DEAE-Agarose


 [57407-08-6]—Agarose beads chemically bonded with diethylaminoethane and suspended in a 20% ethanol solution in water.
[57407-08-6]—Agarose beads chemically bonded with diethylaminoethane and suspended in a 20% ethanol solution in water.
[Note—Commercially available as DEAE-Sepharose. ]
Decanol
(n-Decyl Alcohol),
 C10H22O—158.28
C10H22O—158.28 

 [112-30-1]—A clear, viscous liquid. Specific gravity: about 0.83 at 20
[112-30-1]—A clear, viscous liquid. Specific gravity: about 0.83 at 20 . Solidifies at about 6.5
. Solidifies at about 6.5 . Insoluble in water; soluble in alcohol and in ether.
. Insoluble in water; soluble in alcohol and in ether.
Assay—
When examined by gas-liquid chromatography, using suitable gas chromatographic apparatus and conditions, it shows a purity of not less than 99%.
Decyl Sodium Sulfate,
 C10H21NaO4S—260.33—White, crystalline solid.
C10H21NaO4S—260.33—White, crystalline solid.
Assay—
Transfer about 1 g, accurately weighed, to a suitable, tared crucible, moisten with a few drops of sulfuric acid, and ignite gently to constant weight. Each mg of residue is equivalent to 3.662 mg of C10H21NaO4S. Not less than 95% is found.
Deoxyadenosine Triphosphate,
 C10H16N5O12P3—491.18
C10H16N5O12P3—491.18 

 [1927-31-7]—Use a suitable grade.
[1927-31-7]—Use a suitable grade.
[Note—A suitable grade is available from either BD Biosciences, www.bdbiosciences.com or Applied Biosystems, www.appliedbiosystems.com. ]
Deoxycytidine Triphosphate,
 C9H16N3O13P3—467.16
C9H16N3O13P3—467.16 

 [2056-98-6]—Use a suitable grade.
[2056-98-6]—Use a suitable grade.
[Note—A suitable grade is available from either BD Biosciences, www.bdbiosciences.com or Applied Biosystems, www.appliedbiosystems.com. ]
Deoxyguanosine Triphosphate,
 C10H16N5O13P3—507.18
C10H16N5O13P3—507.18 

 [2564-35-4]—Use a suitable grade.
[2564-35-4]—Use a suitable grade.
[Note—A suitable grade is available from either BD Biosciences, www.bdbiosciences.com, or Applied Biosystems, www.appliedbiosystems.com. ]
Deoxyribonucleic Acid Polymerase—
Thermostable, recombinant DNA polymerase. Use a suitable grade.
[Note—A suitable grade is available from Applied Biosystems, www.appliedbiosystems.com. ]
Deoxythymidine Triphosphate,
 C10H17N2O14P3—482.17—Use a suitable grade.
C10H17N2O14P3—482.17—Use a suitable grade.
[Note—A suitable grade is available from either BD Biosciences, www.bdbiosciences.com or Applied Biosystems, www.appliedbiosystems.com. ]
Deuterated Methanol
 (Methanol-12C-d4, Methyl-12C-d3 alcohol-d1)—36.1
(Methanol-12C-d4, Methyl-12C-d3 alcohol-d1)—36.1 

 [811-98-3]—The degree of deuteration is not less than 99.8%. Is a clear colorless liquid miscible with water, with alcohol, and with methylene chloride; density at 20
[811-98-3]—The degree of deuteration is not less than 99.8%. Is a clear colorless liquid miscible with water, with alcohol, and with methylene chloride; density at 20 : 0.888 g/mL; refractive index at 20
: 0.888 g/mL; refractive index at 20 (D-line): 1.326; boiling point 65.4
(D-line): 1.326; boiling point 65.4 (760 mm Hg).
(760 mm Hg).
Deuterium Chloride (Deutero Hydrochloric Acid),
 DCl—37.47
DCl—37.47

 [7698-05-7]—Toxic gas. Use a suitable grade with a degree of deuteration of NLT 99%.
[7698-05-7]—Toxic gas. Use a suitable grade with a degree of deuteration of NLT 99%.
Deuterium Oxide,
 D2O—20.032
D2O—20.032 

 [7789-20-0]—Use a suitable grade having a minimum isotopic purity of 99.8 atom % of deuterium.
[7789-20-0]—Use a suitable grade having a minimum isotopic purity of 99.8 atom % of deuterium.
Deuterochloroform,
 CDCl3—120.38—Use a suitable grade.
CDCl3—120.38—Use a suitable grade.
Devarda's Alloy
(Devarda's Metal)


 [8049-11-4]—A gray powder composed of 50 parts of copper, 45 parts of aluminum, and 5 parts of zinc.
[8049-11-4]—A gray powder composed of 50 parts of copper, 45 parts of aluminum, and 5 parts of zinc.
Dextran, High Molecular Weight


 [9004-54-0]—A dextran molecular weight standard having a weight-average molecular weight, MW, of 1 to 2 × 106 Da and a weight-average molecular weight to number-average molecular weight ratio, MW / MN, of 1.0 to 1.8.
[9004-54-0]—A dextran molecular weight standard having a weight-average molecular weight, MW, of 1 to 2 × 106 Da and a weight-average molecular weight to number-average molecular weight ratio, MW / MN, of 1.0 to 1.8.
[Note—A suitable grade is available from American Polymer Standards Corporation, www.ampolymer.com. ]
Dextrin,
 (C6H10O5)n·xH2O
(C6H10O5)n·xH2O

 [9004-53-9]—A white amorphous powder. Slowly soluble in cold water; more readily soluble in hot water; insoluble in alcohol.
[9004-53-9]—A white amorphous powder. Slowly soluble in cold water; more readily soluble in hot water; insoluble in alcohol.
Insoluble matter—
Boil 1 g with 30 mL of water in a small flask: the solution is colorless and clear, or not more than opalescent.
Loss on drying  731
731 —
Dry it at 105
—
Dry it at 105 to constant weight: it loses not more than 10.0% of its weight.
to constant weight: it loses not more than 10.0% of its weight.
Residue on ignition (Reagent test)—
Ignite 1 g with 0.5 mL of sulfuric acid: the residue weighs not more than 5 mg (0.5%).
Chloride (Reagent test)—
Dissolve 3 g in 75 mL of boiling water, cool, dilute with water to 75 mL, and filter if necessary. To 25 mL of the filtrate add 2 mL of nitric acid and 1 mL of silver nitrate TS, and allow to stand for 5 minutes: any turbidity produced is not greater than that of a control containing 0.02 mg of added Cl (0.002%).
Sulfate (Reagent test, Method I)—
To a 25-mL portion of the filtrate from the preceding test add 0.5 mL of diluted hydrochloric acid and 2 mL of barium chloride TS, and allow to stand for 10 minutes: any turbidity produced is not greater than that of a control containing 0.2 mg of added SO4 (0.02%).
Alcohol-soluble substances—
Boil 1 g with 20 mL of alcohol for 5 minutes under a reflux condenser, and filter while hot. Evaporate 10 mL of the filtrate on a steam bath, and dry at 105 : the residue weighs not more than 5 mg (1%).
: the residue weighs not more than 5 mg (1%).
Reducing sugars—
Shake 2 g with 100 mL of water for 10 minutes, and filter until clear. To 50 mL of the filtrate add 50 mL of alkaline cupric tartrate TS, and boil for 3 minutes. Filter through a tared filtering crucible, wash with water, then with alcohol, and finally with ether, and dry at 105 for 2 hours: the precipitate of cuprous oxide weighs not more than 115 mg (corresponding to about 5% of reducing sugars as dextrose).
for 2 hours: the precipitate of cuprous oxide weighs not more than 115 mg (corresponding to about 5% of reducing sugars as dextrose).
Dextro Calcium Pantothenate
—Use Calcium Pantothenate (USP monograph).
Dextrose, Anhydrous,
 C6H12O6—180.16—Use ACS reagent grade d-Glucose, Anhydrous.
C6H12O6—180.16—Use ACS reagent grade d-Glucose, Anhydrous.
3,3¢-Diaminobenzidine Hydrochloride,
 (NH2)2C6H3C6H3(NH2)2·4HCl—360.11
(NH2)2C6H3C6H3(NH2)2·4HCl—360.11 

 [7411-49-6]—White to yellowish-tan (occasionally purple), needle-shaped crystals. Soluble in water. Stable in organic solvents but unstable in aqueous solution at room temperature. Store aqueous solutions in a refrigerator.
[7411-49-6]—White to yellowish-tan (occasionally purple), needle-shaped crystals. Soluble in water. Stable in organic solvents but unstable in aqueous solution at room temperature. Store aqueous solutions in a refrigerator.
Insoluble matter—
Dissolve 2 g in 100 mL of water, without heating, and filter immediately: the insoluble residue does not exceed 1 mg (0.05%).
Residue on ignition (Reagent test):
not more than 1 mg, from 2 g (0.05%).
Suitability test for detection of selenium—
Dissolve 1.633 g of selenious acid (H2SeO3) in water, and dilute with water to 1 L. Dilute 10 mL of this solution with water to 1 L, to make a solution containing 0.010 mg of Se per mL. Place 1 mL of the resulting solution in a 100-mL beaker, add 2 mL of formic acid solution (1 in 7), and dilute with water to 50 mL. Add 2 mL of 3,3¢-diaminobenzidine hydrochloride solution (1 in 200), and allow to stand for 30 to 50 minutes. Adjust with 6 N ammonium hydroxide to a pH between 6 and 7. Transfer to a 125-mL separator, add 10.0 mL of toluene, and shake vigorously for 30 seconds: a distinct yellow color is produced in the toluene layer. A blank containing diaminobenzidine hydrochloride but no selenium standard, treated in the same manner, shows no color in the toluene layer.
2,3-Diaminonaphthalene,
 C10H10N2—158.20
C10H10N2—158.20 

