Salmeterol Inhalation Powder
DEFINITION
Salmeterol Inhalation Powder for use in dry powder inhalers contains an amount of salmeterol xinafoate (C25H37NO4·C11H8O3) equivalent to NLT 90% and NMT 110% of the labeled amount of salmeterol (C25H37NO4).
IDENTIFICATION
• A.
The retention time of the major peak of the Sample solution corresponds to that of the Standard solution, as obtained in the test for Delivered-Dose Uniformity.
ASSAY
• Procedure
Buffer:
0.15 M ammonium acetate
Mobile phase:
Methanol, Buffer, and formic acid (65: 35: 0.5)
Diluent:
Methanol and water (70:30)
System suitability solution:
11 µg/mL of USP Salmeterol Resolution Check RS in Diluent
Standard solution:
9 µg/mL of USP Salmeterol Xinafoate RS in Diluent
Sample solution:
Nominally 6 µg/mL of salmeterol free base from NLT 12 unit doses in Diluent
Chromatographic system
Mode:
LC
Detector:
UV 276 nm
Column:
4.6-mm × 20-cm; 5-µm packing L1
Column temperature:
40
Flow rate:
1.5 mL/min
Injection volume:
200 µL
System suitability
Sample:
System suitability solution
[Note—The relative retention times for salmeterol and salmeterol-deoxy are 1.0 and 1.4, respectively. ]
Suitability requirements
Tailing factor:
NMT 1.5 for the salmeterol peak
Resolution:
NLT 2.0 between salmeterol and salmeterol-deoxy
Relative standard deviation:
NMT 2% for the salmeterol peak
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of the labeled amount of salmeterol (C25H37NO4) in the portion of the sample taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × (Mr1/Mr2) × 100
| rU | = | = peak response from the Sample solution |
| rS | = | = peak response from the Standard solution |
| CS | = | = concentration of USP Salmeterol Xinafoate RS in the Standard solution (µg/mL) |
| CU | = | = nominal concentration of salmeterol free base in the Sample solution (µg/mL), based on the target emitted dose of 47 µg |
| Mr1 | = | = molecular weight of salmeterol free base, 415.75 |
| Mr2 | = | = molecular weight of salmeterol xinafoate, 603.75 |
Acceptance criteria:
90%–110%
PERFORMANCE TESTS
• Particle Size Distribution by Cascade Impaction
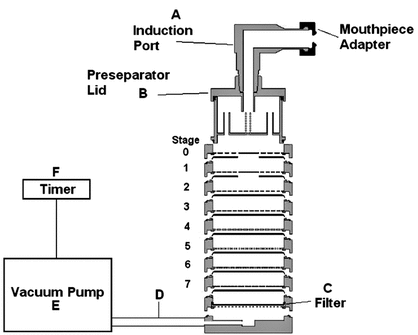
Sampling apparatus:
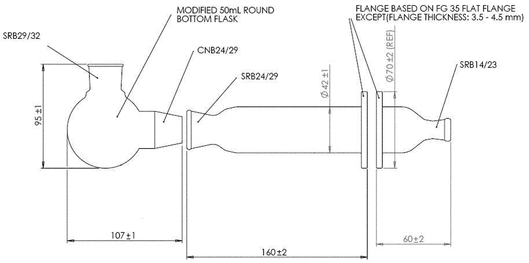
Modified Apparatus 3 (Figure 1) in Inhalation and Nasal Drug Products: Aerosols, Sprays, and Powders—Performance Quality Tests  601
601 with a modified Induction Port (Figure 2), and Preseparator Top (Figure 3) are to be used.
with a modified Induction Port (Figure 2), and Preseparator Top (Figure 3) are to be used.
Figure 1. Cascade impaction sampling apparatus (modified Apparatus 3 in  601
601 ) including Induction Port and Preseparator Top.
) including Induction Port and Preseparator Top.
Buffer:
0.0025 M sodium dodecylsulfate in 1% (v/v) of glacial acetic acid
Mobile phase:
Methanol and Buffer (100:5). [Note—The ratio of methanol to Buffer can be varied up to 100:15. ]
System suitability solution:
0.1 µg/mL of USP Salmeterol Related Compound A RS and 1.4 µg/mL of USP Salmeterol Xinafoate RS in methanol
Standard solution:
0.7 µg/mL of USP Salmeterol Xinafoate RS in methanol
Sample solutions:
Discharge the 10 unit doses into the cascade impaction sampling apparatus described above. Operate the pump for 3 s at an airflow rate of 60 L/min for each dose discharged. Detach the inhaler, and rinse each piece of the apparatus with methanol into a separate suitable volumetric flask. The final expected concentration of salmeterol should be in the range of 0.1–1 µg/mL. Dilute with methanol to volume. Repeat these steps on one additional sample preparation for a total of two Sample solutions.
