye. Dark-green powder, having a metallic luster. Sparingly soluble in water; soluble in glacial acetic acid. Transition interval: from pH 0.0 to 2.0. Color change: from yellow to green.
]2 · C2H2O4—927.00—The oxalate salt, crystallized with oxalic acid, of a triphenylmethane dye. Dark-green powder, having a metallic luster. Sparingly soluble in water; soluble in glacial acetic acid. Transition interval: from pH 0.0 to 2.0. Color change: from yellow to green.
Methyl Orange
(Helianthin or Tropaeolin D), C14H14N3NaO3S—327.33—The sodium salt of dimethylaminoazobenzene sulfonic acid or dimethylaminoazobenzene sodium sulfonate. An orange-yellow powder or crystalline scales. Slightly soluble in cold water; readily soluble in hot water; insoluble in alcohol. Transition interval: from pH 3.2 to 4.4. Color change: from pink to yellow.
Methyl Red
(2-[[4-(Dimethylamino)phenyl]azo]benzoic Acid Hydrochloride), 2-[4-(CH3)2NC6H4N:N]C6H4COOH·HCl—305.76—Dark-red powder or violet crystals. Sparingly soluble in water; soluble in alcohol. Transition interval: from pH 4.2 to 6.2. Color change: from red to yellow.
Methyl Red Sodium
—The sodium salt of 2-[[4-(dimethylamino)phenyl]azo]benzoic acid. 2-[4-(CH3)2NC6H4N:N]C6H4COONa—291.28—Orange-brown powder. Freely soluble in cold water and in alcohol. Transition interval: from pH 4.2 to 6.2. Color change: from red to yellow.
Methyl Yellow
(p-Dimethylaminoazobenzene), C14H15N3—225.29—Yellow crystals, melting between 114 and 117
and 117 . Insoluble in water; soluble in alcohol, in benzene, in chloroform, in ether, in dilute mineral acids, and in oils. Transition interval: from pH 2.9 to 4.0. Color change: from red to yellow.
. Insoluble in water; soluble in alcohol, in benzene, in chloroform, in ether, in dilute mineral acids, and in oils. Transition interval: from pH 2.9 to 4.0. Color change: from red to yellow.
p-Naphtholbenzein
(4-[ -(4-Hydroxy-1-naphthyl)benzylidene]-1(4H)-naphthalenone), (4-HOC10H6)C(:C10H6-4:O)(C6H5)—374.43—Reddish brown powder. Insoluble in water; soluble in alcohol, in benzene, in ether, and in glacial acetic acid. Transition interval: from pH 8.8 to 10.0. Color change: from orange to green.
-(4-Hydroxy-1-naphthyl)benzylidene]-1(4H)-naphthalenone), (4-HOC10H6)C(:C10H6-4:O)(C6H5)—374.43—Reddish brown powder. Insoluble in water; soluble in alcohol, in benzene, in ether, and in glacial acetic acid. Transition interval: from pH 8.8 to 10.0. Color change: from orange to green.
Neutral Red
(3-Amino-7-dimethylamino-2-methylphenazine Monohydrochloride), C15H16N4·HCl—288.78—Reddish to olive-green, coarse powder. Sparingly soluble in water and in alcohol. Transition interval: from pH 6.8 to 8.0. Color change: from red to orange.
Nile Blue Hydrochloride
(Nile Blue A, as the hydrochloride; 5-Amino-9- (diethylamino)benzo[a]phenoxazin-7-ium chloride), C20H20ClN3O—353.85—Slightly soluble in alcohol and in glacial acetic acid. Transition interval: from pH 9.0 to 13.0. Color change: from blue to pink.
Oracet Blue B
(Solvent Blue 19)—A mixture of 1-methyl- amino-4-anilinoanthraquinone (C21H16N2O2) and 1-amino-4-anilinoanthraquinine (C20H14N2O2). Where used for titration in non-aqueous media, it changes from blue (basic) through purple (neutral) to pink (acidic).
Phenol Red
[4,4¢-(3H-2,1-Benzoxathiol-3-ylidene)diphenol, S,S-Dioxide], C19H14O5S—354.38—Crystalline powder, varying in color from bright to dark red. Very slightly soluble in water; freely soluble in solutions of alkali carbonates and hydroxides; slightly soluble in alcohol. Transition interval: from pH 6.8 to 8.2. Color change: from yellow to red.
Phenolphthalein
[3,3-Bis(p-hydroxyphenyl)phthalide], C20H14O4—318.32—White or faintly yellowish-white, crystalline powder. Insoluble in water; soluble in alcohol. Transition interval: from pH 8.0 to 10.0. Color change: from colorless to red.
Quinaldine Red
(5-Dimethylamino-2-styrylethylquinolinium Iodide), C21H23IN2—430.33—Dark blue-black powder. Sparingly soluble in water; freely soluble in alcohol. Melts at about 260 , with decomposition. Transition interval: from pH 1.4 to 3.2. Color change: from colorless to red.
, with decomposition. Transition interval: from pH 1.4 to 3.2. Color change: from colorless to red.
2-(4-Sulfophenylazo)-1,8-dihydroxy-3,6-naphthalenedisulfonic Acid, Trisodium Salt
(4,5-Dihydroxy-3-(p-sulfophenylazo)-2,7-naphthalenedisulfonic Acid, Trisodium Salt), C16H9N2O11S3Na3—570.42—Red powder. Soluble in water.
Thymol Blue
(Thymolsulfonphthalein), C27H30O5S—466.59—Dark-colored, crystalline powder. Slightly soluble in water; soluble in alcohol and in dilute alkali solutions. Acid—Transition interval: from pH 1.2 to 2.8. Color change: from red to yellow. Alkaline—Transition interval: from pH 8.0 to 9.2. Color change: from yellow to blue.
Thymolphthalein,
C28H30O4—430.54—White to slightly yellow, crystalline powder. Insoluble in water; soluble in alcohol and in solutions of alkali hydroxides. Transition interval: from pH 9.3 to 10.5. Color change: from colorless to blue.
Xylenol Orange,
(N,N¢-[3H-2,1-Benzoxathiol-3-ylidenebis-[(6-hydroxy-5-methyl-3,1-phenylene)methylene]]bis[N-(carboxy-methyl)glycine] S,S-dioxide), C31H28N2Na4O13S—760.58—Orange powder. Soluble in alcohol and in water. In acid solution, it is lemon-yellow in color, and its metal complexes are intensely red. It yields a distinct endpoint where a metal such as bismuth, cadmium, lanthanum, lead, mercury, scandium, thorium, or zinc is titrated with edetate disodium.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Reagent | Margareth R. C. Marques, Ph.D.
Senior Scientific Liaison (301) 816-8106 |
(HDQ) Headquarters |