 [771-97-1]—Use a suitable grade.
[771-97-1]—Use a suitable grade.
Diatomaceous Earth


 [91053-39-3]—Use a suitable grade. [Note—A suitable grade is available as Celite 545-AW. ]
[91053-39-3]—Use a suitable grade. [Note—A suitable grade is available as Celite 545-AW. ]
Diatomaceous Earth, Flux-Calcined


 [91053-39-3]—Use a suitable grade.
[91053-39-3]—Use a suitable grade.
[Note—A suitable grade is “Chromosorb W, AW-DMCS”. ]
Diatomaceous Earth, Silanized


 [91053-39-3]—Use a suitable grade.
[91053-39-3]—Use a suitable grade.
[Note—Suitable grades are available commercially as “Anachrome Q,” “Gas-Chrom Q,” and “Varaport 30.” ]
Diatomaceous Silica, Calcined


 [68855-54-9]—A form of silica (SiO2) consisting of fused frustules and fragments of diatoms. It is an amorphous, fine, light pink or white powder. Insoluble in water, in acids, and in dilute solutions of alkali hydroxides.
[68855-54-9]—A form of silica (SiO2) consisting of fused frustules and fragments of diatoms. It is an amorphous, fine, light pink or white powder. Insoluble in water, in acids, and in dilute solutions of alkali hydroxides.
Loss on ignition—
Accurately weigh about 4 g, and ignite to constant weight: it loses not more than 10.0% of its weight.
Organic impurities—
It does not darken appreciably upon ignition.
Loss on drying  731
731 —
Dry it at 110
—
Dry it at 110 for 2 hours: it loses not more than 2.0% of its weight.
for 2 hours: it loses not more than 2.0% of its weight.
[Note—Suitable grades are “Chromosorb P” and “Chromosorb W,” available from Grace, www.grace.com. ]
Diaveridine
(5-([3,4-Dimethoxyphenyl]methyl)-2,4-pyrimidinediamine),
 C13H16N4O2—260.3
C13H16N4O2—260.3

 [5355-16-8]—Use a suitable grade. [Note—A suitable grade is available as catalog number 46174 from www.sigma-aldrich.com. ]
[5355-16-8]—Use a suitable grade. [Note—A suitable grade is available as catalog number 46174 from www.sigma-aldrich.com. ]
2,6-Dibromoquinone-chlorimide
(2,6-Dibromo-N-chloro-p-benzoquinone Imine; DBQ Reagent),
 O:C6H2Br2:NCl—299.35
O:C6H2Br2:NCl—299.35 

 [537-45-1]—A yellow, crystalline powder. Insoluble in water; soluble in alcohol and in dilute alkali hydroxide solutions.
[537-45-1]—A yellow, crystalline powder. Insoluble in water; soluble in alcohol and in dilute alkali hydroxide solutions.
Melting range  741
741 :
between 82
:
between 82 and 84
and 84 .
.
Solubility in alcohol—
A solution of 100 mg in 10 mL of alcohol is not more than faintly turbid.
Residue on ignition (Reagent test)—
Ignite 500 mg with 0.5 mL of sulfuric acid: the residue weighs not more than 1 mg (0.2%).
Sensitiveness—
To 10 mL of a water solution containing 0.01 mg of phenol add 0.3 mL of a sodium borate buffer (made by dissolving 2.84 g of crystallized sodium borate in 90 mL of warm water, adding 8.2 mL of 1 N sodium hydroxide, and diluting with water to 100 mL) and 0.1 mL of a solution of 10 mg of the test specimen in 20 mL of alcohol: a distinct blue color develops within 10 minutes.
Dibutyl Phthalate,
 C16H22O4—278.34
C16H22O4—278.34 

 [84-74-2]—Clear, colorless liquid.
[84-74-2]—Clear, colorless liquid.
Assay—
Accurately weigh about 2 g into a suitable flask, add 25.0 mL of 1 N sodium hydroxide and 30 mL of isopropyl alcohol, and mix. Digest the mixture at a temperature near boiling for 30 minutes, then cool in a water bath to room temperature. Add phenolphthalein TS, and titrate with 1 N sulfuric acid VS to the disappearance of the pink color. Perform a complete blank determination, and make any necessary correction. Each mL of 1 N sulfuric acid consumed is equivalent to 139.2 mg of C16H22O4. Not less than 98% is found.
Refractive index  831
831 :
between 1.491 and 1.493 at 20
:
between 1.491 and 1.493 at 20 .
.
Acid content—
Accurately weigh about 10 g, and dissolve in 100 mL of an alcohol-ether mixture (1:1). Add phenolphthalein TS, and titrate immediately with 0.05 N alcoholic potassium hydroxide VS. Each mL of 0.05 N alcoholic potassium hydroxide is equivalent to 4.15 mg of phthalic acid: not more than 0.02% is found.
Dibutylamine,
 C8H19N—129.24
C8H19N—129.24 

 [111-92-2]—Colorless liquid.
[111-92-2]—Colorless liquid.
Assay—
Inject an appropriate volume into a gas chromatograph (see Chromatography  621
621 ) equipped with a flame-ionization detector, helium being used as the carrier gas. The following conditions have been found suitable: a 0.25-mm × 30-m capillary column coated with a 1-µm layer of phase G2; the injection port temperature is maintained at 200
) equipped with a flame-ionization detector, helium being used as the carrier gas. The following conditions have been found suitable: a 0.25-mm × 30-m capillary column coated with a 1-µm layer of phase G2; the injection port temperature is maintained at 200 ; the detector temperature is maintained at 300
; the detector temperature is maintained at 300 ; and the column temperature is maintained at 100
; and the column temperature is maintained at 100 and programmed to rise 10
and programmed to rise 10 per minute to 200
per minute to 200 . The area of the C8H19N peak is not less than 99% of the total peak area.
. The area of the C8H19N peak is not less than 99% of the total peak area.
Refractive index  831
831 :
between 1.415 and 1.419 at 20
:
between 1.415 and 1.419 at 20 .
.
Dibutylammonium Phosphate—
Use a suitable grade.
[Note—A suitable grade is available as PIC Reagent D4 from Waters Corporation, www.waters.com. ]
1,3-Dicaffeoylquinic Acid (Cynarin; (1R,3R,4S,5R)-1,3-Bis [[3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)propenoyl]oxy]-4,5-dihydroxycyclohexanecarboxylic Acid),
 C25H24O12—516.45
C25H24O12—516.45

 [30964-13-7]—Use a suitable grade.
[30964-13-7]—Use a suitable grade.
[Note— A suitable grade is available as catalog number 3991 from www.chromadex.com. ]
Dichloroacetic Acid,
 C2H2Cl2O2—128.9
C2H2Cl2O2—128.9 

 [79-43-6]—Colorless liquid. Miscible with water, with alcohol, and with ether. Use a suitable grade.
[79-43-6]—Colorless liquid. Miscible with water, with alcohol, and with ether. Use a suitable grade.
2,5-Dichloroaniline,
 Cl2C6H3NH2—162.02
Cl2C6H3NH2—162.02 

 [95-82-9]—White, needle-like crystals. Slightly soluble in water; soluble in alcohol and in ether.
[95-82-9]—White, needle-like crystals. Slightly soluble in water; soluble in alcohol and in ether.
Melting range, Class I  741
741 :
between 49
:
between 49 and 50
and 50 .
.
2,6-Dichloroaniline,
 C6H5Cl2N—162.02
C6H5Cl2N—162.02 

 [608-31-1]—Off-white powder.
[608-31-1]—Off-white powder.
Melting range  741
741 :
between 38
:
between 38 and 41
and 41 .
.
o-Dichlorobenzene,
 C6H4Cl2—147.00
C6H4Cl2—147.00 

 [95-50-1]—Clear liquid, having a light yellowish-brown tint (about APHA 20). Practically insoluble in water. Miscible with alcohol and with ether. Boils at about 180
[95-50-1]—Clear liquid, having a light yellowish-brown tint (about APHA 20). Practically insoluble in water. Miscible with alcohol and with ether. Boils at about 180 .
.
Assay—
When examined by gas–liquid chromatography, with the use of suitable apparatus and conditions, it shows a purity of not less than 98%.
Density:
between 1.299 and 1.301.
Refractive index  831
831 :
between 1.548 and 1.550 at 25
:
between 1.548 and 1.550 at 25 .
.
Residue on evaporation—
Evaporate 80 mL on a steam bath, and dry at 105 for 1 hour: the residue weighs not more than 50 mg (0.005%).
for 1 hour: the residue weighs not more than 50 mg (0.005%).
Acidity—
Add phenolphthalein TS to 25 mL of methanol, and titrate with 0.02 N alcoholic potassium hydroxide VS until a faint pink color persists for 15 seconds. Pipet 25 mL of test specimen into the solution; mix, avoiding exposure to the atmosphere; and titrate with 0.02 N alcoholic potassium hydroxide VS: not more than 2.2 mL is required to restore the pink color (about 0.005%).
Dichlorofluorescein,
 C20H10Cl2O5—401.20
C20H10Cl2O5—401.20 