Chromatographic system
Mode:
LC
Detector:
Fluorescence
Excitation:
225 nm
Emission:
305 nm
Column:
3.0-mm × 5-cm; 5-µm packing L1
Column temperature:
40
Flow rate:
0.5–1.5 mL/min
Injection volume:
100 µL
System suitability
Samples:
System suitability solution and Standard solution
[Note—The relative retention times for salmeterol related compound A and salmeterol are 0.67 and 1.0, respectively. ]
Suitability requirements
Resolution:
NLT 2.0 between salmeterol and salmeterol related compound A, System suitability solution
Relative standard deviation:
NMT 2%, Standard solution
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solutions
Calculate the quantity, in µg/unit dose, of salmeterol free base (C25H37NO4) in each Sample solution:
Result = (rU/rS) × CS × (V/N) × (Mr1/Mr2)
| rU | = | = peak response from the Sample solutions |
| rS | = | = peak response from the Standard solution |
| CS | = | = concentration of USP Salmeterol Xinafoate RS in the Standard solution (µg/mL) |
| V | = | = total volume of the Sample solutions (mL) |
| N | = | = number of unit doses discharged into the apparatus, 10 |
| Mr1 | = | = molecular weight of salmeterol free base, 415.75 |
| Mr2 | = | = molecular weight of salmeterol xinafoate, 603.75 |
Acceptance criteria:
The mean of the two samples for the mass of drug recovered from the cascade impactor component groupings are given in Table 1.
Table 1. Amount of Salmeterol in Cascade Impactor Stage Groupings
| Apparatus Component | Salmeterol Deposited (µg/dose) |
|---|---|
| Mouthpiece adaptor, induction port, preseparator, and Stage 0 | 32–40 |
| Stages 1–5 | 9.0–14 |
| Stages 3 and 4 | 4.0–8.0 |
| Stages 6, 7, and filter | NMT 1 |
• Delivered-Dose Uniformity  601
601
Buffer, Mobile phase, Chromatographic system, and System suitability:
Proceed as directed in Particle Size Distribution by Cascade Impaction.
System suitability solution:
0.1 µg/mL of USP Salmeterol Related Compound A RS and 0.7 µg/mL of USP Salmeterol Xinafoate RS in methanol
Standard solution:
0.36 µg/mL of USP Salmeterol Xinafoate RS in methanol
Sample solutions:
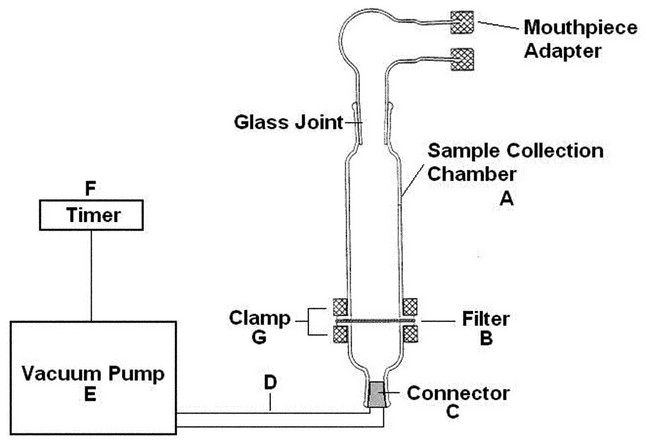
Nominally 0.25 µg/mL of salmeterol free base in methanol prepared as follows. Discharge a single unit dose into the apparatus shown in Figure 4A. Operate the pump for 2 s at an airflow of 60 L/min to collect the dose. Detach the inhaler, and rinse the mouthpiece adaptor and each piece of the sample collection chamber with methanol. Place the filter and washings into a container, and sonicate for NMT 5 min. Transfer the contents to a 200 mL volumetric flask, and dilute with methanol to volume. Prepare 9 additional samples from 9 additional unit doses. For multi-dose inhalers, 1 dose must be collected from 10 inhalers with the 10 doses collected across the minimum number of recommended doses on the label of the inhaler.
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solutions
Calculate the percentage of the target emitted dose of salmeterol (C25H37NO4) delivered by the Inhalation Powder in each of the Sample solutions:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × (Mr1/Mr2) × 100
| rU | = | = peak response from the Sample solutions |
| rS | = | = peak response from the Standard solution |
| CS | = | = concentration of USP Salmeterol xinafoate RS in the Standard solution (µg/mL) |
| CU | = | = nominal concentration of salmeterol free base in the Sample solutions (µg/mL) based on target emitted dose of 47 µg |
| Mr1 | = | = molecular weight of salmeterol free base, 415.75 |
| Mr2 | = | = molecular weight of salmeterol xinafoate, 603.75 |
Acceptance criteria
The mean content of salmeterol of 10 doses is 85%–115% of the target emitted dose.
