- British Pharmacopoeia Volume I & II
- Monographs: Medicinal and Pharmaceutical Substances
Sulpiride |
 |
(Ph Eur monograph 1045)

C15H23N3O4S 341.4 15676-16-1
Dopamine receptor antagonist; neuroleptic.
Ph Eur
(RS)-N-[(1-Ethylpyrrolidin-2-yl)methyl]-2-methoxy-5-sulphamoylbenzamide.
98.5 per cent to 101.0 per cent (dried substance).
White or almost white, crystalline powder.
Practically insoluble in water, sparingly soluble in methanol, slightly soluble in ethanol (96 per cent) and in methylene chloride. It dissolves in dilute solutions of mineral acids and alkali hydroxides.
First identification A, B.
Second identification A, C, D.
A. Melting point (2.2.14): 177 °C to 181 °C.
B. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Preparation Discs.
Comparison Sulpiride CRS.
C. Examine the chromatograms obtained in test A for related substances.
Detection Examine in ultraviolet light at 254 nm.
Results The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with test solution (b) is similar in position and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a).
D. To about 1 mg in a porcelain dish, add 0.5 ml of sulphuric acid R and 0.05 ml of formaldehyde solution R. Examined in ultraviolet light at 365 nm, the solution shows blue fluorescence.
The solution is clear (2.2.1) and not more intensely coloured than reference solution Y6 (2.2.2, Method I).
Dissolve 1.0 g in dilute acetic acid R and dilute to 10 ml with the same acid.
A. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution (a) Dissolve 0.20 g of the substance to be examined in methanol R and dilute to 10 ml with the same solvent. Sonicate until complete dissolution.
Test solution (b) Dilute 1 ml of test solution (a) to 10 ml with methanol R.
Reference solution (a) Dissolve 20 mg of sulpiride CRS in methanol R and dilute to 10 ml with the same solvent.
Reference solution (b) Dissolve 5 mg of sulpiride impurity A CRS in methanol R and dilute to 25 ml with the same solvent.
Reference solution (c) Dilute 1.0 ml of reference solution (b) to 10 ml with methanol R.
Plate TLC silica gel F254 plate R.
Mobile phase Concentrated ammonia R, dioxan R, methanol R, methylene chloride R (2:10:14:90 V/V/V/V).
Application 10 µl.
Development Over a path of 10 cm.
Drying In air.
Detection Examine in ultraviolet light at 254 nm for identification test C and then spray with ninhydrin solution R; heat at 100-105 °C for 15 min and examine in daylight.
Limit Test solution (a):
- — impurity A: any spot due to impurity A is not more intense than the corresponding spot in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) (0.1 per cent).
B. Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Test solution Dissolve 0.100 g of the substance to be examined in the mobile phase and dilute to 100.0 ml with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (a) Dilute 3.0 ml of the test solution to 100.0 ml with the mobile phase. Dilute 1.0 ml of this solution to 10.0 ml with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (b) Dissolve 10 mg of sulpiride CRS and 10 mg of sulpiride impurity B CRS in the mobile phase and dilute to 100.0 ml with the mobile phase.
- — size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
- — stationary phase: octylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 µm) in spherical micro-particles.
Mobile phase Mix 10 volumes of acetonitrile R, 10 volumes of methanol R and 80 volumes of a solution containing 6.8 g/l of potassium dihydrogen phosphate R and 1 g/l of sodium octanesulphonate R, adjusted to pH 3.3 using phosphoric acid R.
Flow rate 1.5 ml/min.
Detection Spectrophotometer at 240 nm.
Injection 10 µl.
Run time 2.5 times the retention time of sulpiride.
System suitability Reference solution (b):
- — resolution: minimum 2.5 between the peaks due to impurity B and sulpiride.
- — total: not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) (0.3 per cent).
Maximum 100 ppm.
Shake 1.0 g with 20 ml of water R. Filter through a sintered-glass filter (40) (2.1.2). To 10 ml of the filtrate add 5 ml of water R.
Maximum 10 ppm.
Ignite 1.0 g in a silica crucible. To the residue add 1 ml of 1 M hydrochloric acid, 3 ml of water R and 0.1 ml of nitric acid R. Heat on a water-bath for a few minutes. Place the solution in a test-tube. Rinse the crucible with 4 ml of water R. Collect the rinsings in the test-tube and dilute to 10 ml with water R.
Maximum 10 ppm.
1.0 g complies with test C. Prepare the reference solution using 1 ml of lead standard solution (10 ppm Pb) R.
Maximum 0.5 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in an oven at 105 °C.
Maximum 0.1 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
Dissolve 0.250 g in 80 ml of anhydrous acetic acid R. Titrate with 0.1 M perchloric acid, determining the end-point potentiometrically (2.2.20).
1 ml of 0.1 M perchloric acid is equivalent to 34.14 mg of C15H23N3O4S.
Specified impurities A.
Other detectable impurities (The following substances would, if present at a sufficient level, be detected by one or other of the tests in the monograph. They are limited by the general acceptance criterion for other/unspecified impurities and/or by the general monograph Substances for pharmaceutical use (2034). It is therefore not necessary to identify these impurities for demonstration of compliance. See also 5.10. Control of impurities in substances for pharmaceutical use): B, C, D, E, F, G.
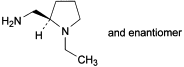
A. [(2RS)-1-ethylpyrrolidin-2-yl]methanamine,
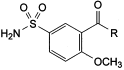
B. R = O-CH3: methyl 2-methoxy-5-sulphamoylbenzoate,
C. R = O-C2H5: ethyl 2-methoxy-5-sulphamoylbenzoate,
D. R = OH: 2-methoxy-5-sulphamoylbenzoic acid,
E. R = NH2: 2-methoxy-5-sulphamoylbenzamide,
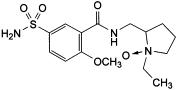
F. 1-ethyl-2-[[(2-methoxy-5-sulphamoylbenzoyl)amino]methyl]pyrrolidine 1-oxide,
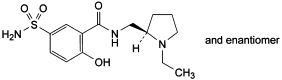
G. (RS)-N-[(1-ethylpyrrolidin-2-yl)methyl]-2-hydroxy-5-sulphamoylbenzamide.
Ph Eur