 [76-54-0]—[Note—This specification covers both the 4,5- and 2,7-isomers of dichlorofluorescein, either of which is suitable for the preparation of dichlorofluorescein TS. ] A weak orange-colored, crystalline powder. Sparingly soluble in water; soluble in alcohol and in solutions of alkali hydroxides.
[76-54-0]—[Note—This specification covers both the 4,5- and 2,7-isomers of dichlorofluorescein, either of which is suitable for the preparation of dichlorofluorescein TS. ] A weak orange-colored, crystalline powder. Sparingly soluble in water; soluble in alcohol and in solutions of alkali hydroxides.
Residue on ignition (Reagent test)—
Ignite 200 mg with 5 drops of sulfuric acid: the residue weighs not more than 1 mg (0.5%).
Sensitiveness—
Dissolve 100 mg in 60 mL of alcohol, add 2.5 mL of 0.1 N sodium hydroxide, and dilute with water to 100 mL. Add 1 mL of this solution to a solution of potassium iodide prepared by dissolving 100 mg of potassium iodide, previously dried at 105 to constant weight and accurately weighed, in 50 mL of water containing 1 mL of glacial acetic acid, and titrate with 0.1 N silver nitrate VS until the color of the precipitate changes from pale yellowish-orange to pink. The volume of 0.1 N silver nitrate consumed is not more than 0.10 mL greater than the calculated volume, the calculated volume being based upon the KI content of the dried specimen as determined in the Assay under Potassium Iodide (USP monograph).
to constant weight and accurately weighed, in 50 mL of water containing 1 mL of glacial acetic acid, and titrate with 0.1 N silver nitrate VS until the color of the precipitate changes from pale yellowish-orange to pink. The volume of 0.1 N silver nitrate consumed is not more than 0.10 mL greater than the calculated volume, the calculated volume being based upon the KI content of the dried specimen as determined in the Assay under Potassium Iodide (USP monograph).
Dichlorofluoromethane,
 CHCl2F—102.92
CHCl2F—102.92 

 [75-43-4]—Colorless gas.
[75-43-4]—Colorless gas.
Assay—
Inject an appropriate specimen into a gas chromatograph (see Chromatography  621
621 ) equipped with a thermal-conductivity detector, helium being used as the carrier gas. The following conditions have been found suitable: a 0.53-mm × 30-m capillary column coated with a 5-µm layer of phase G2; the injection port temperature is maintained at 200
) equipped with a thermal-conductivity detector, helium being used as the carrier gas. The following conditions have been found suitable: a 0.53-mm × 30-m capillary column coated with a 5-µm layer of phase G2; the injection port temperature is maintained at 200 ; the detector temperature is maintained at 200
; the detector temperature is maintained at 200 ; and the column temperature is maintained at 0
; and the column temperature is maintained at 0 and programmed to rise 5
and programmed to rise 5 per minute to 40
per minute to 40 , and then to rise 10
, and then to rise 10 per minute to 180
per minute to 180 . The area of the CHCl2F peak is not less than 98% of the total peak area.
. The area of the CHCl2F peak is not less than 98% of the total peak area.
1,1-Dichloro-2,2-bis(p-chlorophenyl)ethane
(p,p¢-DDD),
 C14H10Cl4—320.03
C14H10Cl4—320.03

 [72-54-8]—Use a suitable grade. [Note—A suitable grade is available as catalog number B0132 at www.tciamerica.com. ]
[72-54-8]—Use a suitable grade. [Note—A suitable grade is available as catalog number B0132 at www.tciamerica.com. ]
2,4-Dichloro-1-naphthol,
 C10H6OCl2—213.06
C10H6OCl2—213.06 

 [2050-76-2]—Light tan powder.
[2050-76-2]—Light tan powder.
Melting range  741
741 :
between 103
:
between 103 and 107
and 107 , but the range between beginning and end of melting does not exceed 2
, but the range between beginning and end of melting does not exceed 2 .
.
2,6-Dichlorophenol-indophenol Sodium
(2,6-Dichloro-indophenol Sodium),
 O:C6H2Cl2:NC6H4ONa with about 2H2O—290.08 (anhydrous)
O:C6H2Cl2:NC6H4ONa with about 2H2O—290.08 (anhydrous)

 [620-45-1] —Use ACS reagent grade.
[620-45-1] —Use ACS reagent grade.
2,6-Dichlorophenylacetic Acid,
 C8H6Cl2O2—205.04
C8H6Cl2O2—205.04 

 [6575-24-2]—White powder.
[6575-24-2]—White powder.
Assay—
Inject an appropriate specimen into a gas chromatograph (see Chromatography  621
621 ) equipped with a flame-ionization detector, helium being used as the carrier gas. The following conditions have been found suitable: a 0.25-mm × 30-m capillary column coated with a 1-µm layer of phase G2; the injection port temperature is maintained at 250
) equipped with a flame-ionization detector, helium being used as the carrier gas. The following conditions have been found suitable: a 0.25-mm × 30-m capillary column coated with a 1-µm layer of phase G2; the injection port temperature is maintained at 250 ; the detector temperature is maintained at 300
; the detector temperature is maintained at 300 ; and the column temperature is maintained at 150
; and the column temperature is maintained at 150 and programmed to rise 10
and programmed to rise 10 per minute to 280
per minute to 280 . The area of the C8H6Cl2O2 peak is not less than 97% of the total peak area.
. The area of the C8H6Cl2O2 peak is not less than 97% of the total peak area.
2,6-Dichloroquinone-chlorimide
(2,6-Dichloro-N-chloro-p-benzoquinone Imine),
 O:C6H2Cl2:NCl—210.44—Pale yellow, crystalline powder. Insoluble in water; soluble in alcohol and in dilute alkali hydroxide solutions.
O:C6H2Cl2:NCl—210.44—Pale yellow, crystalline powder. Insoluble in water; soluble in alcohol and in dilute alkali hydroxide solutions.
Melting range  741
741 :
:
 between 65
between 65 and 67
and 67 .
.
Solubility in alcohol—
A solution of 100 mg in 10 mL of alcohol is complete and clear.
Residue on ignition—
Ignite 500 mg with 0.5 mL of sulfuric acid: the residue weighs not more than 1 mg (0.2%).
Sensitiveness—
It meets the requirements of the test for Sensitiveness under 2,6-Dibromoquinone-chlorimide.
Dicyclohexyl,
(Bicyclohexyl)
 C12H22—166.31
C12H22—166.31 

 [92-51-3]—Use a suitable grade.
[92-51-3]—Use a suitable grade.
Dicyclohexylamine,
 (C6H11)2NH—181.32
(C6H11)2NH—181.32 

 [101-83-7]—Clear, strongly alkaline liquid. Sparingly soluble in water. Miscible with common organic solvents. Use a suitable grade with a content of not less than 98%.
[101-83-7]—Clear, strongly alkaline liquid. Sparingly soluble in water. Miscible with common organic solvents. Use a suitable grade with a content of not less than 98%.
Diethylamine,
 (C2H5)2NH—73.14
(C2H5)2NH—73.14 

 [109-89-7]—Colorless, flammable, strongly alkaline liquid. Miscible with water and with alcohol. Forms a hydrate with water. May be irritating to skin and mucous membranes. Store in well-closed containers. Use ACS reagent grade.
[109-89-7]—Colorless, flammable, strongly alkaline liquid. Miscible with water and with alcohol. Forms a hydrate with water. May be irritating to skin and mucous membranes. Store in well-closed containers. Use ACS reagent grade.
Diethylamine Phosphate
(Phosphoric Acid: Diethylamine),
 C4H11N·H3PO4—171.13
C4H11N·H3PO4—171.13

 [68109-72-8]—Use a suitable grade. [Note—A suitable grade is available from www.richmanchemical.com. ]
[68109-72-8]—Use a suitable grade. [Note—A suitable grade is available from www.richmanchemical.com. ]
N,N-Diethylaniline,
 C6H5N(C2H5)2—149.23
C6H5N(C2H5)2—149.23 

 [91-66-7]—Light yellow to amber liquid.
[91-66-7]—Light yellow to amber liquid.
Assay—
Inject an appropriate specimen (about 0.2 µL) into a suitable gas chromatograph (see Chromatography  621
621 ) equipped with a flame-ionization detector, helium being used as the carrier gas flowing at about 40 mL per minute. The following conditions have been found suitable: a 3-mm × 1.8-m stainless steel column containing 20% phase G16 on support S1A; the injection port temperature is maintained at 250
) equipped with a flame-ionization detector, helium being used as the carrier gas flowing at about 40 mL per minute. The following conditions have been found suitable: a 3-mm × 1.8-m stainless steel column containing 20% phase G16 on support S1A; the injection port temperature is maintained at 250 ; the column temperature is maintained at 140
; the column temperature is maintained at 140 and programmed to rise 6
and programmed to rise 6 per minute to 200
per minute to 200 . The detector temperature is maintained at 310
. The detector temperature is maintained at 310 . The area of the N,N-diethylaniline peak having a retention time of about 4.9 minutes is not less than 99% of the total peak area.
. The area of the N,N-diethylaniline peak having a retention time of about 4.9 minutes is not less than 99% of the total peak area.
Refractive index  831
831 :
between 1.5405 and 1.5425 at 20
:
between 1.5405 and 1.5425 at 20 .
.
Diethylene Glycol,
(Bis(2-hydroxyethyl) Ether; Diglycol; 2-Hydroxyethyl Ether; 2,2¢-Oxydiethanol),
 C4H10O3—106.12
C4H10O3—106.12 

 [111-46-6]—A colorless to faintly yellow, viscous, hygroscopic liquid. Miscible with water, with alcohol, with ether, and with acetone. Insoluble in benzene and in carbon tetrachloride. Use a suitable grade with a content of not less than 99.0%.
[111-46-6]—A colorless to faintly yellow, viscous, hygroscopic liquid. Miscible with water, with alcohol, with ether, and with acetone. Insoluble in benzene and in carbon tetrachloride. Use a suitable grade with a content of not less than 99.0%.
Di(ethylene glycol) Methyl Ether
(2-(2-Methoxyeth oxy)ethanol; Methyldiglycol),
 C5H12O3—120.15
C5H12O3—120.15