NMT 1 dose is outside 80%–120% of the target emitted dose.
No dose is outside 75%–125% of the target emitted dose.
If the first and second requirements described are not met, test an additional 20 unit doses.
The mean dose of salmeterol of 30 doses is NLT 85% and NMT 115% of the target emitted dose.
NMT 3 doses are outside 80%–120% of the target emitted dose.
No dose is outside 75%–125% of the target emitted dose.
IMPURITIES
• Organic Impurities
Diluent:
Methanol and water (70:30)
Solution A:
Trifluoroacetic acid in water (0.05%, v/v)
Solution B:
Trifluoroacetic acid in acetonitrile (0.05%, v/v)
Protect the Sample solution and Standard solution from light.
System suitability solution:
0.1 mg/mL of USP Salmeterol System Suitability RS in Diluent
Standard solution:
2.5 µg/mL of USP Salmeterol Related Compound H RS in Diluent
Sample solution:
Nominally 50 µg/mL of salmeterol free base from NLT 10 unit doses prepared as follows. Weigh, and transfer the contents of the appropriate number of unit doses to a suitable volumetric flask. Add 80% of the flask volume of Diluent, and sonicate for 5 min. Cool to room temperature, and dilute with Diluent to volume. Allow the undissolved material to settle, and inject the supernatant.
Chromatographic system
Mode:
LC
Detector:
UV 215 nm
Column:
4.6-mm × 25-cm; 5-µm packing L1
Column temperature:
30
Flow rate:
1.0 mL/min
Injection volume:
50 µL
System suitability
Samples:
System suitability solution and Standard solution.
[Note—The relative retention times are given in Table 3. ]
Suitability requirements
Resolution:
NLT 2 between salmeterol-N-alkyl and salmeterol related compound H, System suitability solution
Relative standard deviation:
NMT 2 for salmeterol related compound H, Standard solution
Analysis
Sample:
Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of salmeterol related compound H in the portion of the sample taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × CS × V × (WN/WU) × (1/L) × 100
| rU | = | = peak response of each degradation product from the Sample solution |
| rS | = | = peak response of salmeterol related compound H in the Standard solution |
| CS | = | = concentration of USP Salmeterol Related Compound H RS in the Standard solution (µg/mL) |
| V | = | = volume of the Sample solution (mL) |
| WN | = | = theoretical unit dose weight (mg/unit dose) |
| WU | = | = weight of Inhalation Powder in the Sample solution (mg) |
| L | = | = label claim of salmeterol free base (µg/unit dose) |
Acceptance criteria:
See Table 3.
Table 3
| Name | Relative Retention Time |
Acceptance Criteria, NMT (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Salmeterol related compound Ba | 0.59 | — |
| Salmeterol phenylpropoxya,b | 0.77 | — |
| Salmeterol-phenyl-2-butoxya,c | 0.93 | — |
| Salmeterol-O-alkyla,d | 0.97 | — |
| Salmeterol | 1.0 | — |
| Salmeterol-deoxya,e | 1.52 | — |
| Hyrdoxynaphthoic acid | 1.63 | — |
| Salmeterol N-alkyla,f | 2.25 | — |
| Salmeterol related compound H | 2.33 | 1.8 |
| Any unspecified degradation product | — | 0.2 |
| Total impuritiesg | — | 2.4 |
|
a
Included for identification purposes only. Process impurities controlled in the drug substance and not to be included in the total impurities.
b
4-{1-Hydroxy-2-[6-(3-phenylpropoxy)hexylamino]ethyl}-2-(hydroxymethyl)phenol.
c
4-{1-Hydroxy-2-[6-(4-phenylbutan-2-yloxy)hexylamino]ethyl}-2-(hydroxymethyl)phenol.
d
4-{1-Hydroxy-2-[4-{1-hydroxy-2-[6-(4-phenylbutoxy)hexylamino]ethyl}-2-(hydroxymethyl)phenoxy]ethyl}-2-(hydroxymethyl)phenol.
e
4-{1-Hydroxy-2-[6-(4-phenylbutoxy)hexylamino]ethyl}-2-methylphenol.
f
4-{1-Hydroxy-2-[(2-hydroxy-5-{1-hydroxy-2-[6-(4-phenylbutoxy)hexylamino]ethyl}benzyl)[6-(4-phenylbutoxy)hexyl]amino]ethyl}-2-(hydroxymethyl)phenol.
g
Includes all degradation product peaks
|
||
SPECIFIC TESTS
• Microbial Enumeration Tests  61
61 and Tests for Specified Microorganisms
and Tests for Specified Microorganisms  62
62 :
It meets the requirements of the tests for absence of Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli, Salmonella species, and bile-tolerant Gram-negative bacteria in 1 g of bulk powder. The total aerobic microbial count does not exceed 101 cfu/g of bulk powder. The total aerobic yeast and mold count does not exceed 101 cfu/g of bulk powder.