 [111-77-3]—Use a suitable grade.
[111-77-3]—Use a suitable grade.
Diethylene Glycol Succinate Polyester,
 (OCH2CH2OCH2CH2OOCCH2CH2COO)n
(OCH2CH2OCH2CH2OOCCH2CH2COO)n

 [26183-02-8]—Clear, viscous liquid. Soluble in chloroform. Is stabilized by modification of the diethylene glycol succinate polyester, to render it suitable for use in gas–liquid chromatography to a temperature of 200
[26183-02-8]—Clear, viscous liquid. Soluble in chloroform. Is stabilized by modification of the diethylene glycol succinate polyester, to render it suitable for use in gas–liquid chromatography to a temperature of 200 .
.
[Note—A suitable grade is available from Alltech, www.alltechweb.com. ]
Diethylenetriamine,
 C4H13N3—103.17
C4H13N3—103.17 

 [111-40-0]—Colorless liquid.
[111-40-0]—Colorless liquid.
Assay—
Inject an appropriate specimen into a suitable gas chromatograph (see Chromatography  621
621 ) equipped with a flame-ionization detector, helium being used as the carrier gas. The following conditions have been found suitable: a 0.25-mm × 30-m capillary column coated with G2. The injection port temperature is maintained at 200
) equipped with a flame-ionization detector, helium being used as the carrier gas. The following conditions have been found suitable: a 0.25-mm × 30-m capillary column coated with G2. The injection port temperature is maintained at 200 ; the column temperature is maintained at 100
; the column temperature is maintained at 100 and programmed to rise 10
and programmed to rise 10 per minute to 250
per minute to 250 and held there for 5 minutes; and the detector temperature is maintained at 300
and held there for 5 minutes; and the detector temperature is maintained at 300 . The area of the main peak is not less than 95% of the total peak area.
. The area of the main peak is not less than 95% of the total peak area.
Refractive index  831
831 :
between 1.4815 and 1.4845 at 20
:
between 1.4815 and 1.4845 at 20 .
.
Di(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate
[Bis(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate],
 C24H38O4—390.56
C24H38O4—390.56 

 [117-81-7]—Use a suitable grade.
[117-81-7]—Use a suitable grade.
Diethylpyrocarbonate,
 C6H10O5—162.14
C6H10O5—162.14 

 [1609-47-8]—Clear, colorless liquid. Use a suitable grade.
[1609-47-8]—Clear, colorless liquid. Use a suitable grade.
Diethyl Sulfone (Ethyl Sulfone),
 (C2H5)2SO2—122.19
(C2H5)2SO2—122.19

 [597-35-3]—Use a suitable grade with NLT 97%.
[597-35-3]—Use a suitable grade with NLT 97%.
Digitonin,
 C56H92O29—1229.31
C56H92O29—1229.31 

 [11024-24-1]—White, crystalline powder. Almost insoluble in water; soluble in warm alcohol, and in glacial acetic acid and in 75% acetic acid; insoluble in chloroform and in ether. Melts at about 230
[11024-24-1]—White, crystalline powder. Almost insoluble in water; soluble in warm alcohol, and in glacial acetic acid and in 75% acetic acid; insoluble in chloroform and in ether. Melts at about 230 , with decomposition.
, with decomposition.
Specific rotation  781
781 :
between
:
between  47
47 and
and  49
49 , determined in a solution in 75% acetic acid containing 100 mg per mL.
, determined in a solution in 75% acetic acid containing 100 mg per mL.
Solubility in alcohol—
A solution of 500 mg in 20 mL of warm alcohol is colorless and complete.
Loss on drying  731
731 —
Dry it at 105
—
Dry it at 105 to constant weight: it loses not more than 6% of its weight.
to constant weight: it loses not more than 6% of its weight.
Residue on ignition (Reagent test):
not more than 0.3%.
Digoxigenin
(3 ,12
,12 ,14
,14 ,21-Tetrahydroxy-20(22)-norcholenic Acid Lactone; 3
,21-Tetrahydroxy-20(22)-norcholenic Acid Lactone; 3 ,12
,12 ,14-Trihydroxy-5
,14-Trihydroxy-5 ,20(22)-cardenolide; 5
,20(22)-cardenolide; 5 ,20(22)-Cardenolide-3
,20(22)-Cardenolide-3 ,12
,12 ,14-triol; Lanadigenin),
,14-triol; Lanadigenin),
 C23H34O5—390.51
C23H34O5—390.51

 [1672-46-4]—Use a suitable grade.
[1672-46-4]—Use a suitable grade.
Add the following:
Dihydroquinidine Hydrochloride,
 C20H27ClN2O2—362.89
C20H27ClN2O2—362.89 

 [1476-98-8]—Rhombic plates. Freely soluble in methanol and in chloroform.
[1476-98-8]—Rhombic plates. Freely soluble in methanol and in chloroform.
Assay—
Mobile phase—
Prepare a mixture of water, acetonitrile, diethylamine, and methanesulfonic acid (860:100:20:20).
Procedure—
Inject about 20 µL into a suitable liquid chromatograph (see Chromatography  621
621 ) equipped with a 235-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 15-cm column that contains packing L1. The flow rate is about 1.5 mL per minute. The area of the C20H27ClN2O2 peak is not less than 97.5% of the total peak area.
) equipped with a 235-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 15-cm column that contains packing L1. The flow rate is about 1.5 mL per minute. The area of the C20H27ClN2O2 peak is not less than 97.5% of the total peak area.
Dihydroquinine
(Hydroquinine),
 C20H26N2O2—326.43
C20H26N2O2—326.43 

 [522-66-7]—Freely soluble in acetone, in alcohol, and in chloroform; almost insoluble in water.
[522-66-7]—Freely soluble in acetone, in alcohol, and in chloroform; almost insoluble in water.
Assay—
Mobile phase—
Prepare a mixture of water, acetonitrile, diethylamine, and methanesulfonic acid (860:100:20:20) and methanol (82:18).
Procedure—
Inject about 20 µL into a suitable liquid chromatograph (see Chromatography  621
621 ) equipped with a 235-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 15-cm column that contains packing L1. The flow rate is about 1.5 mL per minute. The area of the C20H26N2O2 peak is not less than 97.5% of the total peak area.
) equipped with a 235-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 15-cm column that contains packing L1. The flow rate is about 1.5 mL per minute. The area of the C20H26N2O2 peak is not less than 97.5% of the total peak area.
2,5-Dihydroxybenzoic Acid,
 C7H6O4—154.12
C7H6O4—154.12 

 [303-07-1]—Off-white powder. Freely soluble in alcohol yielding a clear, very pale yellow solution.
[303-07-1]—Off-white powder. Freely soluble in alcohol yielding a clear, very pale yellow solution.
Assay—
Dissolve about 75 mg, accurately weighed, in 30 mL of methanol. Slowly add 40 mL of water. Titrate with 0.1 N sodium hydroxide VS, determining the endpoint potentiometrically. Perform a blank determination, and make any necessary correction. Each mL of 0.1 N sodium hydroxide is equivalent to 15.41 mg of C7H6O4. Not less than 99% is found.
Melting range  741
741 :
about 207
:
about 207 , with decomposition.
, with decomposition.
Diiodofluorescein,
 C20H10I2O5—584.10
C20H10I2O5—584.10 

 [31395-16-1]—Orange-red powder. Slightly soluble in water; soluble in alcohol and in solutions of alkali hydroxides.
[31395-16-1]—Orange-red powder. Slightly soluble in water; soluble in alcohol and in solutions of alkali hydroxides.
Residue on ignition—
Ignite 200 mg with 5 drops of sulfuric acid: the weight of the residue does not exceed 1.0 mg (0.5%).
Sensitiveness—
Accurately weigh about 100 mg of potassium iodide, previously dried at 105 to constant weight, and dissolve it in 50 mL of water. Add 1 mL of diiodofluorescein TS prepared from the test specimen and 1 mL of glacial acetic acid, and titrate with 0.1 N silver nitrate VS until the color of the precipitate changes from brownish-red to a bluish-red. The volume of 0.1 N silver nitrate consumed is not in excess of 0.10 mL over the calculated volume, based on the KI content of the dried potassium iodide determined as follows. Dissolve about 500 mg of potassium iodide, accurately weighed, in about 10 mL of water, and add 35 mL of hydrochloric acid and 5 mL of chloroform. Titrate with 0.05 M potassium iodate VS until the purple color of iodine disappears from the chloroform. Add the last portions of the iodate solution dropwise, agitating vigorously and continuously. After the chloroform has been decolorized, allow the mixture to stand for 5 minutes. If the chloroform develops a purple color, titrate further with the iodate solution. Each mL of 0.05 M potassium iodate is equivalent to 16.60 mg of KI.
to constant weight, and dissolve it in 50 mL of water. Add 1 mL of diiodofluorescein TS prepared from the test specimen and 1 mL of glacial acetic acid, and titrate with 0.1 N silver nitrate VS until the color of the precipitate changes from brownish-red to a bluish-red. The volume of 0.1 N silver nitrate consumed is not in excess of 0.10 mL over the calculated volume, based on the KI content of the dried potassium iodide determined as follows. Dissolve about 500 mg of potassium iodide, accurately weighed, in about 10 mL of water, and add 35 mL of hydrochloric acid and 5 mL of chloroform. Titrate with 0.05 M potassium iodate VS until the purple color of iodine disappears from the chloroform. Add the last portions of the iodate solution dropwise, agitating vigorously and continuously. After the chloroform has been decolorized, allow the mixture to stand for 5 minutes. If the chloroform develops a purple color, titrate further with the iodate solution. Each mL of 0.05 M potassium iodate is equivalent to 16.60 mg of KI.
Diisodecyl Phthalate
[Bis(isodecyl)phthalate],
 C28H46O4—446.66
C28H46O4—446.66 