:
It meets the requirements of the tests for absence of Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Escherichia coli, Salmonella species, and bile-tolerant Gram-negative bacteria in 1 g of bulk powder. The total aerobic microbial count does not exceed 101 cfu/g of bulk powder. The total aerobic yeast and mold count does not exceed 101 cfu/g of bulk powder.
• Foreign Particulate Matter
Particulate Matter in Injections  788
788 , Method 2 describes details of the test apparatus to be used for the determination of particulate matter using a microscopic particle count test methodology. Samples should be carefully prepared to avoid environmental contamination, and testing should be performed with suitable controls, including the appropriate use of blank determinations.
, Method 2 describes details of the test apparatus to be used for the determination of particulate matter using a microscopic particle count test methodology. Samples should be carefully prepared to avoid environmental contamination, and testing should be performed with suitable controls, including the appropriate use of blank determinations.
Diluent:
Methanol and water (65:35), passed through a filter of 0.45-µm pore size
Filter:
Mixed cellulose and ester filter; 25-mm diameter and 0.45-µm pore size
Sample solution:
Transfer the contents of 4 unit doses from each of 2 inhalers into a suitable receptacle, and dissolve the drug and excipient particles in about 75 mL of Diluent.
Analysis
Sample:
Sample solution
Pass the Sample solution through the Filter, and allow the Filter to dry under conditions that will limit particulate contamination. Using a microscopic particle count test method, enumerate the number of particles present in the sample solution.
Calculate the number of particles per dose:
Result = (N<10 + N10–100 + N>100)/8
| N<10 | = | = total number of particles <10 µm |
| N10–100 | = | = total number of particles between 10 and 100 µm |
| N>100 | = | = total number of particles >100 µm |
Acceptance criteria:
See Table 4.
Table 4
| Particle Size Range (µm) |
Number of Particles Per Dose (NMT) |
|---|---|
| <10 | 200 |
| 10–100 | 100 |
| >100 | 10 |
| Total | 300 |
ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
• Packaging and Storage:
Preserve in tight, light-resistant containers. Store at controlled room temperature, in a dry place away from direct heat or sunlight.
• USP Reference Standards  11
11
USP Salmeterol Related Compound A RS 
4-[1-Hydroxy-2-(4-phenylbutylamino)ethyl]-2-(hydroxymethyl)phenol.
C19H25NO3 315.41

4-[1-Hydroxy-2-(4-phenylbutylamino)ethyl]-2-(hydroxymethyl)phenol.
C19H25NO3 315.41
USP Salmeterol Related Compound H RS 
1-Hydroxy-4-[2-hydroxy-5-(1-hydroxy-2-{[6-(4-phenylbutoxy)hexyl]amino}ethyl)benzyl]-2-naphthoic acid.
C36H43NO6 585.73

1-Hydroxy-4-[2-hydroxy-5-(1-hydroxy-2-{[6-(4-phenylbutoxy)hexyl]amino}ethyl)benzyl]-2-naphthoic acid.
C36H43NO6 585.73
USP Salmeterol Resolution Check RS
This is a mixture of salmeterol xinafoate, salmeterol related compound H, and salmeterol-deoxy, also known as
4-{1-Hydroxy-2-[6-(4-phenylbutoxy)hexylamino]ethyl}-2-methylphenol.
This is a mixture of salmeterol xinafoate, salmeterol related compound H, and salmeterol-deoxy, also known as
4-{1-Hydroxy-2-[6-(4-phenylbutoxy)hexylamino]ethyl}-2-methylphenol.
USP Salmeterol System Suitability RS
This is a mixture of salmeterol xinafoate, salmeterol related compound H, and salmeterol-N-alkyl, also known as
4-{1-Hydroxy-2-[(2-hydroxy-5-{1-hydroxy-2-[6-(4-phenylbutoxy)hexylamino]ethyl}benzyl)[6-(4-phenylbutoxy)hexyl]amino]ethyl}-2-(hydroxymethyl)phenol.
This is a mixture of salmeterol xinafoate, salmeterol related compound H, and salmeterol-N-alkyl, also known as
4-{1-Hydroxy-2-[(2-hydroxy-5-{1-hydroxy-2-[6-(4-phenylbutoxy)hexylamino]ethyl}benzyl)[6-(4-phenylbutoxy)hexyl]amino]ethyl}-2-(hydroxymethyl)phenol.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Ravi Ravichandran, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison (301) 816-8330 |
(SM42010) Monographs - Small Molecules 4 |
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison (301) 816-8339 |
(GCM2010) General Chapters - Microbiology | |
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison (301) 816-8339 |
(GCM2010) General Chapters - Microbiology | |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
USP38–NF33 Page 5244
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 39(4)