 [26761-40-0]—Use a suitable grade.
[26761-40-0]—Use a suitable grade.
Diisopropyl Ether
(Isopropyl Ether),
 [(CH3)2CH]2O—102.17
[(CH3)2CH]2O—102.17 

 [108-20-3]—Colorless, mobile liquid. Slightly soluble in water. Miscible with alcohol and with ether. [Caution—It is highly flammable. Do not use where it may be ignited. Do not evaporate to the point of near dryness, since it tends to form explosive peroxides.
]
[108-20-3]—Colorless, mobile liquid. Slightly soluble in water. Miscible with alcohol and with ether. [Caution—It is highly flammable. Do not use where it may be ignited. Do not evaporate to the point of near dryness, since it tends to form explosive peroxides.
]
Specific gravity:
between 0.716 and 0.720.
Distilling range, Method II  721
721 —
Not less than 95% distills between 65
—
Not less than 95% distills between 65 and 70
and 70 .
.
Peroxides—
To 10 mL, contained in a clean, glass-stoppered cylinder previously rinsed with a portion of the ether under examination, add 1 mL of freshly prepared potassium iodide solution (1 in 10). Shake, and allow to stand for 1 minute: no yellow color is observed in either layer (about 0.001% as H2O2).
Residue on evaporation—
[Note—If peroxide is present, do not carry out this procedure. ] Evaporate 14 mL (10 g) from a tared shallow dish, and dry at 105 for 1 hour: the residue weighs not more than 1 mg (0.01%).
for 1 hour: the residue weighs not more than 1 mg (0.01%).
Acidity—
Add 2 drops of bromothymol blue TS to 10 mL of water in a glass-stoppered, 50-mL flask, and titrate with 0.010 N sodium hydroxide until a blue color persists after vigorous shaking. Add 5 mL of diisopropyl ether, and titrate with 0.010 N sodium hydroxide: not more than 0.30 mL is required to restore the blue color (0.005% as CH3COOH).
[Note—For spectrophotometric determinations, use diisopropyl ether that meets the following additional requirement: ]
Absorbance—
Its absorbance at 255 nm, in a 10-mm quartz cell, does not exceed 0.2, water being used as the blank.
Diisopropylamine,
 [(CH3)2CH]2NH—101.19
[(CH3)2CH]2NH—101.19 

 [108-18-9]—Colorless liquid.
[108-18-9]—Colorless liquid.
Assay—
Not less than 98% of C6H15N is found, a suitable gas chromatograph equipped with a flame-ionization detector being used. The following conditions have been found suitable: a 3.2-mm × 1.83-m stainless steel column is packed with a cross-linked polystyrene support; the injection port temperature is maintained at 250 and the detector temperature at 310
and the detector temperature at 310 ; the column temperature is programmed to rise at 10
; the column temperature is programmed to rise at 10 per minute from 50
per minute from 50 to 220
to 220 .
.
Refractive index  831
831 :
between 1.3915 and 1.3935, at 20
:
between 1.3915 and 1.3935, at 20 .
.
Diisopropylethylamine
(N,N-Diisopropylethylamine),
 C8H19N—129.24
C8H19N—129.24 

 [7087-68-5]—Clear, colorless liquid. Soluble in glacial acetic acid.
[7087-68-5]—Clear, colorless liquid. Soluble in glacial acetic acid.
Assay—
Accurately weigh about 500 mg, dissolve in 50 mL of glacial acetic acid, mix, add crystal violet TS, and titrate with 0.1 N perchloric acid VS. Each mL of 0.1 N perchloric acid is equivalent to 12.92 mg of C8H19N. Not less than 98% is found.
Refractive index  831
831 :
between 1.4125 and 1.4145 at 20
:
between 1.4125 and 1.4145 at 20 .
.
1,2-Dilinoleoyl-3-oleoyl-rac-glycerol,
 C57H100O6—881.4
C57H100O6—881.4 

 [2190-21-8]—Use a suitable grade.
[2190-21-8]—Use a suitable grade.
1,2-Dilinoleoyl-3-palmitoyl-rac-glycerol,
 C55H98O6—855.4
C55H98O6—855.4 

 [2190-15-0]—Use a suitable grade.
[2190-15-0]—Use a suitable grade.
Dimethicone, viscosity 500 centistokes
(Poly(dimethylsiloxane), viscosity 500 centistokes),
 [–Si(CH3)2O–]n
[–Si(CH3)2O–]n

 [63148-62-9]—Use a suitable grade.
[63148-62-9]—Use a suitable grade.
2,5-Dimethoxybenzaldehyde,
 C9H10O3—166.17
C9H10O3—166.17 

 [93-02-7]—Off-white crystals.
[93-02-7]—Off-white crystals.
Assay—
Inject an appropriate specimen into a suitable gas chromatograph (see Chromatography  621
621 ) equipped with a flame-ionization detector, nitrogen being used as the carrier gas. The following conditions have been found suitable: a 0.3-mm × 30-m capillary column coated with phase G1; the injection port temperature is maintained at 270
) equipped with a flame-ionization detector, nitrogen being used as the carrier gas. The following conditions have been found suitable: a 0.3-mm × 30-m capillary column coated with phase G1; the injection port temperature is maintained at 270 ; the detector temperature is maintained at 300
; the detector temperature is maintained at 300 ; the column temperature is maintained at 150
; the column temperature is maintained at 150 and programmed to rise 10
and programmed to rise 10 per minute to 270
per minute to 270 . The area of the main peak is not less than 97% of the total peak area.
. The area of the main peak is not less than 97% of the total peak area.
Melting range  741
741 :
between 50
:
between 50 and 52
and 52 .
.
1,2-Dimethoxyethane,
 C4H10O2—90.12
C4H10O2—90.12 

 [110-71-4]—Clear, colorless liquid. Miscible with water and with alcohol. Soluble in hydrocarbon solvents. May form peroxides on standing.
[110-71-4]—Clear, colorless liquid. Miscible with water and with alcohol. Soluble in hydrocarbon solvents. May form peroxides on standing.
Boiling range (Reagent test)—
Not less than 95% distills between 83 and 86
and 86 .
.
Refractive index  831
831 :
between 1.379 and 1.381, at 20
:
between 1.379 and 1.381, at 20 .
.
Acidity—
To 20 mL add bromophenol blue TS, and titrate with 0.020 N sodium hydroxide: not more than 2.0 mL is consumed (about 0.015% as CH3COOH).
Water, Method I  921
921 :
not more than 0.2%.
:
not more than 0.2%.
Dimethoxymethane
(Formaldehyde Dimethyl Acetal, Methylal),
 C3H8O2—76.10
C3H8O2—76.10 

 [109-87-5]—Use a suitable grade.
[109-87-5]—Use a suitable grade.
(3,4-Dimethoxyphenyl)acetonitrile
(Homoveratronitrile),
 C10H11NO2—177.20
C10H11NO2—177.20 

 [93-17-4]—Off-white fibers.
[93-17-4]—Off-white fibers.
Melting range  741
741 :
between 65
:
between 65 and 67
and 67 .
.
Dimethyl Phthalate,
 C10H10O4—194.19
C10H10O4—194.19 

 [131-11-3]—Viscous, colorless liquid.
[131-11-3]—Viscous, colorless liquid.
Assay—
mobile phase—Prepare a filtered and degassed mixture of chromatographic n-heptane and n-propyl alcohol (HPLC grade) (97:3). Make adjustments if necessary (see System Suitability under Chromatography  621
621 ).
).
standard solution—Dissolve a suitable quantity of dimethyl phthalate in Mobile phase to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 0.26 mg per mL.
procedure—Inject about 20 µL into a suitable liquid chromatograph (see Chromatography  621
621 ) equipped with a 238-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 25-cm column that contains packing L10. The flow rate is about 1.0 mL per minute. The area of the dimethyl phthalate peak is not less than 99% of the total peak area.
) equipped with a 238-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 25-cm column that contains packing L10. The flow rate is about 1.0 mL per minute. The area of the dimethyl phthalate peak is not less than 99% of the total peak area.
Refractive index  831
831 :
between 1.514 and 1.518 at 20
:
between 1.514 and 1.518 at 20 .
.
Dimethyl Sulfone
(Methyl Sulfone),
 (CH3)2SO2—94.13
(CH3)2SO2—94.13 

 [67-71-0]—White crystals.
[67-71-0]—White crystals.
Melting range  741
741 :
between 109
:
between 109 and 111
and 111 .
.
Dimethyl Sulfoxide (Methyl Sulfoxide),
 (CH3)2SO—78.13—Use ACS reagent grade methyl sulfoxide.
(CH3)2SO—78.13—Use ACS reagent grade methyl sulfoxide.
Dimethyl Sulfoxide, Spectrophotometric Grade


 [67-68-5]—Use methyl sulfoxide ACS spectrophotometric reagent grade.
[67-68-5]—Use methyl sulfoxide ACS spectrophotometric reagent grade.
N,N-Dimethylacetamide,
 C4H9NO—87.12
C4H9NO—87.12 

 [127-19-5]—Clear, colorless liquid. Miscible with water and with many organic solvents. Use a suitable HPLC or spectroscopic grade.
[127-19-5]—Clear, colorless liquid. Miscible with water and with many organic solvents. Use a suitable HPLC or spectroscopic grade.
p-Dimethylaminoazobenzene
(Methyl Yellow, Butter Yellow),
 C6H5N:NC6H4N(CH3)2—225.29
C6H5N:NC6H4N(CH3)2—225.29 

 [60-11-7]—Yellow leaflets or yellow, crystalline powder.
[60-11-7]—Yellow leaflets or yellow, crystalline powder.
Solubility—
Insoluble in water; sparingly soluble in chloroform, in ether, or in fatty oils. Dissolve 100 mg in 20 mL of alcohol: the solution is complete or practically so and clear.
Melting range  741
741 :
between 115
:
between 115 and 117
and 117 .
.
Residue on ignition  281
281 :
not more than 0.1%.
:
not more than 0.1%.
Sensitiveness—
Add 0.05 mL of an alcohol solution (1 in 200) and 2 g of ammonium chloride to 25 mL of carbon dioxide-free water: the lemon-yellow color of the solution is changed to orange by the addition of 0.05 mL of 0.1 N hydrochloric acid and restored on the subsequent addition of 0.05 mL of 0.1 N sodium hydroxide.
p-Dimethylaminobenzaldehyde,
 (CH3)2NC6H4CHO—149.19
(CH3)2NC6H4CHO—149.19 

 [100-10-7]—Use ACS reagent grade.
[100-10-7]—Use ACS reagent grade.
p-Dimethylaminocinnamaldehyde,
 (CH3)2NC6H4CH:CHCHO—175.23—Orange-yellow powder. Soluble in acetone, in alcohol, and in benzene.
(CH3)2NC6H4CH:CHCHO—175.23—Orange-yellow powder. Soluble in acetone, in alcohol, and in benzene.
Melting range  741
741 :
:
 between 132
between 132 and 136
and 136 .
.
2-Dimethylaminoethyl Methacrylate,
 C8H15NO2——157.2
C8H15NO2——157.2

 [2867-47-2]—Use a suitable grade.
[2867-47-2]—Use a suitable grade.
Dimethylaminophenol
(meta isomer),
 C8H11NO—137.18—Purplish–black, gray, or tan-colored, crystalline solid.
C8H11NO—137.18—Purplish–black, gray, or tan-colored, crystalline solid.
Melting range  741
741 :
:
 between 83
between 83 and 85
and 85 .
.
2,6-Dimethylaniline,
 C8H11N—121.18
C8H11N—121.18 

 [87-62-7]—Yellow liquid.
[87-62-7]—Yellow liquid.
Refractive index  831
831 :
about 1.5609 at 20
:
about 1.5609 at 20 .
.
N,N-Dimethylaniline,
 C6H5N(CH3)2—121.18
C6H5N(CH3)2—121.18 

 [121-69-7]—Light yellow liquid. Clear, colorless liquid when freshly distilled, but acquiring a reddish to reddish-brown color. Specific gravity: about 0.960. Freezing point about 2
[121-69-7]—Light yellow liquid. Clear, colorless liquid when freshly distilled, but acquiring a reddish to reddish-brown color. Specific gravity: about 0.960. Freezing point about 2 . Insoluble in water; soluble in alcohol, in chloroform, in ether, and in dilute mineral acids.
. Insoluble in water; soluble in alcohol, in chloroform, in ether, and in dilute mineral acids.
Assay—
Inject an appropriate specimen (about 0.2 µL) into a suitable gas chromatograph (see Chromatography  621
621 ) equipped with a flame-ionization detector, helium being used as the carrier gas flowing at about 40 mL per minute. The following conditions have been found suitable: a 3-mm × 1.8-m stainless steel column containing 20% phase G16 on support S1A; the injection port temperature is maintained at 250
) equipped with a flame-ionization detector, helium being used as the carrier gas flowing at about 40 mL per minute. The following conditions have been found suitable: a 3-mm × 1.8-m stainless steel column containing 20% phase G16 on support S1A; the injection port temperature is maintained at 250 ; the column temperature is maintained at 50
; the column temperature is maintained at 50 and programmed to rise 10
and programmed to rise 10 per minute to 200
per minute to 200 . The detector temperature is maintained at 310
. The detector temperature is maintained at 310 . The area of the N,N-dimethylaniline peak having a retention time of about 11.5 minutes is not less than 99% of the total peak area.
. The area of the N,N-dimethylaniline peak having a retention time of about 11.5 minutes is not less than 99% of the total peak area.
Refractive index  831
831 :
between 1.5571 and 1.5591 at 20
:
between 1.5571 and 1.5591 at 20 .
.
Boiling range (Reagent test)—
Distill 100 mL: the difference between the temperatures observed, when 1 mL and 95 mL have distilled, is not more than 2.5 . Its boiling temperature at a pressure of 760 mm of mercury is 194.2
. Its boiling temperature at a pressure of 760 mm of mercury is 194.2 .
.
Hydrocarbons—
Dissolve 5 mL in a mixture of 10 mL of hydrochloric acid and 15 mL of water: a clear solution results and it remains clear on cooling to about 10 .
.
Aniline or monomethylaniline—
Place 5 mL in a glass-stoppered flask, add 5 mL of a solution of acetic anhydride in benzene (1 in 10), mix, and allow to stand for 30 minutes. Add 30.0 mL of 0.5 N sodium hydroxide VS, shake the mixture, add phenolphthalein TS, and titrate with 0.5 N hydrochloric acid VS. Perform a blank determination, and make any necessary correction. Not more than 0.30 mL of 0.5 N sodium hydroxide is consumed by the test specimen.
3,4-Dimethylbenzophenone,
 C15H14O—210.27
C15H14O—210.27 

 [2571-39-3]—White chunks melting at about 45
[2571-39-3]—White chunks melting at about 45 .
.
Assay—
Inject an appropriate specimen into a suitable gas chromatograph (see Chromatography  621
621 ) equipped with a flame-ionization detector, helium being used as the carrier gas. The following conditions have been found suitable: a 0.25-mm × 30-m capillary column coated with phase G1: the detector temperature and the injection port temperature are maintained at 300
) equipped with a flame-ionization detector, helium being used as the carrier gas. The following conditions have been found suitable: a 0.25-mm × 30-m capillary column coated with phase G1: the detector temperature and the injection port temperature are maintained at 300 ; the column temperature is maintained at 180
; the column temperature is maintained at 180 and programmed to rise at the rate of 10
and programmed to rise at the rate of 10 per minute to 280
per minute to 280 and held at that temperature for 10 minutes. The area of the main peak is not less than 99% of the total peak area.
and held at that temperature for 10 minutes. The area of the main peak is not less than 99% of the total peak area.
5,5-Dimethyl-1,3-cyclohexanedione,
 C8H12O2—140.18
C8H12O2—140.18 

 [126-81-8]—White, crystalline solid. Slightly soluble in water; soluble in alcohol, in methanol, in chloroform, and in acetic acid.
[126-81-8]—White, crystalline solid. Slightly soluble in water; soluble in alcohol, in methanol, in chloroform, and in acetic acid.
Melting range  741
741 :
between 148
:
between 148 and 150
and 150 .
.
N,N-Dimethyldecylamine
(1-(Dimethylamino)decane),
 C4H9NO—185.35
C4H9NO—185.35 

 [1120-24-7]—Use a suitable grade with a content of not less than 98%.
[1120-24-7]—Use a suitable grade with a content of not less than 98%.
1,5-Dimethyl-1,5-diazaundecamethylene polymethobromide (Polybrene),


 [28728-55-4]—This is a positively charged polymer. It is available as an off-white, crystalline solid or powder and is extremely hygroscopic. Use a suitable reagent grade.
[28728-55-4]—This is a positively charged polymer. It is available as an off-white, crystalline solid or powder and is extremely hygroscopic. Use a suitable reagent grade.
[Note—Commercially available as Polybrene. ]
N,N-Dimethyldodecylamine-N-oxide
(Lauryldimethylamine-N-oxide),
 CH3(CH2)11NO(CH3)2—229.40
CH3(CH2)11NO(CH3)2—229.40 

 [1643-20-5]—Use a suitable grade. [Note—N,N-Dimethyldodecylamine-N-oxide, 0.1 N in Water and N,N-Dimethyldodecylamine-N-oxide, 30 Percent are suitable grades as well. ]
[1643-20-5]—Use a suitable grade. [Note—N,N-Dimethyldodecylamine-N-oxide, 0.1 N in Water and N,N-Dimethyldodecylamine-N-oxide, 30 Percent are suitable grades as well. ]
Dimethylethyl(3-hydroxyphenyl)ammonium Chloride
—See Edrophonium Chloride.
Dimethylformamide
(N,N-Dimethylformamide),
 HCON(CH3)2—73.09
HCON(CH3)2—73.09 

 [68-12-2]—Use ACS reagent grade.
[68-12-2]—Use ACS reagent grade.
N,N-Dimethylformamide Diethyl Acetal
—147.22 

 [1188-33-6]—Use a suitable grade.
[1188-33-6]—Use a suitable grade.
[Note—A suitable grade is available from Sigma-Aldrich, www.sigma-aldrich.com. ]
1,3-Dimethyl-2-imidazolidinone,
 C5H10N2O—114.15
C5H10N2O—114.15 

 [80-73-9]—Use a suitable grade.
[80-73-9]—Use a suitable grade.
1,9-Dimethyl-methylene Blue,
 C36H46Cl4N6OS2Zn—850.1
C36H46Cl4N6OS2Zn—850.1 

 [23481-50-7]—Dark green powder. Use a suitable grade.
[23481-50-7]—Dark green powder. Use a suitable grade.
[Note—A suitable grade is available from Sigma-Aldrich, www.sigma-aldrich.com. ]
N,N-Dimethyl-1-naphthylamine,
 C12H13N—171.24
C12H13N—171.24 

 [86-56-6]—Pale yellow to yellow, aromatic liquid. Soluble in alcohol and in ether.
[86-56-6]—Pale yellow to yellow, aromatic liquid. Soluble in alcohol and in ether.
Assay—
Transfer about 250 mg, accurately weighed, to a suitable beaker, add 100 mL of glacial acetic acid, and dissolve by stirring. When solution is complete, titrate with 0.1 N perchloric acid VS, determining the endpoint potentiometrically. Perform a blank determination, and make any necessary correction. Each mL of 0.1 N perchloric acid is equivalent to 17.12 mg of C12H13N. Not less than 98% is found.
Refractive index  831
831 :
between 1.6210
:
between 1.6210 and 1.6230
and 1.6230 at 20
at 20 , sodium light being used.
, sodium light being used.
Sulfanilamide test—
Dissolve 20 mg of USP Sulfanilamide RS in 100 mL of water to obtain the Sulfanilamide solution. Into two 150-mL beakers pipet 1.0 mL and 2.5 mL of the Sulfanilamide solution, respectively. Dilute with water to 90 mL. To provide a blank, place 90 mL of water in a third beaker. To each beaker add 8.0 mL of trichloroacetic acid solution (3 in 20) and 1.0 mL of sodium nitrite solution (1 in 1000). Stir the solutions for 5 minutes, then add 10 mL of acetate buffer TS, and 1.0 mL of a 1 in 1000 solution of N,N-dimethyl-1-naphthylamine in alcohol. The pH is about 5 to 6, using pH paper. Stir for an additional 5 minutes, then add 20 mL of glacial acetic acid. The pH is about 3 to 4, using pH paper. In comparison with the blank, the beaker containing 1.0 mL of the Sulfanilamide solution shows a pink color, while the other beaker shows a deep pink to red color.
N,N-Dimethyloctylamine,
 C10H23N—157.30
C10H23N—157.30 

 [7378-99-6]—Colorless liquid.
[7378-99-6]—Colorless liquid.
Refractive index  831
831 :
1.4243 at 20
:
1.4243 at 20 .
.
2,5-Dimethylphenol,
 C8H10O—122.16
C8H10O—122.16 

 [95-87-4]—Use a suitable grade.
[95-87-4]—Use a suitable grade.
2,6-Dimethylphenol,
 (CH3)2C6H3OH—122.16
(CH3)2C6H3OH—122.16 

 [576-26-1]—White to pale yellow, crystalline solid.
[576-26-1]—White to pale yellow, crystalline solid.
Assay—
Inject a 1 in 3 solution of it in xylene into a suitable gas chromatograph equipped with a flame-ionization detector, helium being used as the carrier gas at a flow rate of about 40 mL per minute. The following conditions have been found suitable: a 3.2-mm × 1.83-m stainless steel column packed with 10% phase G25 on support S1A; the injection port temperature is maintained at about 250 and the detector temperature at about 310
and the detector temperature at about 310 ; the column temperature is programmed to rise at 8
; the column temperature is programmed to rise at 8 per minute from 100
per minute from 100 to 200
to 200 . Similarly inject a specimen of xylene. The area of the C8H10O peak is not less than 98% of the total peak area corrected for xylene.
. Similarly inject a specimen of xylene. The area of the C8H10O peak is not less than 98% of the total peak area corrected for xylene.
Melting range  741
741 :
between 44
:
between 44 and 46
and 46 .
.
3,5-Dimethylphenol,
 C8H10O—122.16
C8H10O—122.16 

 [108-68-9]—Use a suitable grade.
[108-68-9]—Use a suitable grade.
[Note—A suitable grade is available as product number 5600 from www.alfa.com. ]
N,N-Dimethyl-p-phenylenediamine Dihydrochloride,
 (CH3)2NC6H4NH2·2HCl—209.12
(CH3)2NC6H4NH2·2HCl—209.12 

 [99-89-9]—Nearly white, fine, crystalline, hygroscopic solid that may have a pinkish cast. Freely soluble in water; soluble in alcohol.
[99-89-9]—Nearly white, fine, crystalline, hygroscopic solid that may have a pinkish cast. Freely soluble in water; soluble in alcohol.
Assay—
Transfer about 400 mg, accurately weighed, to a 250-mL beaker, and dissolve in about 75 mL of water. Titrate with 0.1 N sodium hydroxide VS, determining the endpoint potentiometrically. Each mL of 0.1 N sodium hydroxide is equivalent to 10.46 mg of C8H12N2·2HCl. Not less than 98% is found.
Solubility—
A solution of 1 g in 10 mL of water produces not more than a slight haze.
3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl Tetrazolium Bromide,
 C18H16N5SBr—414.3
C18H16N5SBr—414.3 

 [298-93-1]—Yellow to orange powder. Use a suitable grade.
[298-93-1]—Yellow to orange powder. Use a suitable grade.
Dimethyltin Dibromide,
 C2H6Br2Sn—308.59
C2H6Br2Sn—308.59 

 [2767-47-7]—Use a suitable grade.
[2767-47-7]—Use a suitable grade.
m-Dinitrobenzene,
 C6H4(NO2)2—168.11
C6H4(NO2)2—168.11 

 [99-65-0]—Pale yellow crystals or crystalline powder. Almost insoluble in cold water; slightly soluble in hot water. Soluble in chloroform and in benzene; sparingly soluble in alcohol. Is volatile in steam.
[99-65-0]—Pale yellow crystals or crystalline powder. Almost insoluble in cold water; slightly soluble in hot water. Soluble in chloroform and in benzene; sparingly soluble in alcohol. Is volatile in steam.
Melting range  741
741 :
between 89
:
between 89 and 92
and 92 .
.
Residue on ignition (Reagent test):
not more than 0.5%.
3,5-Dinitrobenzoyl Chloride,
 C7H3ClN2O5—230.56
C7H3ClN2O5—230.56 

 [99-33-2]—Pale yellow, crystalline powder. Freely soluble in dilute sodium hydroxide solutions; soluble in alcohol. [Caution—Corrosive, moisture-sensitive, lachrymator, and possible mutagen. Store under nitrogen.
]
[99-33-2]—Pale yellow, crystalline powder. Freely soluble in dilute sodium hydroxide solutions; soluble in alcohol. [Caution—Corrosive, moisture-sensitive, lachrymator, and possible mutagen. Store under nitrogen.
]
Melting range  741
741 :
between 69
:
between 69 and 71
and 71 .
.
Solubility in sodium hydroxide—
A solution of 500 mg in 25 mL of 1 N sodium hydroxide is clear or not more than faintly turbid.
Residue on ignition—
Ignite 1 g with 0.5 mL of sulfuric acid: the residue weighs not more than 1 mg (0.1%).
2,4-Dinitrochlorobenzene,
 C6H3(NO2)2Cl—202.55
C6H3(NO2)2Cl—202.55 

 [97-00-7]—Yellow to brownish-yellow crystals. Insoluble in water; soluble in hot alcohol, in ether, and in benzene.
[97-00-7]—Yellow to brownish-yellow crystals. Insoluble in water; soluble in hot alcohol, in ether, and in benzene.
Melting range  741
741 :
between 51
:
between 51 and 53
and 53 .
.
Residue on ignition—
Ignite 500 mg with 5 drops of sulfuric acid: the residue weighs not more than 1 mg (0.2%).
2,4-Dinitrofluorobenzene
(1-Fluoro-2,4-dinitrobenzene),
 C6H3FN2O4—186.10
C6H3FN2O4—186.10 

 [70-34-8]—Light yellow solid. Use a suitable grade.
[70-34-8]—Light yellow solid. Use a suitable grade.
2,4-Dinitrophenylhydrazine,
 2,4-C6H3(NO2)2NHNH2—198.14
2,4-C6H3(NO2)2NHNH2—198.14 

 [119-26-6]—Orange-red crystals, which under the microscope appear individually to be lemon-yellow, lath-like needles. Very slightly soluble in water; slightly soluble in alcohol; moderately soluble in dilute inorganic acids.
Use a suitable grade with a content of not less than 97%.
[119-26-6]—Orange-red crystals, which under the microscope appear individually to be lemon-yellow, lath-like needles. Very slightly soluble in water; slightly soluble in alcohol; moderately soluble in dilute inorganic acids.
Use a suitable grade with a content of not less than 97%.
Dioctyl Sodium Sulfosuccinate
—Use Docusate Sodium (USP monograph).
Dioxane
(Diethylene Dioxide; 1,4-Dioxane),
 C4H8O2—88.11
C4H8O2—88.11 

 [123-91-1]—Use ACS reagent grade.
[123-91-1]—Use ACS reagent grade.
Diphenyl Ether
(Phenyl Ether),
 (C6H5)2O—170.21
(C6H5)2O—170.21 

 [101-84-8]—A colorless liquid. Insoluble in water; soluble in glacial acetic acid and in most organic solvents. Boils at about 259
[101-84-8]—A colorless liquid. Insoluble in water; soluble in glacial acetic acid and in most organic solvents. Boils at about 259 .
.
Melting range  741
741 :
between 26
:
between 26 and 28
and 28 .
.
Diphenylamine,
 (C6H5)2NH—169.22
(C6H5)2NH—169.22 

 [122-39-4]—Use ACS reagent grade.
[122-39-4]—Use ACS reagent grade.
Diphenylborinic Acid, Ethanolamine Ester,
(2-Aminoethyl Diphenylborinate)
 C14H16BNO—225.09—White, crystalline powder. Use a suitable grade.
C14H16BNO—225.09—White, crystalline powder. Use a suitable grade.
Melting range  741
741 :
:
 between 192
between 192 and 194
and 194 .
.
Diphenylcarbazide,
 (C6H5NHNH)2CO—242.28
(C6H5NHNH)2CO—242.28 

 [140-22-7]—Use ACS reagent grade 1,5-Diphenylcarbohydrazide.
[140-22-7]—Use ACS reagent grade 1,5-Diphenylcarbohydrazide.
Diphenylcarbazone
[Diphenylcarbazone compd. with s-Diphenylcarbazide (1:1)],
 C6H5NHNHCON:NC6H5·C6H5NHNHCONHNHC6H5—482.54
C6H5NHNHCON:NC6H5·C6H5NHNHCONHNHC6H5—482.54 

 [538-62-5]—Use ACS reagent grade Diphenylcarbazone Compound with s-Diphenylcarbazide (1:1).
[538-62-5]—Use ACS reagent grade Diphenylcarbazone Compound with s-Diphenylcarbazide (1:1).
2,2-Diphenylglycine,
 C14H13NO2—227.26
C14H13NO2—227.26 

 [3060-50-2]—Off-white powder. Melts at about 244
[3060-50-2]—Off-white powder. Melts at about 244 , with decomposition.
, with decomposition.
Assay—
Dissolve about 115 mg, accurately weighed, in 30 mL of methanol. Slowly add about 20 mL of water, heating slightly if necessary for complete solution. Titrate with 0.1 N sodium hydroxide VS, determining the endpoint potentiometrically. Perform a blank determination and make any necessary correction. Each mL of 0.1 N sodium hydroxide is equivalent to 22.73 mg of C14H13NO2. Not less than 98.0% is found.
Dipropyl Phthalate,
 C14H18O4—250.29
C14H18O4—250.29 

 [131-16-8]—Viscous, colorless liquid.
[131-16-8]—Viscous, colorless liquid.
Assay—
Mobile phase—
Prepare a mixture of acetonitrile and water (52:48).
Procedure—
Inject about 20 µL into a suitable liquid chromatograph (see Chromatography  621
621 ) equipped with a 230-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 15-cm column that contains packing L1. The flow rate is about 2.0 mL per minute. The area of the C14H18O4 peak is not less than 99% of the total peak area.
) equipped with a 230-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 15-cm column that contains packing L1. The flow rate is about 2.0 mL per minute. The area of the C14H18O4 peak is not less than 99% of the total peak area.
Refractive index  831
831 :
between 1.495 and 1.499 at 20
:
between 1.495 and 1.499 at 20 .
.
4,4¢-Dipyridyl,
 C10H8 N2—156.18
C10H8 N2—156.18 

 [553-26-4]—Use a suitable grade. [Note—A suitable grade is available from Sigma-Aldrich Catalog number 289426. ]
[553-26-4]—Use a suitable grade. [Note—A suitable grade is available from Sigma-Aldrich Catalog number 289426. ]
Disodium Chromotropate
(4,5-Dihydroxy-2,7-naphthalenedisulfonic Acid, Disodium Salt),
 C10H6O8S2Na2·2H2O—400.29—Use ACS reagent grade Chromotropic Acid Disodium Salt.
C10H6O8S2Na2·2H2O—400.29—Use ACS reagent grade Chromotropic Acid Disodium Salt.
5,5¢-Dithiobis(2-nitrobenzoic Acid)
(3-Carboxy-4-nitrophenyl disulfide; Ellman's reagent),
 C14H8N2O8S2—396.35
C14H8N2O8S2—396.35 

 [69-78-3]—Yellow powder, melting at about 242
[69-78-3]—Yellow powder, melting at about 242 . Sparingly soluble in alcohol.
. Sparingly soluble in alcohol.
Dithiothreitol
(Cleland's Reagent; Threo-1,4-dimercapto-2,3-butanediol; DTT),
 HSCH2CH(OH)CH(OH)CH2SH—154.25
HSCH2CH(OH)CH(OH)CH2SH—154.25 

 [3483-12-3]—Slightly hygroscopic needles from ether. Freely soluble in water, in alcohol, in acetone, in ethyl acetate, and in ether.
[3483-12-3]—Slightly hygroscopic needles from ether. Freely soluble in water, in alcohol, in acetone, in ethyl acetate, and in ether.
Melting range  741
741 :
between 42
:
between 42 and 44
and 44 .
.
Dithizone
(Diphenylthiocarbazone; Phenylazothioformic Acid 2-Phenylhydrazide),
 C6H5N:NCSNHNHC6H5—256.33
C6H5N:NCSNHNHC6H5—256.33 

 [60-10-6]—Use ACS reagent grade.
[60-10-6]—Use ACS reagent grade.
1-Dodecanol
(Dodecyl Alcohol),
 CH3(CH2)11OH—186.33
CH3(CH2)11OH—186.33 

 [112-53-8]—A clear, colorless liquid. Crystallizes as leaflets from dilute alcohol solution. Use ACS reagent grade.
[112-53-8]—A clear, colorless liquid. Crystallizes as leaflets from dilute alcohol solution. Use ACS reagent grade.
Dodecyl Lithium Sulfate (Lithium Dodecyl Sulfate, Lithium Lauryl Sulfate),
 C12H25LiO4S—272.3
C12H25LiO4S—272.3 

 [2044-56-6]—White to off-white powder, clear to slightly hazy, colorless to faint yellow solution in water at 50 mg per mL at ambient temperature. The UV absorbance of a 0.1 M solution is less than 0.05 at both 260 and 280 nm. The pH of a 0.1 M solution in water is 7.0 ± 0.5. Use a suitable grade.
[2044-56-6]—White to off-white powder, clear to slightly hazy, colorless to faint yellow solution in water at 50 mg per mL at ambient temperature. The UV absorbance of a 0.1 M solution is less than 0.05 at both 260 and 280 nm. The pH of a 0.1 M solution in water is 7.0 ± 0.5. Use a suitable grade.
t-Dodecyl Mercaptan Ethoxylate
(Poly(oxy-1,2-ethanediyl),  -[2-(tert-Dodecylthio)ethyl]-
-[2-(tert-Dodecylthio)ethyl]-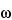 -hydroxy-),
-hydroxy-),
 (C2H4O)nC14H30OS
(C2H4O)nC14H30OS

 [9004-83-5]—Commercially available as a 1% or 2% aqueous solution. Use a suitable grade. [Note—A suitable grade is available as catalog number 805716 from www.fishersci.com or as catalog number R8057000 from www.riccachemical.com. ]
[9004-83-5]—Commercially available as a 1% or 2% aqueous solution. Use a suitable grade. [Note—A suitable grade is available as catalog number 805716 from www.fishersci.com or as catalog number R8057000 from www.riccachemical.com. ]
Dodecyl Sodium Sulfonate
(Sodium 1-Dodecanesulfonate; 1-Dodecanesulfonic Acid, Sodium Salt),
 C12H25SO3Na—272.38
C12H25SO3Na—272.38 

 [2386-53-0]—White, powdery solid. One g dissolves in 50 mL of warm water to yield a clear, colorless solution. Use a suitable grade.
[2386-53-0]—White, powdery solid. One g dissolves in 50 mL of warm water to yield a clear, colorless solution. Use a suitable grade.
Melting point  741
741 :
:
 higher than 300
higher than 300 .
.
3-(Dodecyldimethylammonio)propanesulfonate (Lauryl sulfobetaine, N,N-dimethyl-N-dodecyl-N-(3-sulfopropyl) ammonium betaine),
 C17H37NO3S—335.54
C17H37NO3S—335.54 

 [14933-08-5]—Use a suitable grade.
[14933-08-5]—Use a suitable grade.
Dodecyltriethylammonium Phosphate, 0.5 M,
 [C12H25N·(C2H5)3]3PO4—906.52—Use a suitable grade.
[C12H25N·(C2H5)3]3PO4—906.52—Use a suitable grade.
[Note—A suitable grade is available as Ion Pair Cocktail Q12 (catalogue number 404031) from Regis Technologies, Inc., www.registech.com. ]
Dodecyltrimethylammonium Bromide (Lauryltrimethylammonium bromide),
 CH3(CH2)11N(CH3)3Br—308.3
CH3(CH2)11N(CH3)3Br—308.3 

 [1119-94-4]—Use a suitable grade.
[1119-94-4]—Use a suitable grade.
[Note—A suitable grade is available as catalog number D5047 from Sigma-Aldrich, www.sigma-aldrich.com. ]
Drabkin's Reagent—
The reagent consists of 100 parts of sodium bicarbonate, 20 parts of potassium ferricyanide, and 5 parts of potassium cyanide. [Caution—The reagent is HIGHLY TOXIC. Very toxic by inhalation, in contact with skin, and if swallowed, and there is a risk of serious damage to eyes. Wear suitable protective clothing, gloves, and eye and face protection. Do not mix with acids. Contact with acids liberates a very toxic gas. If ingested, perform gastric lavage, and call a physician.
]
[Note—The reagent can be obtained from many manufacturers and suppliers. Some examples of manufacturers or suppliers are the following: Sigma Chemical Co., St. Louis, MO; and CIMA Scientific, Dallas, TX. ]
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Reagent | Margareth R. C. Marques, Ph.D.
Senior Scientific Liaison (301) 816-8106 |
(HDQ) Headquarters |



